
A particle moves in a circle of radius \[R\] with a constant speed \[v\]. Then, find the magnitude of average acceleration during a time interval \[\dfrac{{\pi R}}{{2v}}\].
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint:Use the formula for average acceleration of a particle in terms of average velocity and time. Then using the formula for the time period of the particle, determine the total path travelled by the particle in the given time interval. Draw the path of the particle on the circle and determine the average velocity of the particle. Then using the formula, determine the average acceleration of the particle.
Formula used:
The average acceleration \[{a_{avg}}\] of an object is given by
\[{a_{avg}} = \dfrac{{{v_{avg}}}}{t}\] …… (1)
Here, \[{v_{avg}}\] is the average velocity of the object and \[t\] is the time.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the radius of the circle in which the particle moves with constant speed \[v\] is \[R\].We have asked to calculate the average acceleration of the particle in the interval \[\dfrac{{\pi R}}{{2v}}\].
\[t = \dfrac{{\pi R}}{{2v}}\]
Let us first determine the path of the circumference travelled by the particle.The time \[T\] required for the particle to complete one circle is given by
\[T = \dfrac{{2\pi R}}{v}\]
So the path on the circle travelled by the particle is
\[s = \dfrac{t}{T}\]
\[ \Rightarrow s = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\pi R}}{{2v}}}}{{\dfrac{{2\pi R}}{v}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow s = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
Hence, the particle has travelled one fourth of the total circle.
Let us draw the diagram of the circle with the velocities of the particle.
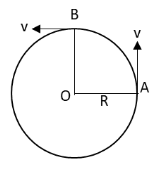
From the above equation, the particle travels from point A to B.
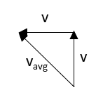
Thus, the average velocity is given by
\[{v_{avg}} = \sqrt {{{\left( v \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - v} \right)}^2}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_{avg}} = \sqrt 2 v\]
Hence, the average velocity of the particle is \[\sqrt 2 v\].
Let us now calculate the average acceleration of the particle.Substitute \[\sqrt 2 v\] for \[{v_{avg}}\] and \[\dfrac{{\pi R}}{{2v}}\] for \[t\] in equation (1).
\[{a_{avg}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 v}}{{\dfrac{{\pi R}}{{2v}}}}\]
\[ \therefore {a_{avg}} = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 {v^2}}}{{\pi R}}\]
Hence, the average velocity of the particle is \[\dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 {v^2}}}{{\pi R}}\].
Note:One can also solve the same question by another method. One can determine the average force acting on the particle by using the formula in terms of change in momentum and time. Then one can use the formula for the average force in terms of the mass and average acceleration of the particle. From which one can determine the average acceleration of the particle.
Formula used:
The average acceleration \[{a_{avg}}\] of an object is given by
\[{a_{avg}} = \dfrac{{{v_{avg}}}}{t}\] …… (1)
Here, \[{v_{avg}}\] is the average velocity of the object and \[t\] is the time.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the radius of the circle in which the particle moves with constant speed \[v\] is \[R\].We have asked to calculate the average acceleration of the particle in the interval \[\dfrac{{\pi R}}{{2v}}\].
\[t = \dfrac{{\pi R}}{{2v}}\]
Let us first determine the path of the circumference travelled by the particle.The time \[T\] required for the particle to complete one circle is given by
\[T = \dfrac{{2\pi R}}{v}\]
So the path on the circle travelled by the particle is
\[s = \dfrac{t}{T}\]
\[ \Rightarrow s = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\pi R}}{{2v}}}}{{\dfrac{{2\pi R}}{v}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow s = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
Hence, the particle has travelled one fourth of the total circle.
Let us draw the diagram of the circle with the velocities of the particle.

From the above equation, the particle travels from point A to B.

Thus, the average velocity is given by
\[{v_{avg}} = \sqrt {{{\left( v \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - v} \right)}^2}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_{avg}} = \sqrt 2 v\]
Hence, the average velocity of the particle is \[\sqrt 2 v\].
Let us now calculate the average acceleration of the particle.Substitute \[\sqrt 2 v\] for \[{v_{avg}}\] and \[\dfrac{{\pi R}}{{2v}}\] for \[t\] in equation (1).
\[{a_{avg}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 v}}{{\dfrac{{\pi R}}{{2v}}}}\]
\[ \therefore {a_{avg}} = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 {v^2}}}{{\pi R}}\]
Hence, the average velocity of the particle is \[\dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 {v^2}}}{{\pi R}}\].
Note:One can also solve the same question by another method. One can determine the average force acting on the particle by using the formula in terms of change in momentum and time. Then one can use the formula for the average force in terms of the mass and average acceleration of the particle. From which one can determine the average acceleration of the particle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




