
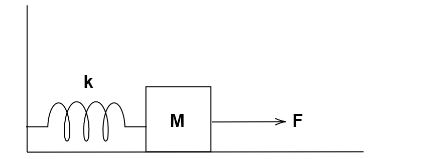
A massless block attached to a spring, pulled by a constant horizontal force,is kept on a smooth surface as shown in Fig. initially ,the spring is in its natural length . Then the maximum positive work that the applied force F can do is ( given that spring does not break)
A. \[\dfrac{{{F^2}}}{k}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{2{F^2}}}{k}\]
C. \[\infty \]
D. \[\dfrac{{{F^2}}}{{2k}}\]

Answer
489.3k+ views
Hint: To solve the given question we use the concepts of work, potential energy and displacement. We are given the force constant of the spring and force applied on the block. Using these we can find displacement. Work done by spring to be positive, should make the block displace in the direction of force i.e. right. Now we put the value of displacement in the potential energy formula which is indeed work done by spring.
Formulae used-
\[U = \dfrac{{k{x^2}}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow F = kx\]
where \[x\] is the displacement of a block and Spring constant is given as \[k\].
Complete step by step answer:
We are given constant force applied on the block as \[F\]. Spring constant is given as \[k\]
Force in spring \[ = \]constant force applied on block (as both act in opposite directions and no other forces are acting horizontally on block)
\[F = kx\]
Now we can write maximum displacement as \[x = \dfrac{F}{k}\]. As we know The Work on a body is stored as converted to energy. There are two main types of mechanical energy namely, kinetic and potential energy. If the body has no velocity then the work done on it is converted entirely to potential energy. work done in stretching a spring is stored as the elastic potential energy given by the equation,
\[U = \dfrac{{k{x^2}}}{2} = W\]
Now taking the value of \[x\] we derived \[ x = \dfrac{F}{k}\] in the above equation we get
\[W = \dfrac{{k{x^2}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{k{{\left( {\dfrac{F}{k}} \right)}^2}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{k{F^2}}}{{2{k^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{{F^2}}}{{2k}}\]
Thus, the maximum positive work that the force can do is
\[ \therefore W = \dfrac{{{F^2}}}{{2k}}\]
Therefore, the correct answer is option \[{\text{D}}\].
Note: When inelastic deformation has not occurred, the work done is equal to the accumulated elastic potential energy. The work also can be visualized because of the area under the force curve. The energy is stored until the energy is removed and therefore the material returns to its original form.
Formulae used-
\[U = \dfrac{{k{x^2}}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow F = kx\]
where \[x\] is the displacement of a block and Spring constant is given as \[k\].
Complete step by step answer:
We are given constant force applied on the block as \[F\]. Spring constant is given as \[k\]
Force in spring \[ = \]constant force applied on block (as both act in opposite directions and no other forces are acting horizontally on block)
\[F = kx\]
Now we can write maximum displacement as \[x = \dfrac{F}{k}\]. As we know The Work on a body is stored as converted to energy. There are two main types of mechanical energy namely, kinetic and potential energy. If the body has no velocity then the work done on it is converted entirely to potential energy. work done in stretching a spring is stored as the elastic potential energy given by the equation,
\[U = \dfrac{{k{x^2}}}{2} = W\]
Now taking the value of \[x\] we derived \[ x = \dfrac{F}{k}\] in the above equation we get
\[W = \dfrac{{k{x^2}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{k{{\left( {\dfrac{F}{k}} \right)}^2}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{k{F^2}}}{{2{k^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{{F^2}}}{{2k}}\]
Thus, the maximum positive work that the force can do is
\[ \therefore W = \dfrac{{{F^2}}}{{2k}}\]
Therefore, the correct answer is option \[{\text{D}}\].
Note: When inelastic deformation has not occurred, the work done is equal to the accumulated elastic potential energy. The work also can be visualized because of the area under the force curve. The energy is stored until the energy is removed and therefore the material returns to its original form.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




