
A mild steel wire of length 1.0 m and cross-sectional area $0.50\times {{10}^{-2}}c{{m}^{2}}$ is stretched, well within its elastic limit, horizontally between two pillars. A mass of 100 g is suspended from the mid-point of the wire. Calculate the depression at the midpoint.
Answer
550.5k+ views
Hint: First, we need to draw a diagram showing the mild steel wire with a mass hanging at its mid-point. The young’s modulus of steel is equal to the ratio of stress and strain on the wire. By using various given information and trigonometry, we can calculate the depression in wire
Formula used:
Stress is defined as follows:
$Stress = \dfrac{F}{A}{\text{ }}...{\text{(i)}}$
where F is the force applied and A represents the area on which force is being applied.
Strain is defined as follows:
$Strain = \dfrac{{\Delta l}}{l}{\text{ }}...{\text{(ii)}}$
where $\Delta l$ is the change in length due to the applied stress while l signifies the original length of the material under stress.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given a mild steel wire of length 1m which is being stretched between two pillars and a mass of 100 g is suspended from its midpoint. Diagrammatically, the situation can be represented as follows:
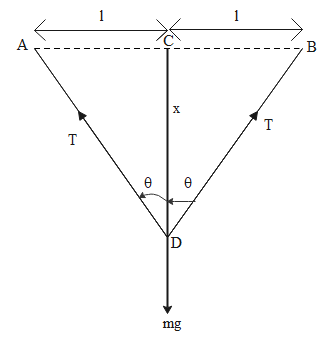
Due to the weight at the centre of the wire, the wire depresses by x.
$\therefore CD = x$
Also, in the figure we have suspended the mass from the mid-point of the wire
$\therefore AC = BC = l = 0.5m$
The mass that is suspended from the middle is given as
$m = 100g = 0.1kg$
Using the Pythagoras theorem in the figure, we get
$AD = BD = {\left( {{l^2} + {x^2}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}$
Since, there is some elasticity in the mild steel, it will get stretched and increase in length due to weight suspended from it. The increase in length is given as
$ \Delta l = AD + BD - AB \\
= 2AD - AB \\
$
Using the known values, we get
$
\Delta l = 2{\left( {{l^2} + {x^2}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} - 2l \\
= 2l{\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{l^2}}}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} - 2l \\
= 2l\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{2{l^2}}}} \right) - 2l \\
$
In the last step, we have used binomial expansion formula given as ${\left( {1 + x} \right)^n} = 1 + nx$ for x<<1
$\Delta l = 2l\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{2{l^2}}} - 1} \right) = \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{l}$
Using this change in length, we can calculate the strain on the wire given by equation (ii), as follows:
$\therefore Strain = \dfrac{{\Delta l}}{{2l}} = \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{2{l^2}}}$
Now, we need to calculate the stress in the wire due to the weight. There is tension in the wire due to stress which is given as
$
2T\cos \theta = mg \\
\Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{mg}}{{2\cos \theta }} \\
$
We can calculate the value of cosine of the angle from the diagram in the following way
$ \cos \theta = \dfrac{{CD}}{{AD}} = \dfrac{x}{{{{\left( {{l^2} + {x^2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}} = \dfrac{x}{{l{{\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{l^2}}}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}} = \dfrac{x}{{l\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{l^2}}}} \right)}} \\
$
Since, $x < < l$ then $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{2{l^2}}} < < 1{\text{ }}\therefore \left( {1 + \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{2{l^2}}}} \right) \approx 1{\text{ }} \Rightarrow {\text{cos}}\theta \approx \dfrac{x}{l}$
Using this, we get
$
T = \dfrac{{mg}}{{2\left( {\dfrac{x}{l}} \right)}} = \dfrac{{mgl}}{{2x}} \\
Stress = \dfrac{T}{A} = \dfrac{{mgl}}{{2xA}} \\
\therefore Y = \dfrac{{Stress}}{{Strain}} = \dfrac{{mgl}}{{2xA}} \times \dfrac{{2{l^2}}}{{{x^2}}} = \dfrac{{mg{l^3}}}{{A{x^3}}} \\
\Rightarrow x = l{\left[ {\dfrac{{mg}}{{YA}}} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \\
$
The value of Young’s modulus for mild steel $ = 2 \times {10^{12}}N/{m^2}$
$
\therefore x = 0.5{\left[ {\dfrac{{0.1 \times 10}}{{2 \times {{10}^{12}} \times 0.5 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} = 1.074 \times {10^{ - 2}}m \\
= 1.074cm \\
$
This is the required answer.
Note: In this question, the depression in the wire is considered to be very small compared to the length of the wire since the wire is stretched with the two pillars and mild steel is hard to compress because of large value of young’s modulus ($x < < l$)
Formula used:
Stress is defined as follows:
$Stress = \dfrac{F}{A}{\text{ }}...{\text{(i)}}$
where F is the force applied and A represents the area on which force is being applied.
Strain is defined as follows:
$Strain = \dfrac{{\Delta l}}{l}{\text{ }}...{\text{(ii)}}$
where $\Delta l$ is the change in length due to the applied stress while l signifies the original length of the material under stress.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given a mild steel wire of length 1m which is being stretched between two pillars and a mass of 100 g is suspended from its midpoint. Diagrammatically, the situation can be represented as follows:

Due to the weight at the centre of the wire, the wire depresses by x.
$\therefore CD = x$
Also, in the figure we have suspended the mass from the mid-point of the wire
$\therefore AC = BC = l = 0.5m$
The mass that is suspended from the middle is given as
$m = 100g = 0.1kg$
Using the Pythagoras theorem in the figure, we get
$AD = BD = {\left( {{l^2} + {x^2}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}$
Since, there is some elasticity in the mild steel, it will get stretched and increase in length due to weight suspended from it. The increase in length is given as
$ \Delta l = AD + BD - AB \\
= 2AD - AB \\
$
Using the known values, we get
$
\Delta l = 2{\left( {{l^2} + {x^2}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} - 2l \\
= 2l{\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{l^2}}}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} - 2l \\
= 2l\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{2{l^2}}}} \right) - 2l \\
$
In the last step, we have used binomial expansion formula given as ${\left( {1 + x} \right)^n} = 1 + nx$ for x<<1
$\Delta l = 2l\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{2{l^2}}} - 1} \right) = \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{l}$
Using this change in length, we can calculate the strain on the wire given by equation (ii), as follows:
$\therefore Strain = \dfrac{{\Delta l}}{{2l}} = \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{2{l^2}}}$
Now, we need to calculate the stress in the wire due to the weight. There is tension in the wire due to stress which is given as
$
2T\cos \theta = mg \\
\Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{mg}}{{2\cos \theta }} \\
$
We can calculate the value of cosine of the angle from the diagram in the following way
$ \cos \theta = \dfrac{{CD}}{{AD}} = \dfrac{x}{{{{\left( {{l^2} + {x^2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}} = \dfrac{x}{{l{{\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{l^2}}}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}} = \dfrac{x}{{l\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{l^2}}}} \right)}} \\
$
Since, $x < < l$ then $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{2{l^2}}} < < 1{\text{ }}\therefore \left( {1 + \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{2{l^2}}}} \right) \approx 1{\text{ }} \Rightarrow {\text{cos}}\theta \approx \dfrac{x}{l}$
Using this, we get
$
T = \dfrac{{mg}}{{2\left( {\dfrac{x}{l}} \right)}} = \dfrac{{mgl}}{{2x}} \\
Stress = \dfrac{T}{A} = \dfrac{{mgl}}{{2xA}} \\
\therefore Y = \dfrac{{Stress}}{{Strain}} = \dfrac{{mgl}}{{2xA}} \times \dfrac{{2{l^2}}}{{{x^2}}} = \dfrac{{mg{l^3}}}{{A{x^3}}} \\
\Rightarrow x = l{\left[ {\dfrac{{mg}}{{YA}}} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \\
$
The value of Young’s modulus for mild steel $ = 2 \times {10^{12}}N/{m^2}$
$
\therefore x = 0.5{\left[ {\dfrac{{0.1 \times 10}}{{2 \times {{10}^{12}} \times 0.5 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} = 1.074 \times {10^{ - 2}}m \\
= 1.074cm \\
$
This is the required answer.
Note: In this question, the depression in the wire is considered to be very small compared to the length of the wire since the wire is stretched with the two pillars and mild steel is hard to compress because of large value of young’s modulus ($x < < l$)
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




