
A particle of mass m is fixed to the end of a light spring of force constant k and unstretched length l. The system is rotated about the other end of the spring with an angular $\omega $ ,in gravity free space. The increase in length of the spring will be
A. $\dfrac{{m{\omega ^2}l}}{k}$
B. $\dfrac{{m{\omega ^2}l}}{{k - m{\omega ^2}}}$
C. $\dfrac{{m{\omega ^2}l}}{{k + m{\omega ^2}}}$
D. $None$
Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: Mass of the particles is given, spring constant is also given to us and the system is rotating in an angular frequency hence we can calculate the above problem by equating the centripetal force with the elastic force. Solving further we can get the value of increase in length of the spring.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given problem,mass of the particle is given by $m$ which is fixed at end of a light spring of force constant $k$ and it unstretched length is $l$ and if the system is rotated about the other end of the spring the there will be a stretched in the spring which is represented as $x$ hence the radius of the ruated system will be $l+x$ and also the angular frequency of the rotated system is $\omega $.
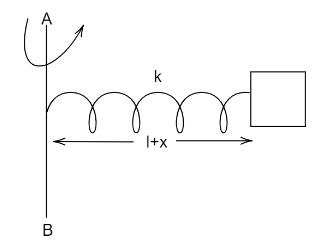
According to the given condition we can conclude that the electric force will provide the required centripetal force or in other word we can say that electric force is equal to centripetal force of the rotated system. We know,
Elastic force of a spring= $kx$
Centripetal force= $m{\omega ^2}r$
Equating both of them we get,
$kx = m{\omega ^2}r$
Here $r=l+x$
Putting the changed r value in the above equation we get,
$kx = m{\omega ^2}\left( {l + x} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow kx = m{\omega ^2}l + m{\omega ^2}x$
Here x is the increased in length of the spring due to rotation of the system
Hence by further solving the [problem we get,
$kx - m{\omega ^2}x = m{\omega ^2}l$
Taking x as common term from LHS side we get,
$x\left( {k - m{\omega ^2}} \right) = m{\omega ^2}l$
Rearranging the above equation we get,
$\therefore x = \dfrac{{m{\omega ^2}l}}{{\left( {k - m{\omega ^2}} \right)}}$
Hence we get the increases in length of the spring is $x = \dfrac{{m{\omega ^2}l}}{{\left( {k - m{\omega ^2}} \right)}}$ .
Therefore the correct option is $\left( B \right)$.
Note: Before solving this kind of problem, first change the length of the spring because if a spring is rotated then their length must change its length. If you don’t change the length of the spring after the system is rotated then you will get the wrong answer.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given problem,mass of the particle is given by $m$ which is fixed at end of a light spring of force constant $k$ and it unstretched length is $l$ and if the system is rotated about the other end of the spring the there will be a stretched in the spring which is represented as $x$ hence the radius of the ruated system will be $l+x$ and also the angular frequency of the rotated system is $\omega $.

According to the given condition we can conclude that the electric force will provide the required centripetal force or in other word we can say that electric force is equal to centripetal force of the rotated system. We know,
Elastic force of a spring= $kx$
Centripetal force= $m{\omega ^2}r$
Equating both of them we get,
$kx = m{\omega ^2}r$
Here $r=l+x$
Putting the changed r value in the above equation we get,
$kx = m{\omega ^2}\left( {l + x} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow kx = m{\omega ^2}l + m{\omega ^2}x$
Here x is the increased in length of the spring due to rotation of the system
Hence by further solving the [problem we get,
$kx - m{\omega ^2}x = m{\omega ^2}l$
Taking x as common term from LHS side we get,
$x\left( {k - m{\omega ^2}} \right) = m{\omega ^2}l$
Rearranging the above equation we get,
$\therefore x = \dfrac{{m{\omega ^2}l}}{{\left( {k - m{\omega ^2}} \right)}}$
Hence we get the increases in length of the spring is $x = \dfrac{{m{\omega ^2}l}}{{\left( {k - m{\omega ^2}} \right)}}$ .
Therefore the correct option is $\left( B \right)$.
Note: Before solving this kind of problem, first change the length of the spring because if a spring is rotated then their length must change its length. If you don’t change the length of the spring after the system is rotated then you will get the wrong answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




