
. A particle of mass m is attached to the ceiling of a cabin with an inextensible light string of length l The cabin is moving upward with an acceleration a. The particle is taken to a position such that string makes an angle $\theta $ with vertical. When the string becomes vertical, find the tension in the string.
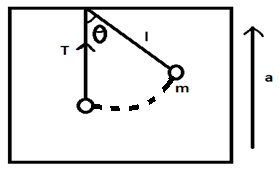

Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint: To calculate the tension, we can consider the frame of the cabin where both acceleration of object and acceleration due to gravity will have the same direction. We can use the law of conservation of energy to get the relationship between various quantities. Then using the fact that the net force acting on the new position will provide the centripetal force, we can find the value of T.
Formulas to be used:
\[Work = FD\cos \theta \]
Potential energy = $m{g_{eff}}h$
Kinetic energy = $\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Centripetal force = $\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}$ (here r = l)
Complete step by step answer:
For calculating the tension, we need to move into the frame of the cabin, where along with gravitational force, acceleration will also act downward as a pseudo force which acts on all the bodies.
The effective acceleration due to gravity can be given as:
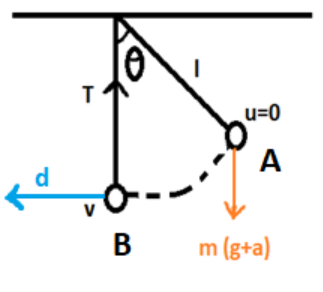
${g_{eff}} = (g + a)$ ______ (1) [ as both are in same downward direction]Work done by the force of tension in changing the position from A to B:
At A the initial velocity (u) is zero (because it is at rest in the beginning) at B, the final velocity becomes v.
The direction of tension is upwards while that of displacement (d) is towards left of B and the angle between them is 90°
Work = Force (F). Displacement (D)
Or
\[Work = FD\cos \theta \]
Work = 0 $\left( \because \theta = {90^o} \implies \cos {90^o} = 0 \right)$
Thus work done by tension is zero.
Now, according to law of conservation of energy, one form of energy gets converted to another so:
Decrease in potential energy = Increase in kinetic energy ________ (2)
Potential energy = $m{g_{eff}}h$
Kinetic energy = $\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Substituting in (2):
$
m{g_{eff}}h = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} \\
\implies {v^2} = 2{g_{eff}}h \\
\implies v = \sqrt {2{g_{eff}}h} \\
$
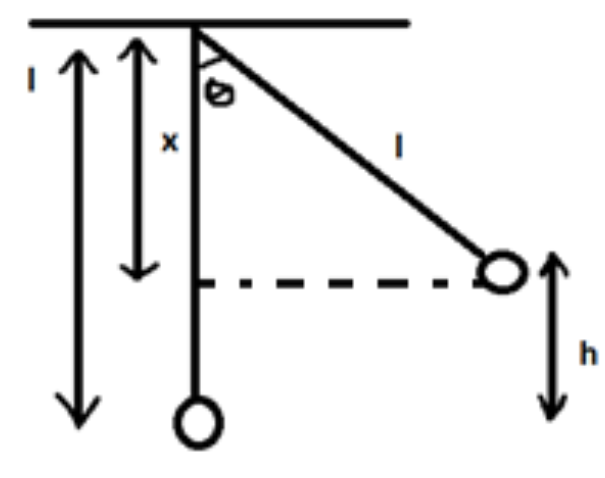
Calculating the value of h by recreating diagram specifically to find the height:
length h = length l – length x ____ (a)
Calculating $\cos \theta $ in the formed triangle:
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{B}{H}$ here,
Base (B) = x Hypotenuse (H) = l
Substituting:
$
\cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{l} \\
x = l\cos \theta \\
$
Substituting in (a) to calculate h:
$
h = l - x \\
\implies h = l - l\cos \theta \\
\implies h = l(1 - \cos \theta ) \\
$
And value of ${g_{eff}}$ from (1) is:
${g_{eff}} = (g + a)$
Now substituting both the values in that of v, we get:
$
v = \sqrt {2{g_{eff}}h} \\
\implies v = \sqrt {2(g + a)l(1 - \cos \theta )} \\
\\
$
As $m{g_{eff}}$ is acting downward on A, it will act in the same way at B. Tension and this force are opposite in directions. This net provides the centripetal force, so:
$T - m{g_{eff}} = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{l}$ [since centripetal force is $\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{l}$]
Calculating the value of T by substituting all the known values:
$
T = m{g_{eff}} + \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{l} \\
\implies T = m(g + a) + \dfrac{m}{l}[2(g + a)l(1 - \cos \theta )] \\
\implies T = m(g + a) + 2m(g + a)(1 - \cos \theta ) \\
\implies T = m(g + a)[1 + 2(1 - \cos \theta )] \\
\therefore T = m(g + a)[3 - 2\cos \theta ] \\
$
Hence,when the string becomes vertical the tension in the string is \[m(g + a)[3 - 2\cos \theta ]\].
Note:
When the two forces acting on the same point are opposite in directions, the net force will be the difference between them whereas when they are same in direction, the net force will be their sum.
For an angle, the perpendicular is the edge opposite to it and hypotenuse is always the longest side of the triangle formed.
According to the law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but changes from one form to another.
Formulas to be used:
\[Work = FD\cos \theta \]
Potential energy = $m{g_{eff}}h$
Kinetic energy = $\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Centripetal force = $\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}$ (here r = l)
Complete step by step answer:
For calculating the tension, we need to move into the frame of the cabin, where along with gravitational force, acceleration will also act downward as a pseudo force which acts on all the bodies.
The effective acceleration due to gravity can be given as:

${g_{eff}} = (g + a)$ ______ (1) [ as both are in same downward direction]Work done by the force of tension in changing the position from A to B:
At A the initial velocity (u) is zero (because it is at rest in the beginning) at B, the final velocity becomes v.
The direction of tension is upwards while that of displacement (d) is towards left of B and the angle between them is 90°
Work = Force (F). Displacement (D)
Or
\[Work = FD\cos \theta \]
Work = 0 $\left( \because \theta = {90^o} \implies \cos {90^o} = 0 \right)$
Thus work done by tension is zero.
Now, according to law of conservation of energy, one form of energy gets converted to another so:
Decrease in potential energy = Increase in kinetic energy ________ (2)
Potential energy = $m{g_{eff}}h$
Kinetic energy = $\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Substituting in (2):
$
m{g_{eff}}h = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} \\
\implies {v^2} = 2{g_{eff}}h \\
\implies v = \sqrt {2{g_{eff}}h} \\
$

Calculating the value of h by recreating diagram specifically to find the height:
length h = length l – length x ____ (a)
Calculating $\cos \theta $ in the formed triangle:
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{B}{H}$ here,
Base (B) = x Hypotenuse (H) = l
Substituting:
$
\cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{l} \\
x = l\cos \theta \\
$
Substituting in (a) to calculate h:
$
h = l - x \\
\implies h = l - l\cos \theta \\
\implies h = l(1 - \cos \theta ) \\
$
And value of ${g_{eff}}$ from (1) is:
${g_{eff}} = (g + a)$
Now substituting both the values in that of v, we get:
$
v = \sqrt {2{g_{eff}}h} \\
\implies v = \sqrt {2(g + a)l(1 - \cos \theta )} \\
\\
$
As $m{g_{eff}}$ is acting downward on A, it will act in the same way at B. Tension and this force are opposite in directions. This net provides the centripetal force, so:
$T - m{g_{eff}} = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{l}$ [since centripetal force is $\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{l}$]
Calculating the value of T by substituting all the known values:
$
T = m{g_{eff}} + \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{l} \\
\implies T = m(g + a) + \dfrac{m}{l}[2(g + a)l(1 - \cos \theta )] \\
\implies T = m(g + a) + 2m(g + a)(1 - \cos \theta ) \\
\implies T = m(g + a)[1 + 2(1 - \cos \theta )] \\
\therefore T = m(g + a)[3 - 2\cos \theta ] \\
$
Hence,when the string becomes vertical the tension in the string is \[m(g + a)[3 - 2\cos \theta ]\].
Note:
When the two forces acting on the same point are opposite in directions, the net force will be the difference between them whereas when they are same in direction, the net force will be their sum.
For an angle, the perpendicular is the edge opposite to it and hypotenuse is always the longest side of the triangle formed.
According to the law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but changes from one form to another.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




