
A merchant plans to sell two types of personal computers - a desktop model and a portable model, that will cost Rs. 25,000 and Rs. 40,000 respectively. He estimates that the total monthly demand of the computers will not exceed 250 units. Determine the number of units of each type of computer which the merchant should stock to get the maximum profit, if he does not want to invest more than Rs. 70 lakhs and his profit on the desktop model is Rs. 4,500 and on the portable model is Rs. 5,000.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Linear Programming Problem (LPP):
(i)Identify the ‘n’ number of decision variables which govern the behavior of the objective function (which needs to be optimized).
n = 2 (no. of units and price) for the given question.
(ii)Identify the set of constraints on the decision variables and express them in the form of linear equations /inequations. This will set up our region in the n-dimensional space within which the objective function needs to be optimized.
(iii)Don’t forget to impose the condition of non-negativity on the decision variables i.e. all of them must be positive since the problem might represent a physical scenario, and such variables can’t be negative.
0 ≤ Demand ≤ 250 and 0 ≤ Total Cost ≤ 70 lakhs.
(iv)Express the objective function in the form of a linear equation in the decision variables.
(v)Optimize the objective function either graphically (corner method) or mathematically.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Formulation of LPP:
Let's say that the merchant stocks x units of desktop model and y units of portable model.
The information given in the question is listed below:
Total cost = $25,000x+40,000y$ .
Objective function is profit $P=4,500x+5,000y$ .
Constraints:
Demand constraint:
$x+y\le 250$ ... (1)
Cost constraint:
$25,000x+40,000y\le 70,00,000$
⇒ $5x+8y\le 1400$ ... (2)
Physical constraint:
$x,y\ge 0$ ... (3)
Graph:
Solving the lines in equation (1) and (2) simultaneously:
Multiplying equation (1) by 5 and subtracting from (2), we get:
$3y=150$
⇒ $y=50$
Substituting this in equation (1), we get:
$x=250-50=200$
∴ The lines intersect at $x=200,y=50$ .
All the points and the feasible region are shown in the graph below:
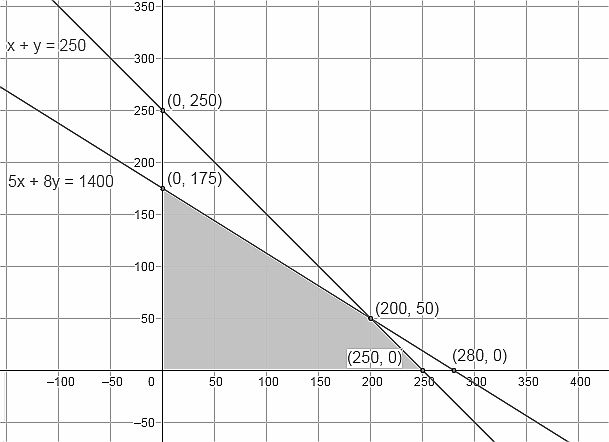
The values of the objective function $P=4,500x+5,000y$ at each of the corner points of the feasible region (shaded) are listed below:
We observe that the maximum value of the profit (P) is for $x=200,y=50$ .
Therefore, the merchant needs to stock 200 desktop and 50 portable computers for maximum profit.
Note: LPP (Linear Programming Problems) method helps in achieving the best outcome in a mathematical model. The best outcome could be maximum profit or the lowest cost or the best possible price. The representation of this model’s requirements is by linear relationships.
In order to calculate LPP, one must follow the following steps:
(i)Formulate the LP problem.
(ii)Construct a graph and then plot the various constraint lines.
(iii)Ascertain the valid side of all constraint lines.
(iv)Identify the region of feasible solutions.
(v)Plot the objective function.
(vi)Finally, find out the optimum point.
(vii)Linear programming is appropriate for solving complex problems.
(i)Identify the ‘n’ number of decision variables which govern the behavior of the objective function (which needs to be optimized).
n = 2 (no. of units and price) for the given question.
(ii)Identify the set of constraints on the decision variables and express them in the form of linear equations /inequations. This will set up our region in the n-dimensional space within which the objective function needs to be optimized.
(iii)Don’t forget to impose the condition of non-negativity on the decision variables i.e. all of them must be positive since the problem might represent a physical scenario, and such variables can’t be negative.
0 ≤ Demand ≤ 250 and 0 ≤ Total Cost ≤ 70 lakhs.
(iv)Express the objective function in the form of a linear equation in the decision variables.
(v)Optimize the objective function either graphically (corner method) or mathematically.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Formulation of LPP:
Let's say that the merchant stocks x units of desktop model and y units of portable model.
The information given in the question is listed below:
| Model | No. of Units | Cost | Profit |
| Desktop | x | 25,000 | 4,500 |
| Portable | y | 40,000 | 5,000 |
Total cost = $25,000x+40,000y$ .
Objective function is profit $P=4,500x+5,000y$ .
Constraints:
Demand constraint:
$x+y\le 250$ ... (1)
Cost constraint:
$25,000x+40,000y\le 70,00,000$
⇒ $5x+8y\le 1400$ ... (2)
Physical constraint:
$x,y\ge 0$ ... (3)
Graph:
Solving the lines in equation (1) and (2) simultaneously:
Multiplying equation (1) by 5 and subtracting from (2), we get:
$3y=150$
⇒ $y=50$
Substituting this in equation (1), we get:
$x=250-50=200$
∴ The lines intersect at $x=200,y=50$ .
All the points and the feasible region are shown in the graph below:

The values of the objective function $P=4,500x+5,000y$ at each of the corner points of the feasible region (shaded) are listed below:
| x | y | P = 4,500x + 5,000y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 175 | 8,75,000 |
| 200 | 50 | 11,50,000 |
| 250 | 0 | 11,25,000 |
We observe that the maximum value of the profit (P) is for $x=200,y=50$ .
Therefore, the merchant needs to stock 200 desktop and 50 portable computers for maximum profit.
Note: LPP (Linear Programming Problems) method helps in achieving the best outcome in a mathematical model. The best outcome could be maximum profit or the lowest cost or the best possible price. The representation of this model’s requirements is by linear relationships.
In order to calculate LPP, one must follow the following steps:
(i)Formulate the LP problem.
(ii)Construct a graph and then plot the various constraint lines.
(iii)Ascertain the valid side of all constraint lines.
(iv)Identify the region of feasible solutions.
(v)Plot the objective function.
(vi)Finally, find out the optimum point.
(vii)Linear programming is appropriate for solving complex problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




