
A monkey of mass 15 kg is climbing on a rope with one end fixed to the ceiling. If it wishes to go up with an acceleration of $1m/{{s}^{2}}$, how much force should it apply to the rope if the rope is 5 m long and the monkey starts from rest?
$\left( a \right)\,150N$
$\left( b \right)\,>160N$
$\left( c \right)\,165N$
$\left( d \right)\,150 < T\le 160N$
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: As we need to find the force that is required to make the monkey go up so, we will apply the formula of the tension which is created by keeping equilibrium in mind. This equilibrium can be created by focusing the two forces in mind which are gravitational and the force exerted by the monkey.
Formula used:
$T=mg+ma$. Here, T is the tension, g is the gravitational force and a is the acceleration of the monkey with m as a mass in kg.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Acceleration: The acceleration is the change in the velocity, direction or both. For example if we consider a toy car which is controlled by a remote then, after applying the remote if the toy car is moving forwards and then takes a round and moves to backwards then, here we can say that there is an acceleration because there is a change of speed and direction both.
Force: The force is basically the action of one object on another. This happens when two objects come under a certain contact. To understand this, we will consider a book kept on a table then, both are exerting force on each other. The table is applying force upwards on the book while the book is applying the downward force on the table. In addition to this the gravitational force is applying on both of them which is forcing them downwards.
Now, we will consider the following required diagram for the question. This is shown below.
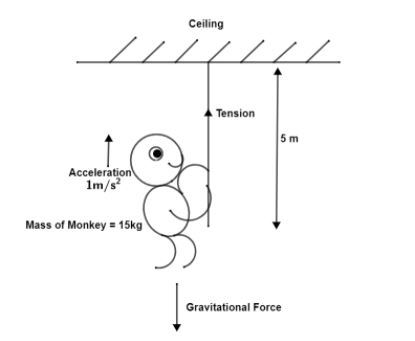
Clearly, in the diagram we can see that a rope of 5 m is tied to the ceiling. A monkey of 15 kg is trying to move upwards with an acceleration of $1m/{{s}^{2}}$. This is creating tension in the rope as there is a gravitational force also acting on the rope as well as on the monkey. This tension will be equal to the addition of the gravitational force exerted on the monkey as well as the force the monkey is creating by moving upwards with an acceleration of $1m/{{s}^{2}}$.
To make such a situation under equilibrium we will consider the equation as $T=mg+ma$….(i). Here, T is the tension created by the gravitational as well as the acceleration of the monkey. As the gravitational force is equal to $9.8N$ and the acceleration as $1m/{{s}^{2}}$ so, we will substitute these values in the equation (i) along with the substitution of the mass as 15 kg. Therefore, we have
$\begin{align}
& T=mg+ma \\
& \Rightarrow T=m\left( g+a \right) \\
& \Rightarrow T=15\left( 9.8+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow T=15\left( 10.8 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow T\approx 15\left( 11 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow T\approx 165N \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The things to be on your finger tips for further questions like this are,
(1) The concept of acceleration in terms of $m/{{s}^{2}}$.
(2) The concept of forces as in terms of gravitational force and the normal force.
(3) The gravitational force: $9.8N$.
(4) The equilibrium equation attained: $T=mg+ma$.
Formula used:
$T=mg+ma$. Here, T is the tension, g is the gravitational force and a is the acceleration of the monkey with m as a mass in kg.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Acceleration: The acceleration is the change in the velocity, direction or both. For example if we consider a toy car which is controlled by a remote then, after applying the remote if the toy car is moving forwards and then takes a round and moves to backwards then, here we can say that there is an acceleration because there is a change of speed and direction both.
Force: The force is basically the action of one object on another. This happens when two objects come under a certain contact. To understand this, we will consider a book kept on a table then, both are exerting force on each other. The table is applying force upwards on the book while the book is applying the downward force on the table. In addition to this the gravitational force is applying on both of them which is forcing them downwards.
Now, we will consider the following required diagram for the question. This is shown below.

Clearly, in the diagram we can see that a rope of 5 m is tied to the ceiling. A monkey of 15 kg is trying to move upwards with an acceleration of $1m/{{s}^{2}}$. This is creating tension in the rope as there is a gravitational force also acting on the rope as well as on the monkey. This tension will be equal to the addition of the gravitational force exerted on the monkey as well as the force the monkey is creating by moving upwards with an acceleration of $1m/{{s}^{2}}$.
To make such a situation under equilibrium we will consider the equation as $T=mg+ma$….(i). Here, T is the tension created by the gravitational as well as the acceleration of the monkey. As the gravitational force is equal to $9.8N$ and the acceleration as $1m/{{s}^{2}}$ so, we will substitute these values in the equation (i) along with the substitution of the mass as 15 kg. Therefore, we have
$\begin{align}
& T=mg+ma \\
& \Rightarrow T=m\left( g+a \right) \\
& \Rightarrow T=15\left( 9.8+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow T=15\left( 10.8 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow T\approx 15\left( 11 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow T\approx 165N \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The things to be on your finger tips for further questions like this are,
(1) The concept of acceleration in terms of $m/{{s}^{2}}$.
(2) The concept of forces as in terms of gravitational force and the normal force.
(3) The gravitational force: $9.8N$.
(4) The equilibrium equation attained: $T=mg+ma$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




