
A man walks in a horizontal circle round the foot of a pole which is inclined to the vertical. The foot of the pole is at the center of the circle. The greatest and least angles which the pole subtends at his eye are ${\text{ta}}{{\text{n}}^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{9}{5}} \right)$and ${\text{ta}}{{\text{n}}^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{6}{5}} \right)$respectively and when he is midway between the corresponding positions, the angle is$\theta $. If the man’s height is neglected, find the length of the pole.
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: From the question we need to find the length of the pole, where ${\text{ta}}{{\text{n}}^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{9}{5}} \right)$and ${\text{ta}}{{\text{n}}^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{6}{5}} \right)$are the greatest and least angles. We can calculate the tangent angle formula that is, if a is angle tan a $ = \dfrac{{{\text{opposite side value}}}}{{{\text{adjacent side value}}}}$. Using this formula assuming angles alpha and beta, we can find the length of the pole.
Complete step-by-step answer:
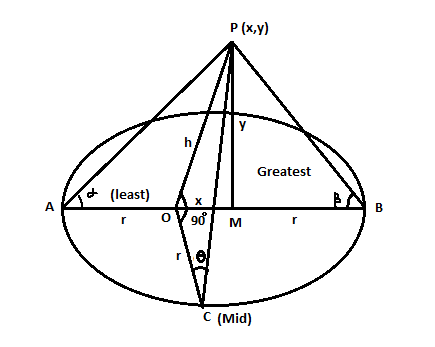
From the diagram, we can see that the man walks in a horizontal circle round the foot of a pole which is inclined to the vertical.
Let angle at A be $\alpha $ and angle at B be $\beta $
OA=OB=OC=r the radius of the horizontal circle where C is a point mid-way between the points A and B. OP is a pole which is inclined to the vertical. It will subtend least angle say $\angle $at A and greatest angle b at B.
From P draw a perpendicular PM to AB and let PM=y and OM=x
From the given,${\text{tan}}\alpha = \dfrac{{{\text{opposite side value}}}}{{{\text{adjacent side value}}}}$
${\text{tan}}\alpha $$ = \dfrac{{\text{y}}}{{{\text{x + r}}}} = \dfrac{6}{5}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y = 6}}\left( {{\text{x + r}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y = 6x + 6r}}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y - 6x = 6r}}$
And, ${\text{tan}}\beta = \dfrac{{\text{y}}}{{{\text{r - x}}}} = \dfrac{9}{5}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y = 9}}\left( {{\text{r - x}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y = 9r - 9x}}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y + 9x = 9r}}$
Therefore, Solving$5{\text{y - 6x = 6r and 5y + 9x = 9r}}$
\[\begin{gathered}
\Rightarrow 5{\text{y + 9x = 9r}} \\
{\text{ - }}\left( {5{\text{y - 6x = 6r}}} \right) \\
\end{gathered} \]
\[\begin{gathered}
\Rightarrow 5{\text{y + 9x = 9r}} \\
{\text{ - 5y + 6x = - 6r}} \\
\end{gathered} \]
\[ \Rightarrow 15{\text{x = 3r}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{x = }}\dfrac{3}{{15}}{\text{r}}\]
$\therefore {\text{x = }}\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}$
Substitute x value in one of the equation that is,
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y - 6x = 6r}} \Rightarrow 5{\text{y - 6}}\left( {\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}} \right){\text{ = 6r}}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y - }}\dfrac{{6{\text{r}}}}{5}{\text{ = 6r}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{25{\text{y - }}6{\text{r}}}}{5}{\text{ = 6r}}$
$ \Rightarrow 25{\text{y - }}6{\text{r = 30r}}$
$ \Rightarrow 25{\text{y = 30r + 6r}}$
$ \Rightarrow 25{\text{y = 36r}}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{y = }}\dfrac{{36}}{{25}}r$
$\therefore {\text{x = }}\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}{\text{ and y = }}\dfrac{{36}}{{25}}r$
Also as given angle subtended at C is $\theta $
$\therefore {\text{tan}}\theta = \dfrac{{\text{h}}}{{\text{r}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2}} }}{{\text{r}}}$
Where, based on Pythagoras theorem
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{h}}^2}{\text{ = }}{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2}$
${\text{h = }}\sqrt {{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{5}{\text{r}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{{36}}{25}{\text{r}}} \right)}^2}} }}{{\text{r}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{{36}}{25}{\text{r}}} \right)}^2}} }}{{\text{r}}}$
Taking $\dfrac{{{{\text{r}}^2}}}{{{5^2}}}$from the root of the equation as it is common divisor to take it out from the equation.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}\sqrt {1 + {{\left( {\dfrac{{36}}{5}} \right)}^2}} }}{{\text{r}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}\sqrt {1 + \left( {\dfrac{{1296}}{{25}}} \right)} }}{{\text{r}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{r}}\sqrt {\dfrac{{25 + 1296}}{{25}}} }}{{{\text{5r}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt {\dfrac{{1321}}{{25}}} }}{{\text{5}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt {\dfrac{{1321}}{{25}}} }}{{\text{5}}}$
$\therefore {\text{h = }}\dfrac{1}{{25}}\sqrt {1321} $
Therefore, the length of the pole, if the man’s height is neglected =$\dfrac{1}{{25}}\sqrt {1321} $
Note: We can use sine and cosine trigonometric formulae to find the length of the pole. In this solution it was clearly given the tangent so we have taken the tangent angles and compared it against the values given. The Pythagoras theorem will be applicable only if it is a right angled triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:

From the diagram, we can see that the man walks in a horizontal circle round the foot of a pole which is inclined to the vertical.
Let angle at A be $\alpha $ and angle at B be $\beta $
OA=OB=OC=r the radius of the horizontal circle where C is a point mid-way between the points A and B. OP is a pole which is inclined to the vertical. It will subtend least angle say $\angle $at A and greatest angle b at B.
From P draw a perpendicular PM to AB and let PM=y and OM=x
From the given,${\text{tan}}\alpha = \dfrac{{{\text{opposite side value}}}}{{{\text{adjacent side value}}}}$
${\text{tan}}\alpha $$ = \dfrac{{\text{y}}}{{{\text{x + r}}}} = \dfrac{6}{5}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y = 6}}\left( {{\text{x + r}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y = 6x + 6r}}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y - 6x = 6r}}$
And, ${\text{tan}}\beta = \dfrac{{\text{y}}}{{{\text{r - x}}}} = \dfrac{9}{5}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y = 9}}\left( {{\text{r - x}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y = 9r - 9x}}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y + 9x = 9r}}$
Therefore, Solving$5{\text{y - 6x = 6r and 5y + 9x = 9r}}$
\[\begin{gathered}
\Rightarrow 5{\text{y + 9x = 9r}} \\
{\text{ - }}\left( {5{\text{y - 6x = 6r}}} \right) \\
\end{gathered} \]
\[\begin{gathered}
\Rightarrow 5{\text{y + 9x = 9r}} \\
{\text{ - 5y + 6x = - 6r}} \\
\end{gathered} \]
\[ \Rightarrow 15{\text{x = 3r}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{x = }}\dfrac{3}{{15}}{\text{r}}\]
$\therefore {\text{x = }}\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}$
Substitute x value in one of the equation that is,
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y - 6x = 6r}} \Rightarrow 5{\text{y - 6}}\left( {\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}} \right){\text{ = 6r}}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{\text{y - }}\dfrac{{6{\text{r}}}}{5}{\text{ = 6r}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{25{\text{y - }}6{\text{r}}}}{5}{\text{ = 6r}}$
$ \Rightarrow 25{\text{y - }}6{\text{r = 30r}}$
$ \Rightarrow 25{\text{y = 30r + 6r}}$
$ \Rightarrow 25{\text{y = 36r}}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{y = }}\dfrac{{36}}{{25}}r$
$\therefore {\text{x = }}\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}{\text{ and y = }}\dfrac{{36}}{{25}}r$
Also as given angle subtended at C is $\theta $
$\therefore {\text{tan}}\theta = \dfrac{{\text{h}}}{{\text{r}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2}} }}{{\text{r}}}$
Where, based on Pythagoras theorem
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{h}}^2}{\text{ = }}{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2}$
${\text{h = }}\sqrt {{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{5}{\text{r}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{{36}}{25}{\text{r}}} \right)}^2}} }}{{\text{r}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{{36}}{25}{\text{r}}} \right)}^2}} }}{{\text{r}}}$
Taking $\dfrac{{{{\text{r}}^2}}}{{{5^2}}}$from the root of the equation as it is common divisor to take it out from the equation.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}\sqrt {1 + {{\left( {\dfrac{{36}}{5}} \right)}^2}} }}{{\text{r}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\text{r}}}{5}\sqrt {1 + \left( {\dfrac{{1296}}{{25}}} \right)} }}{{\text{r}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{r}}\sqrt {\dfrac{{25 + 1296}}{{25}}} }}{{{\text{5r}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt {\dfrac{{1321}}{{25}}} }}{{\text{5}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt {\dfrac{{1321}}{{25}}} }}{{\text{5}}}$
$\therefore {\text{h = }}\dfrac{1}{{25}}\sqrt {1321} $
Therefore, the length of the pole, if the man’s height is neglected =$\dfrac{1}{{25}}\sqrt {1321} $
Note: We can use sine and cosine trigonometric formulae to find the length of the pole. In this solution it was clearly given the tangent so we have taken the tangent angles and compared it against the values given. The Pythagoras theorem will be applicable only if it is a right angled triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




