
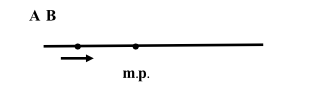
A particle is an oscillating simple harmonically with angular frequency and amplitude. It is at a point (A) at a certain instant (shown in the figure). At this instant, it is moving towards the mean position (B). It takes time to reach the mean position (B). If the time period of oscillation is , the average speed between A and B is:
(a)$\dfrac{A\sin \omega t}{t}$
(b)$\dfrac{A\cos \omega t}{t}$
(c)$\dfrac{A\sin \omega t}{T}$
(d)$\dfrac{A\cos \omega t}{T}$

Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint:In order to calculate the average speed between A and B, we need to use the formula of S.H.M,
Step by step solution, Velocity $(v)=\dfrac{\int dx}{\int dt}$.
Step by step solution,
Let the S.H.M be$x=A\sin \omega t$
$dx=A\omega \cos \omega t\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }dt$
Velocity$(v)=\dfrac{\int dx}{\int dt}$
So, mean speed between A to B is,
$=\dfrac{\mathop{\int }_{0}^{t}A\omega \cos \omega t dt}{\mathop{\int }_{0}^{t}dt}$
$=\dfrac{A\omega \dfrac{\sin \omega t}{\omega }}{t}$
$=\dfrac{A\sin \omega t}{t}$
Thus, the correct answer to this question is option (a).
Additional Information:Simple harmonic motion is the motion in which the object moves to and fro along a line.The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Therefore, the total energy in simple harmonic motion will always be constant. However, kinetic energy and potential energy are interchangeable. Given below is the graph of kinetic and potential energy vs instantaneous displacement.In the simple harmonic motion, the displacement of the object is always in the opposite direction of the restoring force.And, the simple harmonic motion is always oscillatory.Simple harmonic motion examples: the motion of a pendulum, motion of a spring, etc.
Note:While solving this question, one should be familiar with the concept of S.H.M. Some concepts are provided above for the reference.
Step by step solution, Velocity $(v)=\dfrac{\int dx}{\int dt}$.
Step by step solution,
Let the S.H.M be$x=A\sin \omega t$
$dx=A\omega \cos \omega t\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }dt$
Velocity$(v)=\dfrac{\int dx}{\int dt}$
So, mean speed between A to B is,
$=\dfrac{\mathop{\int }_{0}^{t}A\omega \cos \omega t dt}{\mathop{\int }_{0}^{t}dt}$
$=\dfrac{A\omega \dfrac{\sin \omega t}{\omega }}{t}$
$=\dfrac{A\sin \omega t}{t}$
Thus, the correct answer to this question is option (a).
Additional Information:Simple harmonic motion is the motion in which the object moves to and fro along a line.The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Therefore, the total energy in simple harmonic motion will always be constant. However, kinetic energy and potential energy are interchangeable. Given below is the graph of kinetic and potential energy vs instantaneous displacement.In the simple harmonic motion, the displacement of the object is always in the opposite direction of the restoring force.And, the simple harmonic motion is always oscillatory.Simple harmonic motion examples: the motion of a pendulum, motion of a spring, etc.
Note:While solving this question, one should be familiar with the concept of S.H.M. Some concepts are provided above for the reference.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




