
A membranous coiled semicircular structure attached to the plasma membrane and found in blue-green algae is called
(A) Lamellasome
(B) Lomasome
(C) Mesosome
(D) Microsome
Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint: A membranous coiled structure that is semicircular in shape and is attached to the plasma membrane and is named after the thin layer of organic tissue and is mostly found in blue-green algae. This type of algae comes under the bacteria known as Cyanobacteria.
Complete solution:
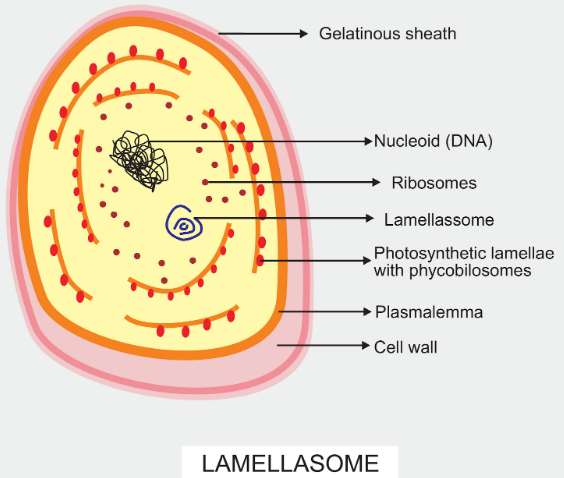
Lamellasome is a coiled membranous semicircular structure that is attached to the plasma membrane of the algae i.e blue-green algae. It's approximately 200 mμ in diameter. Mesosome is a folded invagination found within the plasma membrane of bacteria that increases the area. they're the site of respiration. Microsome is a fragment of the endoplasmic reticulum. it's a synthetic structure and isn't present in a living cell.
Cells of cyanobacteria are larger and more elaborate than bacteria. The cell structure of these types of organisms is usually prokaryotic— one envelope organization with peptidoglycan can wall, naked DNA, 70S ribosomes, and absence of membrane-bound structures like endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, plastids, lysosomes, sap vacuoles.
The cell wall is four layered with peptidoglycan present within the second layer. The outer part of the protoplast contains a variety of photosynthetic thylakoids. It's called chromoplasm. The thylakoids lie freely within the cytoplasm. Their membranes contain chlorophyll, carotenes, and xanthophylls. chlorophyll b is absent. The structures attached to the thylakoid membranes are small granules referred to as phycobilisomes. The latter possess accessory photosynthetic pigments referred to as phycobilins. The phycobilins are found mainly of three types— phycocyanin (blue), allophycocyanin (blue), and phycoerythrin (red).
So, the correct answer is ‘Lamellasome’.
Note:
Multiplication in the cyanobacteria is mostly by asexual methods. There are many different methods of asexual reproduction. Some of the methods include fragmentation with or without the formation of small segments called hormogones (hormogonia), hormospores, akinetes, endospores, nanocytes, exospores, binary fission, etc.
Complete solution:
Lamellasome is a coiled membranous semicircular structure that is attached to the plasma membrane of the algae i.e blue-green algae. It's approximately 200 mμ in diameter. Mesosome is a folded invagination found within the plasma membrane of bacteria that increases the area. they're the site of respiration. Microsome is a fragment of the endoplasmic reticulum. it's a synthetic structure and isn't present in a living cell.
Cells of cyanobacteria are larger and more elaborate than bacteria. The cell structure of these types of organisms is usually prokaryotic— one envelope organization with peptidoglycan can wall, naked DNA, 70S ribosomes, and absence of membrane-bound structures like endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, plastids, lysosomes, sap vacuoles.
The cell wall is four layered with peptidoglycan present within the second layer. The outer part of the protoplast contains a variety of photosynthetic thylakoids. It's called chromoplasm. The thylakoids lie freely within the cytoplasm. Their membranes contain chlorophyll, carotenes, and xanthophylls. chlorophyll b is absent. The structures attached to the thylakoid membranes are small granules referred to as phycobilisomes. The latter possess accessory photosynthetic pigments referred to as phycobilins. The phycobilins are found mainly of three types— phycocyanin (blue), allophycocyanin (blue), and phycoerythrin (red).
So, the correct answer is ‘Lamellasome’.
Note:
Multiplication in the cyanobacteria is mostly by asexual methods. There are many different methods of asexual reproduction. Some of the methods include fragmentation with or without the formation of small segments called hormogones (hormogonia), hormospores, akinetes, endospores, nanocytes, exospores, binary fission, etc.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




