
A mass of 1 kg is suspended by means of a thread. The system is (i) lifted up with an acceleration of \[4.9m{{s}^{-1}}\] (ii) lowered with an acceleration of \[4.9m{{s}^{-2}}\]. The ratio of tension in the first and second case
A. \[3:1\]
B. \[1:2\]
C. \[1:3\]
D. \[2:1\]
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: Use the concept of free body diagram for balancing the force.
Use the application of the second law of newton.
Use the acceleration of gravity in all calculations.
Complete step by step solution:
Students have a clear understanding about free body diagrams and Newton’s Law of Motion.
Newton’s second law is a quantitative description of the changes that a force can produce on the motion of a body. It states that the time rate of change of the momentum of a body is equal in both magnitude and direction to the force imposed on it. The momentum of a body is equal to the product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum, like velocity, is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction. A force applied to a body can change the magnitude of the momentum, or its direction, or both. Newton’s second law is one of the most important in all of physics. For a body whose mass m is constant, it can be written in the form \[F=ma.\] where \[F\] (force) and \[a\] (acceleration) are both vector quantities. If a body has net force acting on it, it is accelerated in accordance with the equation. Conversely, if a body is not accelerated, there is no net force acting on it.
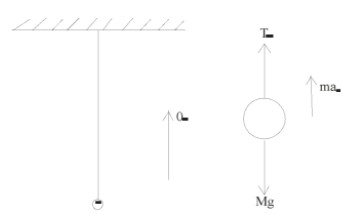
Case (I)
In this case man is lifted up with acceleration \[4.9m{{s}^{-2}}.\]
So with the free body diagram
\[{{T}_{1}}-mg=m\,\,{{a}_{1}}\]
\[{{T}_{1}}=m\left( g+{{a}_{1}} \right)\]
\[=1\left( 10+4.9 \right)=14.9\,\,N\]
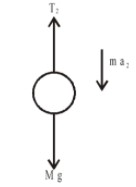
Case (II)
In this case man is moving down with an acceleration \[4.9m{{s}^{-2}}.\]
So with the free body diagram:
\[mg-{{T}_{2}}=m{{a}_{2}}\]
\[{{T}_{2}}=m(g-{{a}_{2}})\]
\[=(10-4.9)\]
\[=5.1\ \ N\]
Ratio: \[\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}=\dfrac{14.9}{5.1}\]
\[=2.92:1\]
\[\simeq 3:1\]
Hence, Option (A) is the correct answer.
Note: Student has clear understanding about free body diagrams.
Students also know how to apply Newton Law of motion.
Use the application of the second law of newton.
Use the acceleration of gravity in all calculations.
Complete step by step solution:
Students have a clear understanding about free body diagrams and Newton’s Law of Motion.
Newton’s second law is a quantitative description of the changes that a force can produce on the motion of a body. It states that the time rate of change of the momentum of a body is equal in both magnitude and direction to the force imposed on it. The momentum of a body is equal to the product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum, like velocity, is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction. A force applied to a body can change the magnitude of the momentum, or its direction, or both. Newton’s second law is one of the most important in all of physics. For a body whose mass m is constant, it can be written in the form \[F=ma.\] where \[F\] (force) and \[a\] (acceleration) are both vector quantities. If a body has net force acting on it, it is accelerated in accordance with the equation. Conversely, if a body is not accelerated, there is no net force acting on it.

Case (I)
In this case man is lifted up with acceleration \[4.9m{{s}^{-2}}.\]
So with the free body diagram
\[{{T}_{1}}-mg=m\,\,{{a}_{1}}\]
\[{{T}_{1}}=m\left( g+{{a}_{1}} \right)\]
\[=1\left( 10+4.9 \right)=14.9\,\,N\]

Case (II)
In this case man is moving down with an acceleration \[4.9m{{s}^{-2}}.\]
So with the free body diagram:
\[mg-{{T}_{2}}=m{{a}_{2}}\]
\[{{T}_{2}}=m(g-{{a}_{2}})\]
\[=(10-4.9)\]
\[=5.1\ \ N\]
Ratio: \[\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}=\dfrac{14.9}{5.1}\]
\[=2.92:1\]
\[\simeq 3:1\]
Hence, Option (A) is the correct answer.
Note: Student has clear understanding about free body diagrams.
Students also know how to apply Newton Law of motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




