
A man standing on the road has to hold his umbrella at ${{30}^{0}}$ with the vertical to keep the rain away. He throws the umbrella and starts running at $10\text{ km}{{\text{h}}^{-1}}$. He finds that the rain drops are hitting his head vertically. What is the speed of rain with respect to ground?
$\begin{align}
& A.\text{ 10}\sqrt{3}\text{ km}{{\text{h}}^{-1}} \\
& B.\text{ 20 km}{{\text{h}}^{-1}} \\
& C.\text{ }\dfrac{20}{\sqrt{3}}\text{ km}{{\text{h}}^{-1}} \\
& D.\text{ }\dfrac{10}{\sqrt{2}}\text{ km}{{\text{h}}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: In this question we have two stages, initially man was in rest and rain was hitting at an angle of ${{30}^{0}}$. After that man is running and rain is hitting vertically. So take direction of man’s speed along x and speed of rain along -y or (-j). In between i and -j, take direction of velocity of rain with respect to ground at an angle ${{30}^{0}}$. Take the horizontal and vertical component of velocity of the rain with respect to ground and find the velocity of rain with respect to man.
Complete step by step answer:
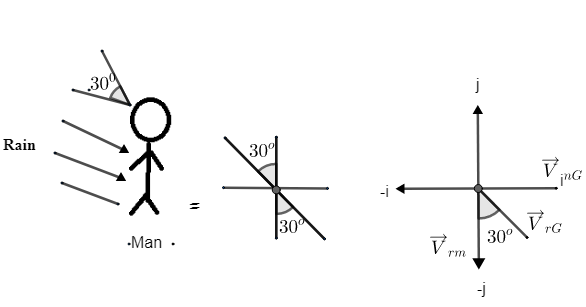
The question has been staked that, initially man is standing by holding his umbrella at ${{30}^{0}}$, it means rain must be coming in the direction of umbrella i.e. initially direction of rain is ${{30}^{0}}$ now, man throws the umbrella and he started running with the speed of $10km{{h}^{1}}$. While running, he noticed that rain was hitting vertically on his head. Here, we need to find out the speed of rain with respect to ground. Now we know that rain is hitting vertically mean direction must by a long –j shown in figure 2. Consider the velocity of man with respect to ground i.e. ${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rm}}$ must be along (-j). And we know that man is running from $\overrightarrow{-i}\text{ to i}$ on the road. Initially, rain was coming at an angle of ${{30}^{0}}$ to the ground, so if ${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}$ is the velocity of rain with respect to ground then angle between ${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}\text{ And }{{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rm}}$ is ${{30}^{0}}$, as shown in the figure (2).
Now take a horizontal component of ${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}$ which is nothing but the sine component, we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}\text{ sin30 = }\overrightarrow{V}mG \\
& {{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{V}mG}{\sin {{30}^{0}}} \\
\end{align}$
In this question, it is given that velocity of man with respect to ground is 10 km/h
Therefore,
${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{V}mG}{1/2}=\dfrac{10}{0.5}=20$
Hence, velocity of rain with respect to ground is 20 km/h now take vertical component of ${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}$ which is nothing but cosine component, we get,
${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}\text{ cos (3}{{\text{0}}^{0}}\text{)=}{{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rM}}$
$\begin{align}
& {{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rm}}=20\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& {{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rm}}=10\sqrt{3}\text{ km/h} \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Concept of above solution is based on relativity. To solve this kind of question, we usually have to consider frames of reference of different bodies. Frame of reference is nothing but a system of coordinate axes which represents the position of a particle or an event in two or three dimensional space. The position of any body is specified by the position vector from the origin.
Complete step by step answer:

The question has been staked that, initially man is standing by holding his umbrella at ${{30}^{0}}$, it means rain must be coming in the direction of umbrella i.e. initially direction of rain is ${{30}^{0}}$ now, man throws the umbrella and he started running with the speed of $10km{{h}^{1}}$. While running, he noticed that rain was hitting vertically on his head. Here, we need to find out the speed of rain with respect to ground. Now we know that rain is hitting vertically mean direction must by a long –j shown in figure 2. Consider the velocity of man with respect to ground i.e. ${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rm}}$ must be along (-j). And we know that man is running from $\overrightarrow{-i}\text{ to i}$ on the road. Initially, rain was coming at an angle of ${{30}^{0}}$ to the ground, so if ${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}$ is the velocity of rain with respect to ground then angle between ${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}\text{ And }{{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rm}}$ is ${{30}^{0}}$, as shown in the figure (2).
Now take a horizontal component of ${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}$ which is nothing but the sine component, we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}\text{ sin30 = }\overrightarrow{V}mG \\
& {{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{V}mG}{\sin {{30}^{0}}} \\
\end{align}$
In this question, it is given that velocity of man with respect to ground is 10 km/h
Therefore,
${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{V}mG}{1/2}=\dfrac{10}{0.5}=20$
Hence, velocity of rain with respect to ground is 20 km/h now take vertical component of ${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}$ which is nothing but cosine component, we get,
${{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rG}}\text{ cos (3}{{\text{0}}^{0}}\text{)=}{{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rM}}$
$\begin{align}
& {{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rm}}=20\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& {{\overrightarrow{V}}_{rm}}=10\sqrt{3}\text{ km/h} \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Concept of above solution is based on relativity. To solve this kind of question, we usually have to consider frames of reference of different bodies. Frame of reference is nothing but a system of coordinate axes which represents the position of a particle or an event in two or three dimensional space. The position of any body is specified by the position vector from the origin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




