
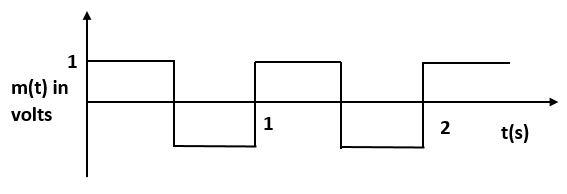
A modulating signal is a square wave as shown in the figure. The Carrier wave is given by$c(t) = 2\sin (8\pi t)volts,$the modulation index is
A.$2$
B.$0.75$
C.$0.5$
D.$1.05$

Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Modulation index of a modulation scheme is the measure of variation in carrier signal around its unmodulated level. It is given by the ratio of amplitude of modulating signal to the amplitude of carrier wave.
Formula Used: $m = \dfrac{{{A_m}}}{{{A_c}}}$
Where,
$m$ is modulation index
${A_m}$ is amplitude of modulating signal
${A_c}$ is amplitude of carrier wave
Complete step by step answer:Observe the diagram:
In simple terms, amplitude is the maximum length covered by the wave on the vertical axis (Y-axis).
We can clearly observe in the diagram that the maximum length covered by the wave on the vertical axis is 1. Thus, from the diagram, it can be observed that the amplitude of the modulating signal ${A_m} = 1V$
It is given that, the carrier wave is given by
$c(t) = 2\sin (8\pi t)volts$ . . . (1)
We know that, the maximum value of $\sin \theta = 1$. Thus the maximum length covered by the carrier wave on the vertical axis will be $2 \times 1 = 2$
Therefore, the amplitude of the career wave will be ${A_c} = 2V$
From the diagram, we can observe that the time taken for one rotation is one second.
Therefore, time period $T = 1s$
Now, we know that, the modulation index is given by
$m = \dfrac{{{A_m}}}{{{A_c}}}$
Where,
$m$ is modulation index
${A_m}$ is amplitude of modulating signal
${A_c}$ is amplitude of carrier wave
$ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow m = 0.5$
Thus, the modulation index is$0.5$
Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct answer is, option (C)$0.5$.
Note:Maximum value of sine function is 1 and the minimum value of sine function is -1. Therefore, the maximum value of the carrier wave in equation (1) is $2 \times 1 = 2$. That is why the amplitude of the carrier wave is $2V$. When a particle starts from one position on vertical axis, follows a particular path, and comes back to its position on vertical axis. And after that, repeats the same path, then we say that the particle has completed one cycle or one rotation. And the minimum time taken to complete that one rotation is time period.
Formula Used: $m = \dfrac{{{A_m}}}{{{A_c}}}$
Where,
$m$ is modulation index
${A_m}$ is amplitude of modulating signal
${A_c}$ is amplitude of carrier wave
Complete step by step answer:Observe the diagram:
In simple terms, amplitude is the maximum length covered by the wave on the vertical axis (Y-axis).
We can clearly observe in the diagram that the maximum length covered by the wave on the vertical axis is 1. Thus, from the diagram, it can be observed that the amplitude of the modulating signal ${A_m} = 1V$
It is given that, the carrier wave is given by
$c(t) = 2\sin (8\pi t)volts$ . . . (1)
We know that, the maximum value of $\sin \theta = 1$. Thus the maximum length covered by the carrier wave on the vertical axis will be $2 \times 1 = 2$
Therefore, the amplitude of the career wave will be ${A_c} = 2V$
From the diagram, we can observe that the time taken for one rotation is one second.
Therefore, time period $T = 1s$
Now, we know that, the modulation index is given by
$m = \dfrac{{{A_m}}}{{{A_c}}}$
Where,
$m$ is modulation index
${A_m}$ is amplitude of modulating signal
${A_c}$ is amplitude of carrier wave
$ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow m = 0.5$
Thus, the modulation index is$0.5$
Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct answer is, option (C)$0.5$.
Note:Maximum value of sine function is 1 and the minimum value of sine function is -1. Therefore, the maximum value of the carrier wave in equation (1) is $2 \times 1 = 2$. That is why the amplitude of the carrier wave is $2V$. When a particle starts from one position on vertical axis, follows a particular path, and comes back to its position on vertical axis. And after that, repeats the same path, then we say that the particle has completed one cycle or one rotation. And the minimum time taken to complete that one rotation is time period.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




