
A particle is projected from the origin $(0,0)$ in the X-Y plane at an angle of ${37^o}$ with the X axis with a speed of $10m{s^{ - 1}}$ its acceleration being $( - 5\hat i + 10\hat j)m{s^{ - 2}}$ what is the speed of the particle when the x- coordinate is again zero?
Answer
478.2k+ views
Hint:In order to solve this question, we will first resolve the initial velocity in X and Y components and then formulate the velocity expression in terms of time t and later we will integrate the velocity expression to express distance in terms of t and then find the time at which x coordinate of distance became zero and using this we will finally find speed of the particle.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first draw the diagram showing velocity vectors in black arrows while acceleration vectors are in blue arrows as,
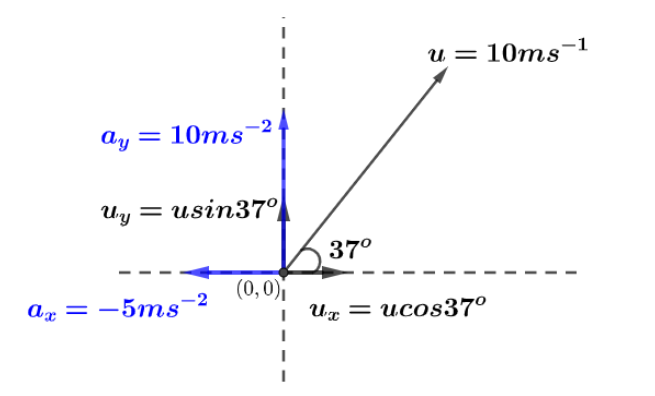
From the diagram and given information we can see that,s
$u = 10m{s^{ - 1}}$ initial velocity of the particle.
Let x and y component of initial velocity is denoted by ${u_x},{u_y}$ and given that angle with x axis is $\theta = {37^o}$. so,
${u_x} = u\cos {37^o}$
On putting the value of $u$ and $\cos {37^o} = 0.76$ we get,
${u_x} = 7.6m{s^{ - 1}}$
similarly,
${u_y} = u\sin {37^o}$
On putting the value of u and $\sin {37^o} = 0.64$ we get,
${u_y} = 6.4\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Now, given the acceleration components in x and y directions from expression $a = ( - 5\hat i + 10\hat j)m{s^{ - 2}}$ we get,
${a_x} = - 5m{s^{ - 2}}$ and ${a_y} = 10m{s^{ - 2}}$
Let ${v_x},{v_y}$ represent velocity of the particle in x and y direction at any time t then, using equation of motion $v = u + at$ we can write for x and y component as
${v_x} = {u_x} + {a_x}t$
On putting the values we get,
${v_x} = 7.6 - 5t \to (i)$
similarly we get,
${v_y} = {u_y} + {a_y}t$
On putting the values we get,
${v_y} = 6.4 + 10t \to (ii)$
Now, if X component distance of particle is represented by x then it’s calculated as
$x = \int {{v_x}dt} $
On putting the expression of ${v_x} = 7.6 - 5t \to (i)$ we get,
$x = \int {(7.6 - 5t)dt} $
using integration rules as $\int {{r^n}dr = \dfrac{{{r^{n + 1}}}}{{n + 1}}} $ we get,
$x = 7.6t - \dfrac{{5{t^2}}}{2}$
Now according to the question, for x component to be zero again we have,
$x = 7.6t - \dfrac{{5{t^2}}}{2} = 0$ so we get,
$15.2t = 5{t^2}$
$ \Rightarrow t = 3.04s$
So, we now need to calculate velocity of particle at $t = 3.04s$ so, on putting this value in expressions of velocity we get,
${v_x} = 7.6 - 5t$
$\Rightarrow {v_x} = 7.6 - 15.2$
$\Rightarrow {v_x} = - 7.6\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
And
${v_y} = 6.4 + 10t$
$\Rightarrow {v_y} = 6.4 + 30.4$
$\Rightarrow {v_y} = 36.8\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Now, we have the components of speed as ${v_x} = - 7.6\,m{s^{ - 1}}$ and ${v_y} = 36.8\,m{s^{ - 1}}$ so, net speed of the particle can be found as,
$v = \sqrt {{v_x}^2 + {v_y}^2} $
On putting the value of parameters we get,
$v = \sqrt {57.76 + 1354.24} $
$\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {1412} $
$ \therefore v = 37.57\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Hence, the velocity of the particle when x coordinate became again zero is $v = 37.57m{s^{ - 1}}.$
Note: It should be remembered that velocity is the derivative of distance with respect to time so distance is the integration of velocity with respect to time and remember all the integration rules and formulas while solving such questions.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first draw the diagram showing velocity vectors in black arrows while acceleration vectors are in blue arrows as,

From the diagram and given information we can see that,s
$u = 10m{s^{ - 1}}$ initial velocity of the particle.
Let x and y component of initial velocity is denoted by ${u_x},{u_y}$ and given that angle with x axis is $\theta = {37^o}$. so,
${u_x} = u\cos {37^o}$
On putting the value of $u$ and $\cos {37^o} = 0.76$ we get,
${u_x} = 7.6m{s^{ - 1}}$
similarly,
${u_y} = u\sin {37^o}$
On putting the value of u and $\sin {37^o} = 0.64$ we get,
${u_y} = 6.4\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Now, given the acceleration components in x and y directions from expression $a = ( - 5\hat i + 10\hat j)m{s^{ - 2}}$ we get,
${a_x} = - 5m{s^{ - 2}}$ and ${a_y} = 10m{s^{ - 2}}$
Let ${v_x},{v_y}$ represent velocity of the particle in x and y direction at any time t then, using equation of motion $v = u + at$ we can write for x and y component as
${v_x} = {u_x} + {a_x}t$
On putting the values we get,
${v_x} = 7.6 - 5t \to (i)$
similarly we get,
${v_y} = {u_y} + {a_y}t$
On putting the values we get,
${v_y} = 6.4 + 10t \to (ii)$
Now, if X component distance of particle is represented by x then it’s calculated as
$x = \int {{v_x}dt} $
On putting the expression of ${v_x} = 7.6 - 5t \to (i)$ we get,
$x = \int {(7.6 - 5t)dt} $
using integration rules as $\int {{r^n}dr = \dfrac{{{r^{n + 1}}}}{{n + 1}}} $ we get,
$x = 7.6t - \dfrac{{5{t^2}}}{2}$
Now according to the question, for x component to be zero again we have,
$x = 7.6t - \dfrac{{5{t^2}}}{2} = 0$ so we get,
$15.2t = 5{t^2}$
$ \Rightarrow t = 3.04s$
So, we now need to calculate velocity of particle at $t = 3.04s$ so, on putting this value in expressions of velocity we get,
${v_x} = 7.6 - 5t$
$\Rightarrow {v_x} = 7.6 - 15.2$
$\Rightarrow {v_x} = - 7.6\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
And
${v_y} = 6.4 + 10t$
$\Rightarrow {v_y} = 6.4 + 30.4$
$\Rightarrow {v_y} = 36.8\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Now, we have the components of speed as ${v_x} = - 7.6\,m{s^{ - 1}}$ and ${v_y} = 36.8\,m{s^{ - 1}}$ so, net speed of the particle can be found as,
$v = \sqrt {{v_x}^2 + {v_y}^2} $
On putting the value of parameters we get,
$v = \sqrt {57.76 + 1354.24} $
$\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {1412} $
$ \therefore v = 37.57\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Hence, the velocity of the particle when x coordinate became again zero is $v = 37.57m{s^{ - 1}}.$
Note: It should be remembered that velocity is the derivative of distance with respect to time so distance is the integration of velocity with respect to time and remember all the integration rules and formulas while solving such questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




