
A particle has initial velocity 10m/s and its retardation is $5m/{s^2}$. Then find its displacement in 2.5 seconds and also find its distance in 2.5 seconds.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Rate of change of velocity is acceleration and rate of change of displacement is velocity. We have kinematic formulas which will relate the velocity and displacement and the acceleration. If the acceleration is opposite to motion direction then it is deceleration. We use those formulas here to solve this problem.
Formula used:
$v = u + at$
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Complete answer:
DISTANCE:
It is the total length travelled by a particle in a certain time interval. The path in which it travels matters too. It is a scalar quantity i.e it has only magnitude. Since it has only magnitude it is Always positive. Its value will be greater than or equal to the displacement. Its unit is meter.
DISPLACEMENT:
It is the shortest distance or shortest length the particle had travelled in a given time interval. Path of travel doesn’t matter over here. It is a vector quantity so it has both direction and magnitude. It can be positive or negative or even can be zero. It can never be greater than distance it is always lesser than or equal to distance. Its unit is meter.
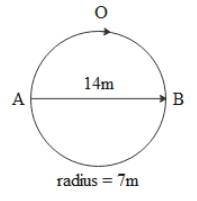
In the above circle if a particle had travelled from A to B along AOB then distance is half of the perimeter of the circle i.e 22m while displacement is its diameter i.e 14m and if it reaches point A again then distance is its perimeter 44m while displacement is zero.
Now coming to the question, we will find out at what time particle velocity will become zero because after that particle reverses its direction. We have formula
$v = u + at$
So in the above equation we have ‘v’ is the velocity at time instant ‘t’ and ‘a’ is the uniform acceleration and ‘u’ is the initial velocity. Here it is retardation so we should use negative symbol before ‘a’
$\eqalign{
& v = u + at \cr
& \Rightarrow 0 = 10 - 5t \cr
& \Rightarrow t = 2\sec \cr} $
So after 2 seconds it will reverse its direction. We should find displacement till 2 sec and from 2 to 2.5 seconds and add magnitudes of both of them to get the distance travelled in 2.5 seconds. We have formula
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Where ‘s’ is the displacement not distance.
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {s_2} = 10 \times 2 - \dfrac{1}{2}(5){(2)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {s_2} = 10 \cr} $
Now from 2sec to 2.5 sec the displacement will be
$\eqalign{
& {s_{0.5}} = (0)t - \dfrac{1}{2}(5){(0.5)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {s_{0.5}} = - \dfrac{1}{2}(5){(0.5)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {s_{0.5}} = - 0.625 \cr} $
So distance travelled in 2.5 seconds will be
$\eqalign{
& {s_2} + \left| {{s_{0.5}}} \right| = 10 + 0.625 \cr
& \Rightarrow {s_2} + \left| {{s_{0.5}}} \right| = 10.625 \cr} $
So displacement travelled in 2.5 seconds will be
$\eqalign{
& {s_2} + {s_{0.5}} = 10 - 0.625 \cr
& \Rightarrow {s_2} + {s_{0.5}} = 9.375 \cr} $
Therefore, the particle’s displacement in 2.5 seconds is 9.375 meters and also its distance in 2.5 seconds is 10.625 meters.
Note:
Both formulas which we had used are only valid if the acceleration is uniform. If it is not uniform then that will be a function of time and we have to integrate acceleration too with respect to time and we get entirely different results. If a body is travelling in the straight lane path without reversing its direction, we call distance and displacement are equal.
Formula used:
$v = u + at$
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Complete answer:
DISTANCE:
It is the total length travelled by a particle in a certain time interval. The path in which it travels matters too. It is a scalar quantity i.e it has only magnitude. Since it has only magnitude it is Always positive. Its value will be greater than or equal to the displacement. Its unit is meter.
DISPLACEMENT:
It is the shortest distance or shortest length the particle had travelled in a given time interval. Path of travel doesn’t matter over here. It is a vector quantity so it has both direction and magnitude. It can be positive or negative or even can be zero. It can never be greater than distance it is always lesser than or equal to distance. Its unit is meter.

In the above circle if a particle had travelled from A to B along AOB then distance is half of the perimeter of the circle i.e 22m while displacement is its diameter i.e 14m and if it reaches point A again then distance is its perimeter 44m while displacement is zero.
Now coming to the question, we will find out at what time particle velocity will become zero because after that particle reverses its direction. We have formula
$v = u + at$
So in the above equation we have ‘v’ is the velocity at time instant ‘t’ and ‘a’ is the uniform acceleration and ‘u’ is the initial velocity. Here it is retardation so we should use negative symbol before ‘a’
$\eqalign{
& v = u + at \cr
& \Rightarrow 0 = 10 - 5t \cr
& \Rightarrow t = 2\sec \cr} $
So after 2 seconds it will reverse its direction. We should find displacement till 2 sec and from 2 to 2.5 seconds and add magnitudes of both of them to get the distance travelled in 2.5 seconds. We have formula
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Where ‘s’ is the displacement not distance.
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {s_2} = 10 \times 2 - \dfrac{1}{2}(5){(2)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {s_2} = 10 \cr} $
Now from 2sec to 2.5 sec the displacement will be
$\eqalign{
& {s_{0.5}} = (0)t - \dfrac{1}{2}(5){(0.5)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {s_{0.5}} = - \dfrac{1}{2}(5){(0.5)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {s_{0.5}} = - 0.625 \cr} $
So distance travelled in 2.5 seconds will be
$\eqalign{
& {s_2} + \left| {{s_{0.5}}} \right| = 10 + 0.625 \cr
& \Rightarrow {s_2} + \left| {{s_{0.5}}} \right| = 10.625 \cr} $
So displacement travelled in 2.5 seconds will be
$\eqalign{
& {s_2} + {s_{0.5}} = 10 - 0.625 \cr
& \Rightarrow {s_2} + {s_{0.5}} = 9.375 \cr} $
Therefore, the particle’s displacement in 2.5 seconds is 9.375 meters and also its distance in 2.5 seconds is 10.625 meters.
Note:
Both formulas which we had used are only valid if the acceleration is uniform. If it is not uniform then that will be a function of time and we have to integrate acceleration too with respect to time and we get entirely different results. If a body is travelling in the straight lane path without reversing its direction, we call distance and displacement are equal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




