
A n-type semiconductor is
A. Positively charged
B. Negatively charged
C. Electrically neutral
D. None of the above
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: A substance that is neither conductor or insulator is called semiconductor.
Complete step by step answer:
Semiconductors have conductivity in a natural state. But it is not good enough to carry current through them.
Conductors have conductivity in their natural state and they can carry electric charge but they can carry electric charge but they are very costly to be used as connectivity commercially.
Therefore, we try to convert semiconductors to conductors so that it could be used on a commercial level.
To make that possible, we add some impurities to the semiconductors. This process of adding an impurity is called doping.
Let us consider an example.
Silicon is a semiconductor. It has $4$ valence electrons in its outer shell. Now, when silicon atoms combine, they form bonds with each tree electron. (As shown in diagram).

Therefore, there is no free valence electron available to carry current.
But if we add some pent ante impurity like phosphorus. Phosphorus has $5$ valence electrons.
So, when phosphorus is added to silicon metal by doping, $4$ silicon metals will form bonds with $4$valence electrons of silicon, but $1$ electron of phosphorus will still be left:
This one electron will help in carrying the current.
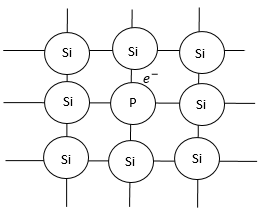
Since, in this type of a semiconductor, we have a free electron available it is called n-type semiconductor.
Where, n represents negative charge.
But even though n-type semiconductor has a valence electron, it is an electron of a neutral atom. So n-type semiconductor is in an electrically neutral state.
Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (C) Electrically neutral.
Note:here is also a p-type semiconductor. P-type semiconductor has one less electron. i.e. one extra positive charge.
N and p-type semiconductors are used manufacturing electronic components n-type and p-type are combined to form diodes which are used in transistors.
Complete step by step answer:
Semiconductors have conductivity in a natural state. But it is not good enough to carry current through them.
Conductors have conductivity in their natural state and they can carry electric charge but they can carry electric charge but they are very costly to be used as connectivity commercially.
Therefore, we try to convert semiconductors to conductors so that it could be used on a commercial level.
To make that possible, we add some impurities to the semiconductors. This process of adding an impurity is called doping.
Let us consider an example.
Silicon is a semiconductor. It has $4$ valence electrons in its outer shell. Now, when silicon atoms combine, they form bonds with each tree electron. (As shown in diagram).

Therefore, there is no free valence electron available to carry current.
But if we add some pent ante impurity like phosphorus. Phosphorus has $5$ valence electrons.
So, when phosphorus is added to silicon metal by doping, $4$ silicon metals will form bonds with $4$valence electrons of silicon, but $1$ electron of phosphorus will still be left:
This one electron will help in carrying the current.

Since, in this type of a semiconductor, we have a free electron available it is called n-type semiconductor.
Where, n represents negative charge.
But even though n-type semiconductor has a valence electron, it is an electron of a neutral atom. So n-type semiconductor is in an electrically neutral state.
Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (C) Electrically neutral.
Note:here is also a p-type semiconductor. P-type semiconductor has one less electron. i.e. one extra positive charge.
N and p-type semiconductors are used manufacturing electronic components n-type and p-type are combined to form diodes which are used in transistors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




