
A particle moves from A to P and from P to B, as shown in the figure. Find the path length and displacement.
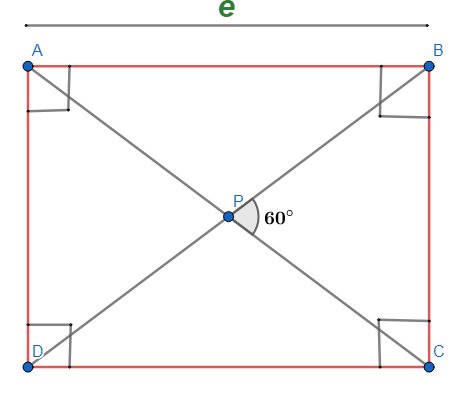

Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: We need to determine the length AP and PB to answer this question. From the figure, it is clear that AP=PB. Also, we should know the distinction between path length and displacement.
Complete step by step answer:
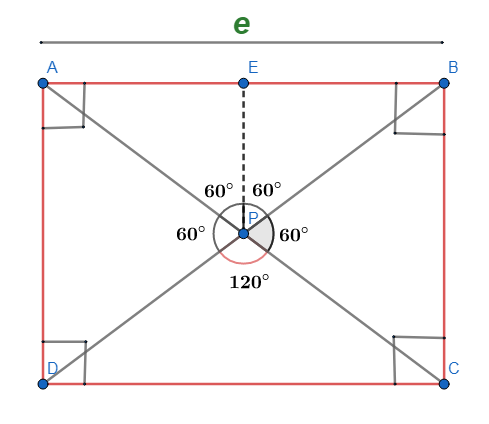
From the figure, we can see that the $\angle BPD=\angle APC={{60}^{\circ }}\text{ (VOA)}$ because they are vertically opposite angles. We also know that the sum of all the angles will be ${{360}^{\circ }}$. So the other two angles which are equal (vertically opposite angles), can be found out by,
$\begin{align}
& \angle BPD+\angle APC+\angle APB+\angle CPD={{360}^{\circ }} \\
& {{60}^{\circ }}+{{60}^{\circ }}+2\angle APB={{360}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore \angle APB={{120}^{\circ }}$
After figuring out $\angle APB={{120}^{\circ }}$, we will drop a perpendicular from P to E on AB, which will divide AB into two equal parts AE and EB, which are equal sections of length $\dfrac{e}{2}$. The line PE splits the angle $\angle APB$ into two equal angles, i.e. $\angle APE=\angle BPE={{60}^{\circ }}$.
Considering the right triangle AEP, we can write
$\sin \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{AE}{AP}=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{e}{2} \right)}{AP}$
$AP=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{e}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)}$
$\therefore AP=\dfrac{e}{\sqrt{3}}$
So, due to symmetry, PB will also be equal to $\dfrac{e}{\sqrt{3}}$.
So the path length is equal to the total distance travelled. So we can define path length as the sum of the lengths AP and PB,
$P.L=AP+PB$
$\text{P}\text{.L}=\dfrac{2e}{\sqrt{3}}$.
So the path length is the distance that the particle travelled from A to P and from P to B, which is equal to $\left( \text{P}\text{.L} \right)=\dfrac{2e}{\sqrt{3}}$.
But, the displacement will always be the shortest distance travelled; in this case, it will be the length of AB = e.
Note: In mechanics, displacement is a vector whose length is the shortest distance from the initial to the final position of a point P undergoing motion.
In mechanics, the Path length is the total distance travelled by the body from an initial point to a final point.
Complete step by step answer:

From the figure, we can see that the $\angle BPD=\angle APC={{60}^{\circ }}\text{ (VOA)}$ because they are vertically opposite angles. We also know that the sum of all the angles will be ${{360}^{\circ }}$. So the other two angles which are equal (vertically opposite angles), can be found out by,
$\begin{align}
& \angle BPD+\angle APC+\angle APB+\angle CPD={{360}^{\circ }} \\
& {{60}^{\circ }}+{{60}^{\circ }}+2\angle APB={{360}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore \angle APB={{120}^{\circ }}$
After figuring out $\angle APB={{120}^{\circ }}$, we will drop a perpendicular from P to E on AB, which will divide AB into two equal parts AE and EB, which are equal sections of length $\dfrac{e}{2}$. The line PE splits the angle $\angle APB$ into two equal angles, i.e. $\angle APE=\angle BPE={{60}^{\circ }}$.
Considering the right triangle AEP, we can write
$\sin \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{AE}{AP}=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{e}{2} \right)}{AP}$
$AP=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{e}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)}$
$\therefore AP=\dfrac{e}{\sqrt{3}}$
So, due to symmetry, PB will also be equal to $\dfrac{e}{\sqrt{3}}$.
So the path length is equal to the total distance travelled. So we can define path length as the sum of the lengths AP and PB,
$P.L=AP+PB$
$\text{P}\text{.L}=\dfrac{2e}{\sqrt{3}}$.
So the path length is the distance that the particle travelled from A to P and from P to B, which is equal to $\left( \text{P}\text{.L} \right)=\dfrac{2e}{\sqrt{3}}$.
But, the displacement will always be the shortest distance travelled; in this case, it will be the length of AB = e.
Note: In mechanics, displacement is a vector whose length is the shortest distance from the initial to the final position of a point P undergoing motion.
In mechanics, the Path length is the total distance travelled by the body from an initial point to a final point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




