
A man walks for some time $'t'$ with velocity $\left( V \right)$ due east. Then he walks for the same time $'t'$ with velocity $\left( V \right)$ due north. The average velocity of the man is
$A.$ $2V$
$B.$ $\sqrt 2 V$
$C.$ $V$
$D.$ $\dfrac{V}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: It is given that the man walks initially with the velocity $V$ in east direction in the diagram below it is indicated by $OA$ .Next the man walks with $V$ in west direction which is indicated by $AB$ . First we will calculate the displacement $S$ and we will calculate the average velocity by using the formula.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to the given question the figure can be drawn as shown below
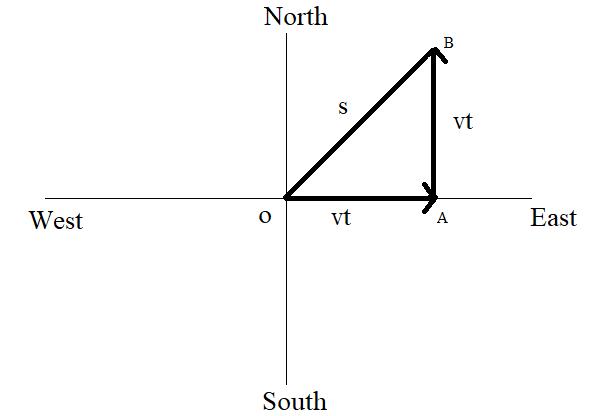
From the figure, on applying Pythagoras theorem to the triangle $OAB$
The displacement, $S = OB = \sqrt {{{\left( {OA} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {AB} \right)}^2}} $ …….. $\left( 1 \right)$
And also $OA = AB = Vt$ $\left[ {\because Displacement = velocity \times time} \right]$
Substituting in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get
$S = \sqrt {{{\left( {Vt} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {Vt} \right)}^2}} $
Therefore, $S = \sqrt 2 Vt$ ………..$\left( 2 \right)$
Let us consider total time as $T$
And $T = 2t$……….$\left( 3 \right)$
We known that average velocity $\left( {{V_{avg}}} \right)$ $ = \dfrac{{Displacement}}{{Total{\text{ }}time}}$ ………..$\left( 4 \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 2 \right)$ and equation $\left( 3 \right)$ in equation $\left( 4 \right)$ we get
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 Vt}}{{2t}}$
On simplification
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{V}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Hence, option $D$ is correct. Average velocity $\left( {{V_{avg}}} \right)$ $ = \dfrac{V}{{\sqrt 2 }}m{s^{ - 1}}$
Note: The average velocity is defined as the total displacement to that of the total time taken. In another world we can define the average velocity as the rate at which an object changes its position from one place to the other place.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to the given question the figure can be drawn as shown below

From the figure, on applying Pythagoras theorem to the triangle $OAB$
The displacement, $S = OB = \sqrt {{{\left( {OA} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {AB} \right)}^2}} $ …….. $\left( 1 \right)$
And also $OA = AB = Vt$ $\left[ {\because Displacement = velocity \times time} \right]$
Substituting in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get
$S = \sqrt {{{\left( {Vt} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {Vt} \right)}^2}} $
Therefore, $S = \sqrt 2 Vt$ ………..$\left( 2 \right)$
Let us consider total time as $T$
And $T = 2t$……….$\left( 3 \right)$
We known that average velocity $\left( {{V_{avg}}} \right)$ $ = \dfrac{{Displacement}}{{Total{\text{ }}time}}$ ………..$\left( 4 \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 2 \right)$ and equation $\left( 3 \right)$ in equation $\left( 4 \right)$ we get
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 Vt}}{{2t}}$
On simplification
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{V}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Hence, option $D$ is correct. Average velocity $\left( {{V_{avg}}} \right)$ $ = \dfrac{V}{{\sqrt 2 }}m{s^{ - 1}}$
Note: The average velocity is defined as the total displacement to that of the total time taken. In another world we can define the average velocity as the rate at which an object changes its position from one place to the other place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




