
A particle of mass $ 200g $ is whirled into a vertical circle of radius $ 80cm $ using a massless string. The speed of the particle when the string makes an angle of $ {60^ \circ } $ with the vertical line is $ 1.5m{s^{ - 1}} $. The tension in the string at the position is
$ (A) 1.1N \\
(B) 2.1.56N \\
(C) 3.2N \\
(D) 4.3N \\
$
Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint: In the question, we have to first make the tension equal to the cosine component of the gravitational force just to make the two opponent force balance to each other. Alternative angles are equal in concept should be used. Then pseudo force should be applied and tension is the sum of the centrifugal and the component force of the gravitation.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given question, we have;
Particle is doing circular motion, the radius of the circle is $ 80cm $ .
After a particle is at $ {60^ \circ } $ , so the new position of the particle is somewhere above the original point, and speed is also given which is $ 1.5m{s^{ - 1}} $ .
Here first we draw the diagram of the circular motion and the movement of the particle;
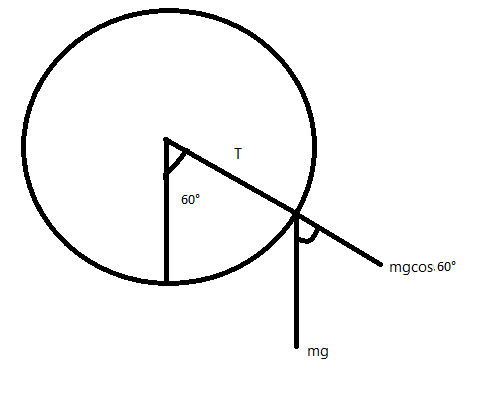
Now the mg will act on downwards, and tension is at the center of the circle.
Since the alternative angles are equal so the point where gravitational force is acting also has the same angle that is $ {60^ \circ } $ .
Now pseudo force is been applied which is $ \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $ ,
So;
Given tension is equal to the component of the gravitational force applied (to balance the force we have to do it);
$ T = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} + mg\cos {60^ \circ } \\
= \dfrac{{200 \times {{10}^{ - 3}} \times {{(1.5)}^2}}}{{80 \times {{10}^{ - 2}}}} + 200 \times {10^{ - 3}} \times 10 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \\
= \dfrac{{0.2 \times 9}}{{4 \times 0.8}} + 0.1 \times 10 \\
= \dfrac{9}{{16}} + 1 \\
= \dfrac{{25}}{{16}} \\
= 1.56N \\ $
Hence, B option is the correct answer.
Note:
In the circular motion the speed of the moving particle when came into rest then the energy at height of the particle which it travels from the initial point is equal to the kinetic energy. Hence from this we can find the different speed of the particle at different heights.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given question, we have;
Particle is doing circular motion, the radius of the circle is $ 80cm $ .
After a particle is at $ {60^ \circ } $ , so the new position of the particle is somewhere above the original point, and speed is also given which is $ 1.5m{s^{ - 1}} $ .
Here first we draw the diagram of the circular motion and the movement of the particle;

Now the mg will act on downwards, and tension is at the center of the circle.
Since the alternative angles are equal so the point where gravitational force is acting also has the same angle that is $ {60^ \circ } $ .
Now pseudo force is been applied which is $ \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $ ,
So;
Given tension is equal to the component of the gravitational force applied (to balance the force we have to do it);
$ T = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} + mg\cos {60^ \circ } \\
= \dfrac{{200 \times {{10}^{ - 3}} \times {{(1.5)}^2}}}{{80 \times {{10}^{ - 2}}}} + 200 \times {10^{ - 3}} \times 10 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \\
= \dfrac{{0.2 \times 9}}{{4 \times 0.8}} + 0.1 \times 10 \\
= \dfrac{9}{{16}} + 1 \\
= \dfrac{{25}}{{16}} \\
= 1.56N \\ $
Hence, B option is the correct answer.
Note:
In the circular motion the speed of the moving particle when came into rest then the energy at height of the particle which it travels from the initial point is equal to the kinetic energy. Hence from this we can find the different speed of the particle at different heights.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




