
A part of the circuit is shown in figure. Here reading of ammeter is 5 ampere and voltmeter is 96V and voltmeter resistance is 480ohm. Then find the resistance R in Ohms
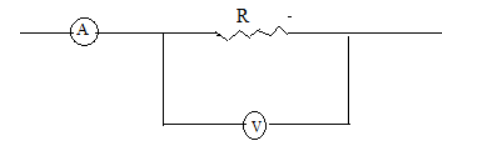

Answer
599.7k+ views
Hint: In this question, first of all we will see the definition and connection of ammeter and voltmeter. The reading of ammeter gives total current entering the circuit. So we will calculate the current through the lower branch i.e. current through voltmeter. Then we will calculate the current through the given resistance R. Finally use formula V = IR to find the value of resistance.
Complete answer:
Voltmeter is an electrical instrument which is used to measure the potential difference between two points. It is always connected in parallel to the element across which voltage is to be measured. The resistance of the voltmeter is kept high so that current flowing through the voltmeter is very less.
Ammeter is an electrical instrument which measures the current flowing the circuit. It is connected in series to the element in which current is to be measured.. The resistance of the ammeter is kept very small such that the reading of the ammeter does not give wrong reading.
The circuit for the question is shown below:
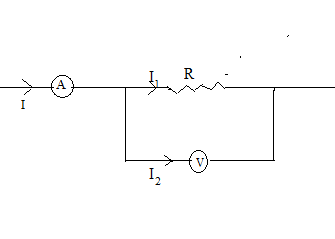
Let the current through the ammeter be I A
$\therefore $ I = 5 A
Now this current is getting divided into two parts.
I =${{\text{I}}_1} + {{\text{I}}_2}$ (1)
Voltage across voltmeter = voltage measured by voltmeter = 96V
Resistance of voltmeter = ${{\text{R}}_v}$ =480 ohm
According to ohm law, we can write:
V= IR
$ \Rightarrow {\text{I = }}\dfrac{V}{R}$
Putting the values of voltage and resistance, we get:
${{\text{I}}_2} = \dfrac{{96}}{{480}}A = 0.2A$
Putting the value of ${I_2}$ in equation 1, we get:
${{\text{I}}_1} = {\text{I - }}{{\text{I}}_2} = 5 - 0.2 = 4.8A$
Now, we know that voltage across the resistance =96V
So, by using ohm’s law we can write:
V= IR
$ \Rightarrow R{\text{ = }}\dfrac{V}{I}$
Putting the value of current through resistance R and voltage across R, we get:
$ \Rightarrow R{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{96}}{{4.8}} = 20$ ohm
Therefore the value of resistance R = 20ohm.
Note- In parallel circuit, the is divided in inverse ratio of the resistances. For an ideal voltmeter, the resistance is infinity so that the current drawn by the voltmeter is zero and also power loss in voltmeter is zero. Similarly, the resistance of the ammeter ideally should be zero so that it does not change the current in the circuit.
Complete answer:
Voltmeter is an electrical instrument which is used to measure the potential difference between two points. It is always connected in parallel to the element across which voltage is to be measured. The resistance of the voltmeter is kept high so that current flowing through the voltmeter is very less.
Ammeter is an electrical instrument which measures the current flowing the circuit. It is connected in series to the element in which current is to be measured.. The resistance of the ammeter is kept very small such that the reading of the ammeter does not give wrong reading.
The circuit for the question is shown below:

Let the current through the ammeter be I A
$\therefore $ I = 5 A
Now this current is getting divided into two parts.
I =${{\text{I}}_1} + {{\text{I}}_2}$ (1)
Voltage across voltmeter = voltage measured by voltmeter = 96V
Resistance of voltmeter = ${{\text{R}}_v}$ =480 ohm
According to ohm law, we can write:
V= IR
$ \Rightarrow {\text{I = }}\dfrac{V}{R}$
Putting the values of voltage and resistance, we get:
${{\text{I}}_2} = \dfrac{{96}}{{480}}A = 0.2A$
Putting the value of ${I_2}$ in equation 1, we get:
${{\text{I}}_1} = {\text{I - }}{{\text{I}}_2} = 5 - 0.2 = 4.8A$
Now, we know that voltage across the resistance =96V
So, by using ohm’s law we can write:
V= IR
$ \Rightarrow R{\text{ = }}\dfrac{V}{I}$
Putting the value of current through resistance R and voltage across R, we get:
$ \Rightarrow R{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{96}}{{4.8}} = 20$ ohm
Therefore the value of resistance R = 20ohm.
Note- In parallel circuit, the is divided in inverse ratio of the resistances. For an ideal voltmeter, the resistance is infinity so that the current drawn by the voltmeter is zero and also power loss in voltmeter is zero. Similarly, the resistance of the ammeter ideally should be zero so that it does not change the current in the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




