
A particle of mass 1kg and carrying 0.01C is at rest on an inclined plane of angle ${{30}^{\circ }}$ with horizontal when an electric field of $\dfrac{490}{\sqrt{3}}N{{C}^{-1}}$ applied parallel to horizontal, the coefficient of friction is
$\begin{align}
& \left( 1 \right)0.5 \\
& \left( 2 \right)\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \left( 3 \right)\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& \left( 4 \right)\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{7} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: For a body inclined in a plane to come to rest, all forces acting on that object must balance with each other. For finding this, draw the free body diagram with the given data and mark all the forces that are acting on the body. Then by equating the forces we will get the coefficient of friction.
Formula used:
According to Newton’s second law,
F = ma = qE
where, F is the force
m is the mass
a is the acceleration
q is the charge
and E is the electric field
Complete step by step answer:
For a body inclined in a plane to come to rest, all forces acting on that object must balance with each other.
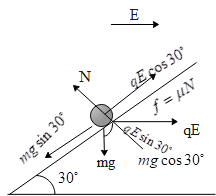
$\begin{align}
& qE\cos \theta =\dfrac{490}{\sqrt{3}}\times 0.01\times \cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{490}{\sqrt{3}}\times 0.01\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}=2.45N$
$mg\sin \theta =1\times 9.8\times \sin {{30}^{\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta =1\times 9.8\times \dfrac{1}{2}=4.9N$
Therefore $qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}\langle mg\sin {{30}^{\circ }}$
$N=mg\cos {{30}^{\circ }}+qE\sin {{30}^{\circ }}$
Substitute the value of m, g,q and E in the above equation we get,
$N=1\times 9.8\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}+0.01\times \dfrac{490}{\sqrt{3}}\times \dfrac{1}{2}$
$N=4.9\sqrt{3}+\dfrac{4.9}{2\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow N=4.9\left( \sqrt{3}+\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{3}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow N=9.9N$
$mg\sin \theta =1\times 9.8\times \sin {{30}^{\circ }}$$=f+qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}$
Here, $f=\mu N$
Where, $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction.
Substitute in the above equation we get,
$\Rightarrow 4.9=\mu N+qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}=2.45N$
$\Rightarrow \mu N=4.9-2.45$
$\mu =\dfrac{2.45}{N}$
$\begin{align}
& \mu =\dfrac{2.45}{9.9} \\
& \therefore \mu =0.0247=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{7} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore option (4) is correct.
Additional information:
Electric field can also be defined as the electric force acting per unit charge. The direction of the field is the same as the direction of the force. The electric field always goes out from a positive charge and always goes into a negative charge.
Note:
For a body inclined in a plane to come to rest, all forces acting on that object must balance with each other. Electric field can also be defined as the electric force acting per unit charge. The direction of the field is the same as the direction of the force. The electric field always goes out from a positive charge and always goes into a negative charge.
Formula used:
According to Newton’s second law,
F = ma = qE
where, F is the force
m is the mass
a is the acceleration
q is the charge
and E is the electric field
Complete step by step answer:
For a body inclined in a plane to come to rest, all forces acting on that object must balance with each other.

$\begin{align}
& qE\cos \theta =\dfrac{490}{\sqrt{3}}\times 0.01\times \cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{490}{\sqrt{3}}\times 0.01\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}=2.45N$
$mg\sin \theta =1\times 9.8\times \sin {{30}^{\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta =1\times 9.8\times \dfrac{1}{2}=4.9N$
Therefore $qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}\langle mg\sin {{30}^{\circ }}$
$N=mg\cos {{30}^{\circ }}+qE\sin {{30}^{\circ }}$
Substitute the value of m, g,q and E in the above equation we get,
$N=1\times 9.8\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}+0.01\times \dfrac{490}{\sqrt{3}}\times \dfrac{1}{2}$
$N=4.9\sqrt{3}+\dfrac{4.9}{2\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow N=4.9\left( \sqrt{3}+\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{3}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow N=9.9N$
$mg\sin \theta =1\times 9.8\times \sin {{30}^{\circ }}$$=f+qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}$
Here, $f=\mu N$
Where, $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction.
Substitute in the above equation we get,
$\Rightarrow 4.9=\mu N+qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow qE\cos {{30}^{\circ }}=2.45N$
$\Rightarrow \mu N=4.9-2.45$
$\mu =\dfrac{2.45}{N}$
$\begin{align}
& \mu =\dfrac{2.45}{9.9} \\
& \therefore \mu =0.0247=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{7} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore option (4) is correct.
Additional information:
Electric field can also be defined as the electric force acting per unit charge. The direction of the field is the same as the direction of the force. The electric field always goes out from a positive charge and always goes into a negative charge.
Note:
For a body inclined in a plane to come to rest, all forces acting on that object must balance with each other. Electric field can also be defined as the electric force acting per unit charge. The direction of the field is the same as the direction of the force. The electric field always goes out from a positive charge and always goes into a negative charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




