
A particle B of mass 0.6 kg slides down the smooth face PR of a wedge A of mass 1.7 kg which can move freely on a smooth horizontal surface. If the inclination of the face PR to the horizontal is 45°, then,
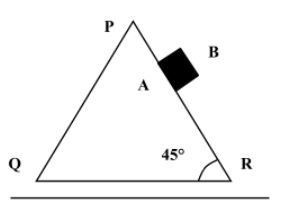
A.the acceleration of A is $\dfrac {3g}{20}$
B.the vertical component of the acceleration of the B is $\dfrac {23g}{40}$
C.the horizontal component of the acceleration of the B is $\dfrac {17g}{40}$
D.the vertical and horizontal components of the acceleration of B must be equal

Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: It is a multiple-choice question, so more than one option are correct. Start solving this problem by finding the acceleration of the wedge. Acceleration can be found using the contact force between the wedge and the particle i.e. A and B. Then, using this obtained value for acceleration, find the vertical component of acceleration. As the options are in terms of g, don’t substitute the value for g. Then, subtract the acceleration of A from the vertical component of acceleration. This will give the horizontal component of acceleration.
Complete answer:
Given: Mass of the particle B (m)= 0.6 kg
Mass of the wedge (M)= 1.7 kg
Let the acceleration of the wedge be a
On the wedge, a force $N \cos{\theta}$ acts towards the left
Where, N is the contact force between the wedge and the particle.
Thus, wedge’s acceleration towards the left will be,
$N \sin {\theta} = Ma$ …(1)
When the particle moves down the incline and is normal to the face then
$mg \cos{\theta} = N + ma \sin{\theta}$
Rearranging the above equation we get,
$N= mg \cos{\theta}- ma \sin{\theta}$ …(2)
Substituting equation. (2) in equation. (1) we get,
$ (mg \cos{\theta}- ma \sin{\theta}) \sin {\theta} = Ma$
$\Rightarrow mg \sin{\theta} \cos {\theta}- ma {\sin}{^2}{\theta}= Ma$
$\Rightarrow mg \sin{\theta} \cos {\theta} = Ma + ma{\sin}{^2}{\theta}$
$\Rightarrow mg \sin{\theta} \cos {\theta}= a(M + m{\sin}{^2}{\theta})$
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac {mg \sin{\theta} \cos{\theta}}{M + m {\sin}^{2}{\theta}}$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
$ a = \dfrac {0.6g \times \sin{45°} \cos{45°}}{1.7 + 0.6 \times {\sin}^{2}{45°}}$
$\therefore a = \dfrac {3g}{20}$ …(3)
Now, acceleration of m relative to the wedge is given by,
${a}_{1} = a\cos{\theta} + g\sin{\theta}$ …(4)
Vertical component will be given by,
${V}_{C} = {a}_{1} \sin {\theta}$ …(5)
Where, ${V}_{C}$ is the vertical component
Substituting equation. (4) in equation. (5) we get,
${V}_{C} = (a\cos{\theta} + g\sin{\theta})\sin {\theta}$
Now, substituting the values in above equation we get,
${V}_{C} = (\dfrac {3g}{20} \times \cos{45°} + g\sin{45°})\sin {45°}$
$\Rightarrow { V}_{C}=( \dfrac {3g}{20} \times \dfrac {1}{\sqrt {2}} + g \times \dfrac {1}{\sqrt {2}}) \dfrac {1}{\sqrt {2}}$
$\Rightarrow { V}_{C}= ( \dfrac {3g}{20} + g) \dfrac {1}{\sqrt{2}} \times \dfrac {1}{\sqrt{2}}$
$\Rightarrow { V}_{C}= ( \dfrac {3g}{20} + g) \dfrac {1}{2}$
$\therefore{ V}_{C}= \dfrac {23g}{40}$ …(6)
Now, horizontal component = vertical component – a
$ {H}_{C} = {V}_{C} – a$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
$ {H}_{C} = \dfrac {23g}{40} – \dfrac {3g}{20}$
$\therefore {H}_{C} = \dfrac {17g}{40}$ …(7)
Hence, the acceleration of A is $\dfrac {3g}{20}$, the vertical component of the acceleration of the B is $\dfrac {23g}{40}$ and the horizontal component of the acceleration of the B is $\dfrac {17g}{40}$.
So, the correct answers are option A, B and C.
Note:
Students should understand that sometimes more than one option can be correct. So, if you get one option correct, don’t ignore the other options. Check the remaining options as well. All the correct options are related to each other, so you have to solve the earlier option to reach the next option. The solution to this problem is long, so go step-by-step and don’t forget to give the equation numbers. Giving the equations numbers helps you in solving problems with a lot of equations.
Complete answer:
Given: Mass of the particle B (m)= 0.6 kg
Mass of the wedge (M)= 1.7 kg
Let the acceleration of the wedge be a
On the wedge, a force $N \cos{\theta}$ acts towards the left
Where, N is the contact force between the wedge and the particle.
Thus, wedge’s acceleration towards the left will be,
$N \sin {\theta} = Ma$ …(1)
When the particle moves down the incline and is normal to the face then
$mg \cos{\theta} = N + ma \sin{\theta}$
Rearranging the above equation we get,
$N= mg \cos{\theta}- ma \sin{\theta}$ …(2)
Substituting equation. (2) in equation. (1) we get,
$ (mg \cos{\theta}- ma \sin{\theta}) \sin {\theta} = Ma$
$\Rightarrow mg \sin{\theta} \cos {\theta}- ma {\sin}{^2}{\theta}= Ma$
$\Rightarrow mg \sin{\theta} \cos {\theta} = Ma + ma{\sin}{^2}{\theta}$
$\Rightarrow mg \sin{\theta} \cos {\theta}= a(M + m{\sin}{^2}{\theta})$
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac {mg \sin{\theta} \cos{\theta}}{M + m {\sin}^{2}{\theta}}$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
$ a = \dfrac {0.6g \times \sin{45°} \cos{45°}}{1.7 + 0.6 \times {\sin}^{2}{45°}}$
$\therefore a = \dfrac {3g}{20}$ …(3)
Now, acceleration of m relative to the wedge is given by,
${a}_{1} = a\cos{\theta} + g\sin{\theta}$ …(4)
Vertical component will be given by,
${V}_{C} = {a}_{1} \sin {\theta}$ …(5)
Where, ${V}_{C}$ is the vertical component
Substituting equation. (4) in equation. (5) we get,
${V}_{C} = (a\cos{\theta} + g\sin{\theta})\sin {\theta}$
Now, substituting the values in above equation we get,
${V}_{C} = (\dfrac {3g}{20} \times \cos{45°} + g\sin{45°})\sin {45°}$
$\Rightarrow { V}_{C}=( \dfrac {3g}{20} \times \dfrac {1}{\sqrt {2}} + g \times \dfrac {1}{\sqrt {2}}) \dfrac {1}{\sqrt {2}}$
$\Rightarrow { V}_{C}= ( \dfrac {3g}{20} + g) \dfrac {1}{\sqrt{2}} \times \dfrac {1}{\sqrt{2}}$
$\Rightarrow { V}_{C}= ( \dfrac {3g}{20} + g) \dfrac {1}{2}$
$\therefore{ V}_{C}= \dfrac {23g}{40}$ …(6)
Now, horizontal component = vertical component – a
$ {H}_{C} = {V}_{C} – a$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
$ {H}_{C} = \dfrac {23g}{40} – \dfrac {3g}{20}$
$\therefore {H}_{C} = \dfrac {17g}{40}$ …(7)
Hence, the acceleration of A is $\dfrac {3g}{20}$, the vertical component of the acceleration of the B is $\dfrac {23g}{40}$ and the horizontal component of the acceleration of the B is $\dfrac {17g}{40}$.
So, the correct answers are option A, B and C.
Note:
Students should understand that sometimes more than one option can be correct. So, if you get one option correct, don’t ignore the other options. Check the remaining options as well. All the correct options are related to each other, so you have to solve the earlier option to reach the next option. The solution to this problem is long, so go step-by-step and don’t forget to give the equation numbers. Giving the equations numbers helps you in solving problems with a lot of equations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




