
A mass of 10 kg is suspended vertically by a rope from the roof. When a horizontal force is applied on the rope at some point, the rope is deviated by an angle of $45^\circ $ at the roof point. If the suspended mass is at equilibrium, the magnitude of the force is? (Assume $g = 10m{s^{ - 2}}$)
A. 200 N
B. 100 N
C. 140 N
D. 70 N
Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint
When a mass is suspended, the force of gravity due to its mass and the tension due to the suspension rope acts on it. When at equilibrium, all the forces acting on this body will be equal and opposite to each other so that the net force acting on the mass is zero.
Complete step by step answer
We are provided with a suspended mass that is pushed by some angle $\theta $ due to a force. To determine this force when the mass is in equilibrium, we first draw the free body diagram to understand what forces are acting on the mass and in which direction.
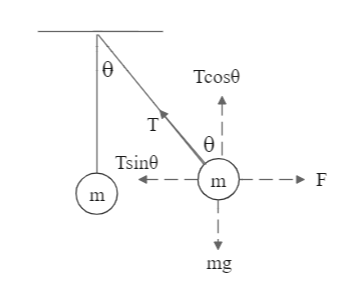
External force on the mass is F
Tension due to the rope is T
Mass of the body is $m = 10$ kg
Angle by which the rope is moved is $\theta = 45^\circ $
We balance the forces on the mass by taking their horizontal and vertical components. From the FBD, we can see that:
$F = T\sin \theta $ [Eq. 1]
And $mg = T\cos \theta $ [Eq. 2]
Putting the values in Eq. 2, we get:
$10 \times 10 = T\cos 45 = \dfrac{T}{{\sqrt2 }}$
Also, from Eq. 1:
$F = T\sin 45 = \dfrac{T}{{\sqrt2 }}$
Comparing the two equations, we get:
$F = 10 \times 10 = 100$ N
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note
Remembering to draw the free body diagram in these kinds of cases is an important step as it helps us to visualize all the forces acting on a body along with their directions. As the state of equilibrium implies that neither the state of motion nor the internal energy of the object changes with time, force and energy balance is used accordingly.
When a mass is suspended, the force of gravity due to its mass and the tension due to the suspension rope acts on it. When at equilibrium, all the forces acting on this body will be equal and opposite to each other so that the net force acting on the mass is zero.
Complete step by step answer
We are provided with a suspended mass that is pushed by some angle $\theta $ due to a force. To determine this force when the mass is in equilibrium, we first draw the free body diagram to understand what forces are acting on the mass and in which direction.

External force on the mass is F
Tension due to the rope is T
Mass of the body is $m = 10$ kg
Angle by which the rope is moved is $\theta = 45^\circ $
We balance the forces on the mass by taking their horizontal and vertical components. From the FBD, we can see that:
$F = T\sin \theta $ [Eq. 1]
And $mg = T\cos \theta $ [Eq. 2]
Putting the values in Eq. 2, we get:
$10 \times 10 = T\cos 45 = \dfrac{T}{{\sqrt2 }}$
Also, from Eq. 1:
$F = T\sin 45 = \dfrac{T}{{\sqrt2 }}$
Comparing the two equations, we get:
$F = 10 \times 10 = 100$ N
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note
Remembering to draw the free body diagram in these kinds of cases is an important step as it helps us to visualize all the forces acting on a body along with their directions. As the state of equilibrium implies that neither the state of motion nor the internal energy of the object changes with time, force and energy balance is used accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




