
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as
A) TTWW
B) TTww
C) TtWW
D) TtWw
Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint: To determine the genotype of an individual with dominant phenotype (whether it is homozygous or heterozygous); it is crossed with its pure recessive parent. This cross is known as a test cross.
Complete Answer:
- In the given experiment, tall pea plants bearing violet flowers were crossed with short pea plants bearing white flowers. This is a dihybrid cross in which two pairs of characters are studied, namely, length of plant and flower colour.
- Mendel’s Principle of Independent Assortment demonstrates that one pair of characters is completely independent of another pair of characters when two or more than two pairs of characters are studied. Therefore, the two traits, the length of plant and flower colour will assort independently.
- According to Mendel’s Law of dominance, the trait which appears in the F1 generation is the dominant and the other which does not appear is called recessive.
- Here, all the progeny bore violet flowers. This suggests that violet flower colour is dominant over white flower colour.
- The experiment given here is a testcross as it involves breeding of tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with a phenotypically recessive individual (short pea plants bearing white flowers).
- Since, all the progeny are showing the dominant trait for flower colour, the parent plant would be dominant homozygous for flower colour (i.e. WW).
- Contrary to this, almost half of the progeny were short and the other half were tall, that means the ratio of tall and short plants is 1: 1. This result of the test cross suggests that the parent plant would be heterozygous for the plant length (I.e. Tt). So, the genotype of the tall parent will be TtWW.
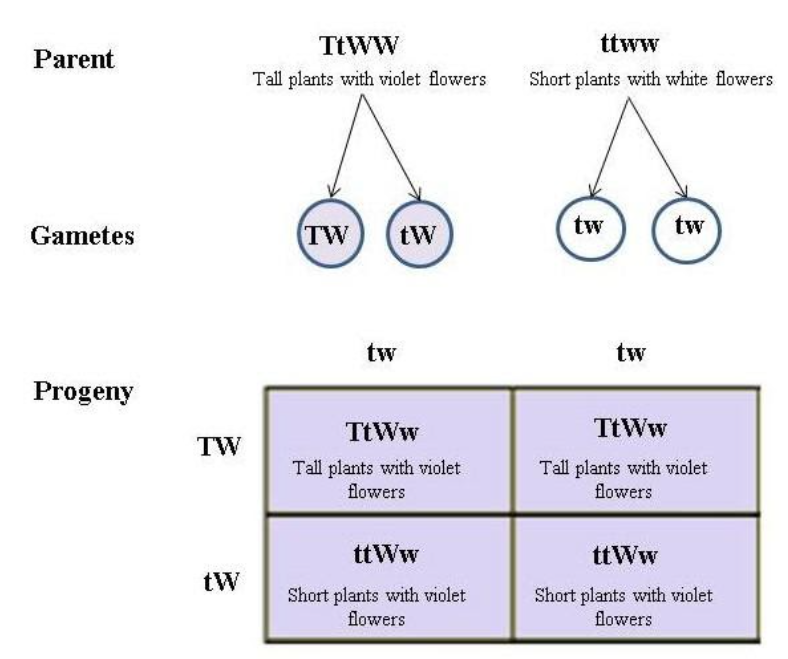
Figure showing the cross between tall pea plants bearing violet flowers and short pea plants bearing white flowers
Thus, the correct answer is C i.e., TtWW.
Note: In test cross, the analysis of proportions of dominant and recessive progenies determines the genotype of the testing individual. If all the progenies from the test cross show the dominant phenotype then the testing individual is homozygous dominant, and, if 50% progenies show dominant phenotype and 50% progenies show recessive phenotype then the testing individual is heterozygous.
Complete Answer:
- In the given experiment, tall pea plants bearing violet flowers were crossed with short pea plants bearing white flowers. This is a dihybrid cross in which two pairs of characters are studied, namely, length of plant and flower colour.
- Mendel’s Principle of Independent Assortment demonstrates that one pair of characters is completely independent of another pair of characters when two or more than two pairs of characters are studied. Therefore, the two traits, the length of plant and flower colour will assort independently.
- According to Mendel’s Law of dominance, the trait which appears in the F1 generation is the dominant and the other which does not appear is called recessive.
- Here, all the progeny bore violet flowers. This suggests that violet flower colour is dominant over white flower colour.
- The experiment given here is a testcross as it involves breeding of tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with a phenotypically recessive individual (short pea plants bearing white flowers).
- Since, all the progeny are showing the dominant trait for flower colour, the parent plant would be dominant homozygous for flower colour (i.e. WW).
- Contrary to this, almost half of the progeny were short and the other half were tall, that means the ratio of tall and short plants is 1: 1. This result of the test cross suggests that the parent plant would be heterozygous for the plant length (I.e. Tt). So, the genotype of the tall parent will be TtWW.

Figure showing the cross between tall pea plants bearing violet flowers and short pea plants bearing white flowers
Thus, the correct answer is C i.e., TtWW.
Note: In test cross, the analysis of proportions of dominant and recessive progenies determines the genotype of the testing individual. If all the progenies from the test cross show the dominant phenotype then the testing individual is homozygous dominant, and, if 50% progenies show dominant phenotype and 50% progenies show recessive phenotype then the testing individual is heterozygous.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




