
A particle aimed at a target, projected with an angle ${15^ \circ }$ with the horizontal is short of the target by $10m$. If projected with an angle of ${45^ \circ }$ is away from the target by $15m$, then the angle of projection to hit the target is:
A) $\dfrac{1}{2}{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{10}}} \right)$
B) $\dfrac{1}{2}{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{{10}}} \right)$
C) $\dfrac{1}{2}{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{9}{{10}}} \right)$
D) $\dfrac{1}{2}{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{7}{{10}}} \right)$
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: Here we will be using a concept of projectile motion. And applying a range of projectile formulas to calculate angle of projectile. Anybody projected into the air at an angle other than ${90^ \circ }$ with the horizontal is called projectile motion. There are three parameters which are related to projectile motion.
Formula used: Range of projectile,
$R = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$
Where, $u$ is velocity of projection, $\theta $ is angle of projection, $g$ is acceleration due to gravity, \[g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, case (i)$\theta = {15^{^0}}$
Let ‘$x$’ be the horizontal range travelled by the projectile which we need to calculate.
$ \Rightarrow {R_1} = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$...................... (a)
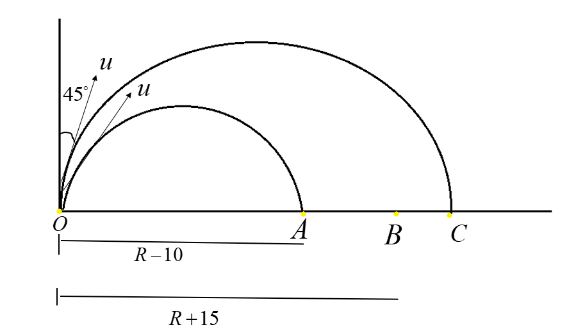
Here ${R_1}$ is the horizontal distance travelled by the projectile at an angle ${15^{^0}}$. Then from figure,
Here, a particle is projected at an angle of ${15^{^0}}$ and it has reached $10m$ short before reaching the target.
$ \Rightarrow {R_1} = x - 10$
Substitute in equation (a) we get,
$ \Rightarrow x - 10 = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2 \times 15}}{g}$
\[ \Rightarrow x - 10 = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin {{30}^ \circ }}}{g}\]
Here we can substitute the trigonometry value
$ \Rightarrow \sin {30^0} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{{2g}} = x - 10$ ……………….. (1)
Case (ii) $\theta = {45^{^0}}$
Here ${R_2}$ is the horizontal distance travelled by the projectile at an angle${45^{^0}}$. Then from figure,
$ \Rightarrow {R_2} = x + 15$
A particle is projected at an angle of ${45^{^0}}$ and it has reached a point which is $15m$ away from the target.
$ \Rightarrow {R_2} = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$
$ \Rightarrow x + 15 = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2 \times 45}}{g}$
We have,
$ \Rightarrow \sin {90^0} = 1$
from the trigonometry formula we get
$ \Rightarrow x + 15 = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin {{90}^0}}}{g}$
$ \Rightarrow x + 15 = \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{g}$ ………….. (2)
Substitute equation (2) in (1), we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{x + 15}}{2} = x - 10$
$ \Rightarrow x + 15 = 2x - 20$
$ \Rightarrow x = 35{\text{m}}$
$\because x = m$
After substituting the value of $x$ in equation (2),
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{g} = 50$
Now we can calculate angle of projection$\theta $ ,
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$
$ \Rightarrow 35 = 50 \times \sin 2\theta $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{7}{{10}} = \sin 2\theta $
$ \Rightarrow 2\theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{7}{{10}}} \right)$
$\therefore \theta = \dfrac{1}{2}{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{7}{{10}}} \right)$
Thus, the correct option is (D).
Note: (i) Time of flight: Total time to reach the horizontal surface of the projectile is called time of flight. It is the total time for which the projectile remains in air.
(ii) Maximum height: The vertical displacement of the projectile during time of ascent (For a projectile the time to reach maximum height).
(iii) Horizontal range: The horizontal distance covered by the projectile during its motion.
Formula used: Range of projectile,
$R = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$
Where, $u$ is velocity of projection, $\theta $ is angle of projection, $g$ is acceleration due to gravity, \[g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, case (i)$\theta = {15^{^0}}$
Let ‘$x$’ be the horizontal range travelled by the projectile which we need to calculate.
$ \Rightarrow {R_1} = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$...................... (a)

Here ${R_1}$ is the horizontal distance travelled by the projectile at an angle ${15^{^0}}$. Then from figure,
Here, a particle is projected at an angle of ${15^{^0}}$ and it has reached $10m$ short before reaching the target.
$ \Rightarrow {R_1} = x - 10$
Substitute in equation (a) we get,
$ \Rightarrow x - 10 = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2 \times 15}}{g}$
\[ \Rightarrow x - 10 = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin {{30}^ \circ }}}{g}\]
Here we can substitute the trigonometry value
$ \Rightarrow \sin {30^0} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{{2g}} = x - 10$ ……………….. (1)
Case (ii) $\theta = {45^{^0}}$
Here ${R_2}$ is the horizontal distance travelled by the projectile at an angle${45^{^0}}$. Then from figure,
$ \Rightarrow {R_2} = x + 15$
A particle is projected at an angle of ${45^{^0}}$ and it has reached a point which is $15m$ away from the target.
$ \Rightarrow {R_2} = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$
$ \Rightarrow x + 15 = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2 \times 45}}{g}$
We have,
$ \Rightarrow \sin {90^0} = 1$
from the trigonometry formula we get
$ \Rightarrow x + 15 = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin {{90}^0}}}{g}$
$ \Rightarrow x + 15 = \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{g}$ ………….. (2)
Substitute equation (2) in (1), we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{x + 15}}{2} = x - 10$
$ \Rightarrow x + 15 = 2x - 20$
$ \Rightarrow x = 35{\text{m}}$
$\because x = m$
After substituting the value of $x$ in equation (2),
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{g} = 50$
Now we can calculate angle of projection$\theta $ ,
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$
$ \Rightarrow 35 = 50 \times \sin 2\theta $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{7}{{10}} = \sin 2\theta $
$ \Rightarrow 2\theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{7}{{10}}} \right)$
$\therefore \theta = \dfrac{1}{2}{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{7}{{10}}} \right)$
Thus, the correct option is (D).
Note: (i) Time of flight: Total time to reach the horizontal surface of the projectile is called time of flight. It is the total time for which the projectile remains in air.
(ii) Maximum height: The vertical displacement of the projectile during time of ascent (For a projectile the time to reach maximum height).
(iii) Horizontal range: The horizontal distance covered by the projectile during its motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




