
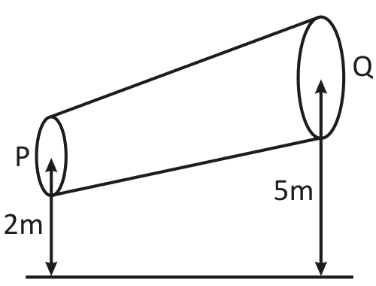
A non-viscous liquid of constant density \[1000\,{\text{kg}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] flows in a streamlined motion along a tube of variable cross section. The tube is kept inclined in the vertical plane as shown in the figure. The area of cross-section of the tube \[P\] and \[Q\] at heights of \[2\,{\text{m}}\] and \[5\,{\text{m}}\] are respectively \[4 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,{{\text{m}}^2}\] and \[8 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,{{\text{m}}^2}\] . The velocity of the liquid at point \[P\] is \[1\,{\text{m}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] . Then,
A. Work done by pressure per unit volume is \[ - 29625\,{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\]
B. Work done by pressure per unit volume is \[ + 29625\,{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\]
C. Work done by gravity is \[ - 30000\,{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\]
D. Work done by gravity is \[ + 30000\,{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\]

Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: First of all, we will use the equation of continuity to find the velocity at the tube \[Q\] . After that we will use Bernoulli's theorem to find the work done by pressure. Lastly, we will use the expression for the work done by gravity to calculate the value. Multiple options may be correct.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given question, we are supplied the following information:
The density of the non-viscous liquid is \[1000\,{\text{kg}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] .The area of the cross section of the tube \[P\] is \[4 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,{{\text{m}}^2}\] .The area of the cross section of the tube \[Q\] is \[8 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,{{\text{m}}^2}\] .The velocity of the liquid at point \[P\] is \[1\,{\text{m}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] .We are asked to find the amount of work done and its type.
To begin with, we will use the equation of continuity at the tube \[P\] and \[Q\] .
The equation of continuity is given below:
\[{a_{\text{P}}} \times {v_{\text{P}}} = {a_{\text{Q}}} \times {v_{\text{Q}}}\] …… (1)
Where,
\[{a_{\text{P}}}\] indicates the area of the cross section of \[P\] .
\[{v_{\text{P}}}\] indicates the velocity of fluid at \[P\] .
\[{a_{\text{Q}}}\] indicates the area of the cross section of \[Q\] .
\[{v_{\text{Q}}}\] indicates the velocity of fluid at \[Q\] .
Now,
${a_{\text{P}}} \times {v_{\text{P}}} = {a_{\text{Q}}} \times {v_{\text{Q}}} \\
\Rightarrow {v_{\text{Q}}} = \dfrac{{{a_{\text{P}}}}}{{{a_{\text{Q}}}}} \times {v_{\text{P}}} \\
\Rightarrow {v_{\text{Q}}} = \dfrac{{4 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}\,{{\text{m}}^2}}}{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}\,{{\text{m}}^2}}} \times 1 \\
\Rightarrow {v_{\text{Q}}} = 0.5\,{\text{m}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$
Therefore, the velocity of the fluid at \[Q\] is \[0.5\,{\text{m}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] .
From Bernoulli's theorem at points \[P\] and \[Q\] .
\[{p_{\text{P}}} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_{\text{P}}^2 + \rho g{h_{\text{P}}} = {p_{\text{Q}}} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_{\text{Q}}^2 + \rho g{h_{\text{Q}}}\]
Expression for the work done by pressure is given below:
\[ \Rightarrow {p_{\text{P}}} - {p_{\text{Q}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho \left( {v_{\text{Q}}^2 - v_{\text{P}}^2} \right) + \rho g\left( {{h_{\text{Q}}} - {h_{\text{P}}}} \right)\] …… (2)
Where,
\[\rho \] indicates the density of the liquid.
\[g\] indicates the acceleration due to gravity.
\[p\] indicates pressure exerted by the liquid.
All the terms in the equation (2) represents energy per unit volume of the liquid.
Substituting the required values in the equation (2), we get:
$ {p_{\text{P}}} - {p_{\text{Q}}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1000 \times \left( {{{0.5}^2} - {1^2}} \right) + 1000 \times 10 \times \left( {5 - 2} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {p_{\text{P}}} - {p_{\text{Q}}} = 500 \times \left( { - 0.75} \right) + 10000 \times 3 \\
\Rightarrow {p_{\text{P}}} - {p_{\text{Q}}} = 29.625 \times {10^3}\,{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}$
Therefore, work done by pressure is \[29.625 \times {10^3}\,{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] .
Now, we calculate the work done by gravity is:
$W = \rho g{h_{\text{P}}} - \rho g{h_{\text{Q}}} \\
\Rightarrow W = \rho g\left( {{h_{\text{P}}} - {h_{\text{Q}}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow W = 1000 \times 10 \times \left( {2 - 5} \right) \\
\therefore W = - 3 \times {10^4}{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}$
Therefore, work done by gravity is \[ - 3 \times {10^4}{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] .
The correct options are B and C.
Note: In the given question, we must remember that the work done by the gravity is always negative when the substance or the object goes up. This is due to the fact that gravity tries to decrease the kinetic energy of the substance.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given question, we are supplied the following information:
The density of the non-viscous liquid is \[1000\,{\text{kg}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] .The area of the cross section of the tube \[P\] is \[4 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,{{\text{m}}^2}\] .The area of the cross section of the tube \[Q\] is \[8 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,{{\text{m}}^2}\] .The velocity of the liquid at point \[P\] is \[1\,{\text{m}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] .We are asked to find the amount of work done and its type.
To begin with, we will use the equation of continuity at the tube \[P\] and \[Q\] .
The equation of continuity is given below:
\[{a_{\text{P}}} \times {v_{\text{P}}} = {a_{\text{Q}}} \times {v_{\text{Q}}}\] …… (1)
Where,
\[{a_{\text{P}}}\] indicates the area of the cross section of \[P\] .
\[{v_{\text{P}}}\] indicates the velocity of fluid at \[P\] .
\[{a_{\text{Q}}}\] indicates the area of the cross section of \[Q\] .
\[{v_{\text{Q}}}\] indicates the velocity of fluid at \[Q\] .
Now,
${a_{\text{P}}} \times {v_{\text{P}}} = {a_{\text{Q}}} \times {v_{\text{Q}}} \\
\Rightarrow {v_{\text{Q}}} = \dfrac{{{a_{\text{P}}}}}{{{a_{\text{Q}}}}} \times {v_{\text{P}}} \\
\Rightarrow {v_{\text{Q}}} = \dfrac{{4 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}\,{{\text{m}}^2}}}{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}\,{{\text{m}}^2}}} \times 1 \\
\Rightarrow {v_{\text{Q}}} = 0.5\,{\text{m}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$
Therefore, the velocity of the fluid at \[Q\] is \[0.5\,{\text{m}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] .
From Bernoulli's theorem at points \[P\] and \[Q\] .
\[{p_{\text{P}}} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_{\text{P}}^2 + \rho g{h_{\text{P}}} = {p_{\text{Q}}} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_{\text{Q}}^2 + \rho g{h_{\text{Q}}}\]
Expression for the work done by pressure is given below:
\[ \Rightarrow {p_{\text{P}}} - {p_{\text{Q}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho \left( {v_{\text{Q}}^2 - v_{\text{P}}^2} \right) + \rho g\left( {{h_{\text{Q}}} - {h_{\text{P}}}} \right)\] …… (2)
Where,
\[\rho \] indicates the density of the liquid.
\[g\] indicates the acceleration due to gravity.
\[p\] indicates pressure exerted by the liquid.
All the terms in the equation (2) represents energy per unit volume of the liquid.
Substituting the required values in the equation (2), we get:
$ {p_{\text{P}}} - {p_{\text{Q}}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1000 \times \left( {{{0.5}^2} - {1^2}} \right) + 1000 \times 10 \times \left( {5 - 2} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {p_{\text{P}}} - {p_{\text{Q}}} = 500 \times \left( { - 0.75} \right) + 10000 \times 3 \\
\Rightarrow {p_{\text{P}}} - {p_{\text{Q}}} = 29.625 \times {10^3}\,{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}$
Therefore, work done by pressure is \[29.625 \times {10^3}\,{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] .
Now, we calculate the work done by gravity is:
$W = \rho g{h_{\text{P}}} - \rho g{h_{\text{Q}}} \\
\Rightarrow W = \rho g\left( {{h_{\text{P}}} - {h_{\text{Q}}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow W = 1000 \times 10 \times \left( {2 - 5} \right) \\
\therefore W = - 3 \times {10^4}{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}$
Therefore, work done by gravity is \[ - 3 \times {10^4}{\text{J}}\,{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] .
The correct options are B and C.
Note: In the given question, we must remember that the work done by the gravity is always negative when the substance or the object goes up. This is due to the fact that gravity tries to decrease the kinetic energy of the substance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




