
A particle performs uniform circular motion with an angular momentum L. If the angular frequency of the particle is doubled and kinetic energy is halved, its angular momentum becomes:
a. $2L$
b. $4L$
c. $\dfrac{L}{2}$
d. $\dfrac{L}{4}$
Answer
561k+ views
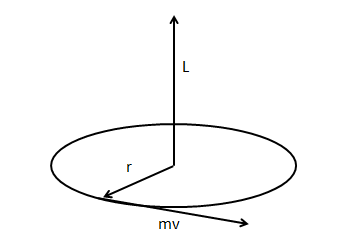
Hint: Angular momentum is momentum of a body in rotational motion. Kilometer square per second is the SI units for angular momentum. Formula for calculating the angular momentum is \[L = mvr\] where L is angular momentum, m is mass, v is velocity and r is radius. Torque is the rate of change of angular momentum. Kinetic energy is transferred between bodies and transformed into other forms of energies.
Formula for kinetic energy is $K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$ where m is mass of the object and v is the velocity of the object.
Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity. Kinetic energy describes magnitude.
Formula Used:
$L = I\omega $
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Angular frequency of the particle is doubled
Kinetic energy of the particle is halved
Angular momentum, $L = I\omega $
Here L is angular momentum, I is moment of inertia, $\omega $ is angular velocity.
Frequency f =$\dfrac{\omega }{{2\pi }}$
Bring $2\pi $ to LHS
$\omega = f$$2\pi $……..equation$1$
Kinetic energy (KE), K = $\dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2}$
To find I bring values in RHS to LHS
$I = \dfrac{{2K}}{{{\omega ^2}}}$ ……..equation$2$
Put equation $1$ and equation$2$ in Angular momentum, $L = I\omega $
$L = \dfrac{{2K}}{{{{(f2\pi )}^2}}} \times f2\pi $
Cancelling the values and simplifying
$L = \dfrac{K}{{f\pi }}$
By applying the conditions given in question Angular frequency of the particle is doubled, Kinetic energy of the particle is halved
$K = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$f = 2$
$L = \dfrac{K}{{f\pi }}$
By applying the K and f values in above equation
$L = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi }}$
Therefore correct answer is $\dfrac{L}{4}$
Hence, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Angular momentum is a vector quantity. It represents the object rotational of a product of a rotational velocity and inertia about a particular axis. Angular momentum \[L\;\] is proportional to angular speed \[\omega \] and moment of inertia \[I\]. It is measured in radians per second.
If there are no net external forces linear momentum is conserved, when the net torque is zero angular momentum is constant or conserved.
Formula for kinetic energy is $K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$ where m is mass of the object and v is the velocity of the object.
Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity. Kinetic energy describes magnitude.
Formula Used:
$L = I\omega $
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Angular frequency of the particle is doubled
Kinetic energy of the particle is halved
Angular momentum, $L = I\omega $
Here L is angular momentum, I is moment of inertia, $\omega $ is angular velocity.
Frequency f =$\dfrac{\omega }{{2\pi }}$
Bring $2\pi $ to LHS
$\omega = f$$2\pi $……..equation$1$
Kinetic energy (KE), K = $\dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2}$
To find I bring values in RHS to LHS
$I = \dfrac{{2K}}{{{\omega ^2}}}$ ……..equation$2$
Put equation $1$ and equation$2$ in Angular momentum, $L = I\omega $
$L = \dfrac{{2K}}{{{{(f2\pi )}^2}}} \times f2\pi $
Cancelling the values and simplifying
$L = \dfrac{K}{{f\pi }}$
By applying the conditions given in question Angular frequency of the particle is doubled, Kinetic energy of the particle is halved
$K = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$f = 2$
$L = \dfrac{K}{{f\pi }}$
By applying the K and f values in above equation
$L = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi }}$
Therefore correct answer is $\dfrac{L}{4}$
Hence, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Angular momentum is a vector quantity. It represents the object rotational of a product of a rotational velocity and inertia about a particular axis. Angular momentum \[L\;\] is proportional to angular speed \[\omega \] and moment of inertia \[I\]. It is measured in radians per second.
If there are no net external forces linear momentum is conserved, when the net torque is zero angular momentum is constant or conserved.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




