
A particle is moving along a circular path with a constant speed of \[10m{{s}^{-1}}\]. What is the magnitude of the change in the velocity of the particle, when it moves through an angle of \[{{60}^{0}}\] around the center of the circle?
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A) 0} \\
& \text{B) 10m}{{\text{s}}^{-1}} \\
& \text{C) 10}\sqrt{3}m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& \text{D) 10}\sqrt{2}m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: We need to understand the relation between the speed of a moving particle in a circular motion and the magnitude of velocity of the particle in the same motion. We can easily solve using the details of the angle given for the motion between two points.
Complete answer:
We are given a particle which undergoes a circular motion with a constant speed of \[\text{10m}{{\text{s}}^{-1}}\]. We are asked to find the magnitude of velocity of the same particle when it moves from a point A to point B which describes an angle of \[{{60}^{0}}\].
We can use the method of finding the magnitude of resultant vectors in order to find the magnitude of the velocity due to the velocities at two points.
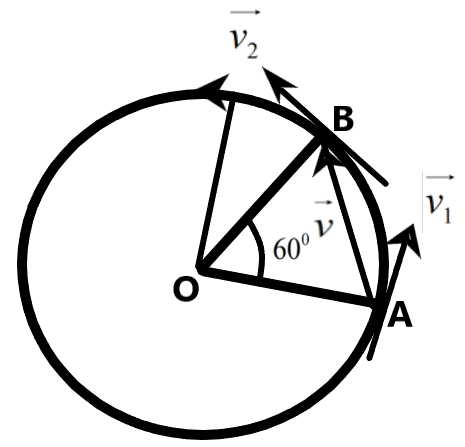
From the figure, we can understand the velocity can be given as –
\[\begin{align}
& \left| \overrightarrow{v} \right|=\sqrt{{{\left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{1}}} \right|}^{2}}+{{\left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{2}}} \right|}^{2}}+2\left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{1}}} \right|\left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{2}}} \right|\cos \theta } \\
& \text{but,} \\
& \left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{1}}} \right|=\left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{2}}} \right|=10m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| \overrightarrow{v} \right|=\sqrt{{{10}^{2}}+{{10}^{2}}+2(10)(10)\cos (\pi -{{60}^{0}})} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| \overrightarrow{v} \right|=\sqrt{100+100-200\dfrac{1}{2}} \\
& \therefore \left| \overrightarrow{v} \right|=10m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, the magnitude of the velocity of the particle turns out to be equal to the speed at which the particle is moving at every instant.
This is the required solution
The correct answer is option is B.
Note:
We need to understand that the angle here is taken as \[\pi -{{60}^{0}}\]. This is clear from the geometry that the cosine of the angle gives the resultant velocity for the given system which is very commonly happening. We need to be careful in such cases.
Complete answer:
We are given a particle which undergoes a circular motion with a constant speed of \[\text{10m}{{\text{s}}^{-1}}\]. We are asked to find the magnitude of velocity of the same particle when it moves from a point A to point B which describes an angle of \[{{60}^{0}}\].
We can use the method of finding the magnitude of resultant vectors in order to find the magnitude of the velocity due to the velocities at two points.

From the figure, we can understand the velocity can be given as –
\[\begin{align}
& \left| \overrightarrow{v} \right|=\sqrt{{{\left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{1}}} \right|}^{2}}+{{\left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{2}}} \right|}^{2}}+2\left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{1}}} \right|\left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{2}}} \right|\cos \theta } \\
& \text{but,} \\
& \left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{1}}} \right|=\left| \overrightarrow{{{v}_{2}}} \right|=10m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| \overrightarrow{v} \right|=\sqrt{{{10}^{2}}+{{10}^{2}}+2(10)(10)\cos (\pi -{{60}^{0}})} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| \overrightarrow{v} \right|=\sqrt{100+100-200\dfrac{1}{2}} \\
& \therefore \left| \overrightarrow{v} \right|=10m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, the magnitude of the velocity of the particle turns out to be equal to the speed at which the particle is moving at every instant.
This is the required solution
The correct answer is option is B.
Note:
We need to understand that the angle here is taken as \[\pi -{{60}^{0}}\]. This is clear from the geometry that the cosine of the angle gives the resultant velocity for the given system which is very commonly happening. We need to be careful in such cases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




