
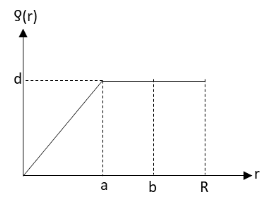
A nuclear charge (Ze) is non-uniformly distributed within a nucleus of radius \[R\]. The charge density \[\rho \left( r \right)\] [charge per unit volume] is dependent on the radial distance from the centre of the nucleus as shown in figure. Select correct alternative/s.
A. Electric potential at \[r = R\] is independent of \[b\]
B. Electric potential at \[r = R\] is proportional to \[b\]
C. Electric field at \[r = R\] is proportional to \[a\]
D. Electric potential at \[r = R\] is proportional to \[a\]

Answer
558k+ views
Hint:Use the formulae for the electric field and electric potential at a point inside a nucleus in which the charge is not distributed uniformly. From these two formulae, derive the relation between the electric field and electric potential at a point inside the nucleus and check which of the statements given in the options are correct.
Complete answer:
We have given that the charge in the nucleus is non-uniformly distributed and the radius of the nucleus is \[R\].The charge density of the nucleus depends on the distance of the charge from the centre of the nucleus.The graph of variation of the charge density with the distance from the centre of the nucleus is given in the question.
The electric field \[E\left( r \right)\] at any point inside the nucleus is given by
\[E\left( r \right) = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{Qr}}{{{R^3}}}\] …… (1)
Here, \[{\varepsilon _0}\] is the permittivity of free space, \[Q\] is the charge, \[r\] is the distance from the centre of the nucleus and \[R\] is radius of the nucleus.
The electric potential \[V\left( r \right)\] at a point due to charge is given by
\[V\left( r \right) = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{Q}{r}\] …… (2)
Here, \[{\varepsilon _0}\] is the permittivity of free space and \[r\] is the distance from the centre of the nucleus.
From equations (1) and (2), we can see that the electric field and electric potential at any point inside the nucleus depends on the distance \[r\] of that point from the centre of the nucleus.The electric potential at a point \[r = R\] is inversely proportional to the \[R\]. Thus, the electric potential at \[r = R\] is independent of \[b\]. Also the electric potential at is not proportional to \[a\] and \[b\].Hence, the statement given in option A is correct and the statements given in options B and D are incorrect.The electric field at a point \[r = R\] is proportional to \[R\] and not to \[a\].Hence, the statement given in option C is incorrect.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: The students should be careful while using the formula for the electric field and electric potential at a point inside the nucleus because the students may assume that these two physical quantities electric field and electric potential are the same. But these two are different physical quantities with different formulae.
Complete answer:
We have given that the charge in the nucleus is non-uniformly distributed and the radius of the nucleus is \[R\].The charge density of the nucleus depends on the distance of the charge from the centre of the nucleus.The graph of variation of the charge density with the distance from the centre of the nucleus is given in the question.
The electric field \[E\left( r \right)\] at any point inside the nucleus is given by
\[E\left( r \right) = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{Qr}}{{{R^3}}}\] …… (1)
Here, \[{\varepsilon _0}\] is the permittivity of free space, \[Q\] is the charge, \[r\] is the distance from the centre of the nucleus and \[R\] is radius of the nucleus.
The electric potential \[V\left( r \right)\] at a point due to charge is given by
\[V\left( r \right) = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{Q}{r}\] …… (2)
Here, \[{\varepsilon _0}\] is the permittivity of free space and \[r\] is the distance from the centre of the nucleus.
From equations (1) and (2), we can see that the electric field and electric potential at any point inside the nucleus depends on the distance \[r\] of that point from the centre of the nucleus.The electric potential at a point \[r = R\] is inversely proportional to the \[R\]. Thus, the electric potential at \[r = R\] is independent of \[b\]. Also the electric potential at is not proportional to \[a\] and \[b\].Hence, the statement given in option A is correct and the statements given in options B and D are incorrect.The electric field at a point \[r = R\] is proportional to \[R\] and not to \[a\].Hence, the statement given in option C is incorrect.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: The students should be careful while using the formula for the electric field and electric potential at a point inside the nucleus because the students may assume that these two physical quantities electric field and electric potential are the same. But these two are different physical quantities with different formulae.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




