
A monobasic acid A has a neutralization equivalent 116 and does not decolorize Baeyer's reagent. Also, A is enantiomeric. A on treatment with $B{{r}_{2}}/red$ phosphorus produces B which is still resolvable. B on dehydrobromination produces C which shows stereoisomerism C on decarboxylation produced. D which does not show stereoisomerism. Deduce structures of A, B, C, and D.
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: A in monobasic means the compound is having a carboxylic acid group at the terminal carbon atom. A does not decolorize Baeyer's reagent means there is no double or triple bond. Stereoisomerism means the compound can be written in the cis and trans form.
Complete step by step answer:
A is a monobasic compound that means the terminal carbon atom has a carboxyl group. It has a neutralization equivalent of 116, so the compound will be 3-Methyl pentanoic acid.
So, when 3-Methyl pentanoic acid is treated with $B{{r}_{2}}/red$ phosphorus, one bromine atom will attach to the carbon atom next to the carboxylic acid and forms 2-Bromo-3-Methyl pentanoic acid (This is B).
The compound B which is 2-Bromo-3-Methyl pentanoic acid on dehydrobromination produces C. When the dehydrobromination occurs, there is the removal of one molecule of $HBr$ and there is the formation of an alkene. So, compound C will be 3-Methylpent-2-en-1-oic acid.
Now this compound C on decarboxylation produces D which does not show stereoisomerism i.e., it cannot be written in the cis and trans-form. Or we can say that the double bond is on the terminal carbon atom. So the compound D is 2-Methyl butene. The complete one by one reaction is given below:
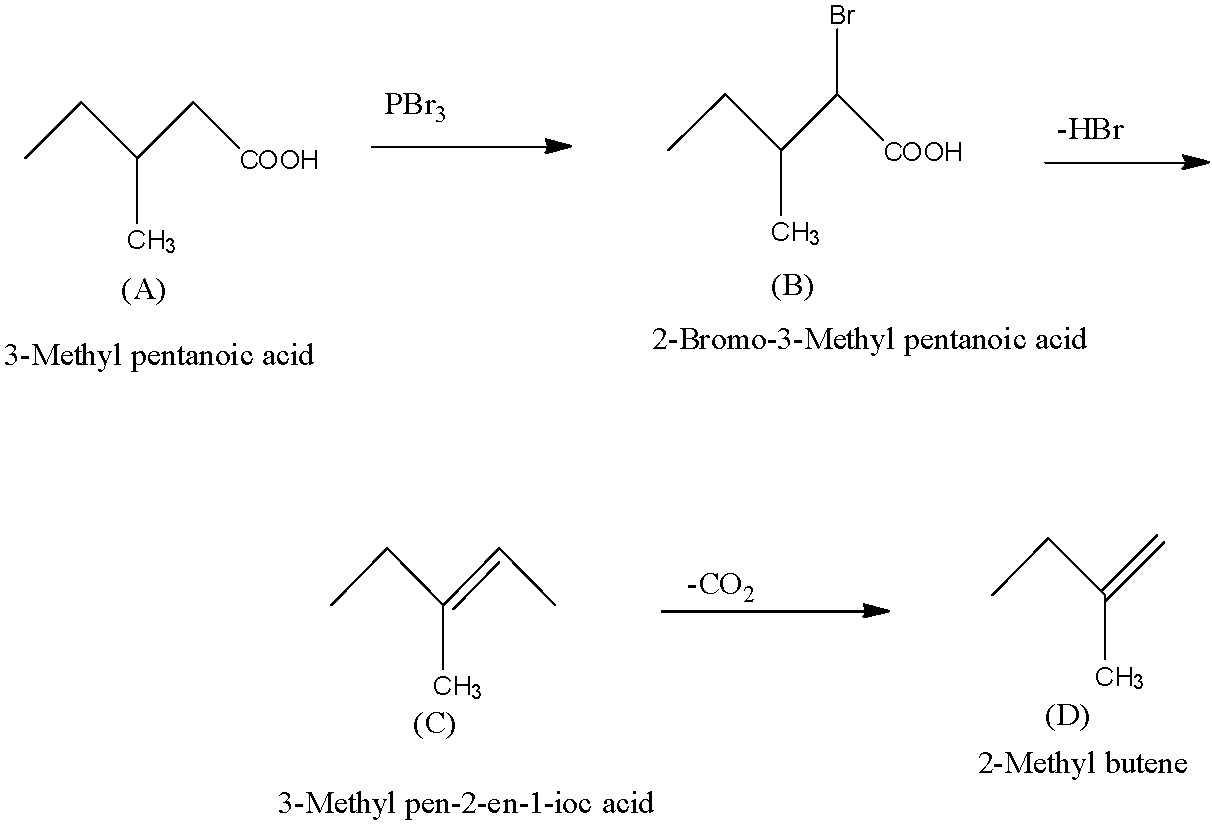
So, A is 3-Methyl pentanoic acid, B is 2-Bromo-3-Methyl pentanoic acid, C is 3-Methylpent-2-en-1-oic acid, and D is 2-Methyl butene.
Note: Stereoisomers are those which can be written in cis-form and trans-form. Cis-form is the isomer in which the same compounds are on the same side of the double bond and trans-form is the isomer in which the same compounds are on the opposite side.
Complete step by step answer:
A is a monobasic compound that means the terminal carbon atom has a carboxyl group. It has a neutralization equivalent of 116, so the compound will be 3-Methyl pentanoic acid.
So, when 3-Methyl pentanoic acid is treated with $B{{r}_{2}}/red$ phosphorus, one bromine atom will attach to the carbon atom next to the carboxylic acid and forms 2-Bromo-3-Methyl pentanoic acid (This is B).
The compound B which is 2-Bromo-3-Methyl pentanoic acid on dehydrobromination produces C. When the dehydrobromination occurs, there is the removal of one molecule of $HBr$ and there is the formation of an alkene. So, compound C will be 3-Methylpent-2-en-1-oic acid.
Now this compound C on decarboxylation produces D which does not show stereoisomerism i.e., it cannot be written in the cis and trans-form. Or we can say that the double bond is on the terminal carbon atom. So the compound D is 2-Methyl butene. The complete one by one reaction is given below:

So, A is 3-Methyl pentanoic acid, B is 2-Bromo-3-Methyl pentanoic acid, C is 3-Methylpent-2-en-1-oic acid, and D is 2-Methyl butene.
Note: Stereoisomers are those which can be written in cis-form and trans-form. Cis-form is the isomer in which the same compounds are on the same side of the double bond and trans-form is the isomer in which the same compounds are on the opposite side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




