
A man sitting at the height of 20m on a tall tree on a small island in the middle of a river observes two poles directly opposite to each other on the two banks of the river and in line with the foot of the tree. If the angles of depression of the feet of the two poles from a point at which the man is sitting on either side of the river are $60{}^\circ $ and $30{}^\circ $ respectively, then find the width of the river.
Answer
620.1k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that $DE\parallel BC,$ and hence $\angle EDB=\angle DBA\text{ and }\angle FDC=\angle DCA$. Use $\tan \alpha =\dfrac{AD}{AB}$ and hence find the length AB. Use $\tan \beta =\dfrac{AD}{AC}$ and hence find the length of AC. Use BC = AC+AB and hence find the width of the river.
Complete step-by-step solution -
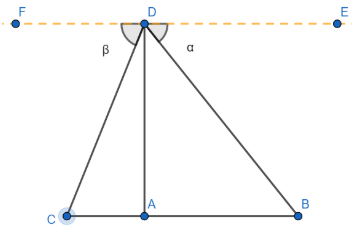
Given: AB is a tree on an island in the middle of a river and B and C are points on the bank of the river directly along the foot of the tree. The angle of depression from point D to point B is $\alpha =60{}^\circ $, and to the point C is $\beta =30{}^\circ $. AD = 20m
To determine: The width of the river (BC).
We know that $DE\parallel BC$.
Hence, we have $\angle FDC=\angle DCA$ (alternate interior angles) and $\angle EDB=\angle DBA$ (alternate interior angles).
Hence, we have $\angle DBA=\alpha $ and $\angle DCA=\beta $
Now in triangle DAB, we have AD is opposite to $\angle DBA$ and AB is adjacent to $\angle DBA$.
We know that in a triangle $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite side }}{\text{Adjacent side}}$
Hence, we have $\tan \alpha =\dfrac{AD}{AB}$
Multiplying both sides by $\dfrac{AB}{\tan \alpha }$, we get
$AB=\dfrac{AD}{\tan \alpha }\text{ }\left( i \right)$
Also in triangle ADC, we have AD is the side opposite to $\angle DCA$ and AC is the side adjacent to $\angle DCA$
We know that in a triangle $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite side }}{\text{Adjacent side}}$
Hence, we have $\tan \beta =\dfrac{AD}{AC}$
Multiplying both sides by $\dfrac{AC}{\tan \beta }$, we get
$AC=\dfrac{AD}{\tan \beta }\text{ }\left( ii \right)$
Adding equation (i) and equation (ii), we get
$AC+AB=\dfrac{AD}{\tan \alpha }+\dfrac{AD}{\tan \beta }$
We know that AC+AB = BC.
Hence, we have
$BC=\dfrac{AD}{\tan \alpha }+\dfrac{AD}{\tan \beta }$
Put $AD=20,\alpha =30{}^\circ \text{ and }\beta \text{=}60{}^\circ $, we get
$BC=20\left( \dfrac{1}{\tan 30{}^\circ }+\dfrac{1}{\tan 60{}^\circ } \right)$
We know that $\tan 30{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$ and $\tan 60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3}$
Hence, we have
$BC=20\left( \sqrt{3}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right)=\dfrac{80}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{80\sqrt{3}}{3}$
Also, from equation (i), we have
$AB=20\sqrt{3}$
Hence the width of the river is $\dfrac{80\sqrt{3}}{3}m$
Note: Verification:
We have AB $=20\sqrt{3}$
Hence, we have
$\dfrac{AD}{AB}=\dfrac{20}{20\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\tan 30{}^\circ $
Hence, we have
$\alpha =30{}^\circ $
Also, we have
$AC=BC-AB=\dfrac{80}{\sqrt{3}}-\dfrac{60}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{20}{\sqrt{3}}m$
Hence, we have $\dfrac{AD}{AC}=\dfrac{20}{\dfrac{20}{\sqrt{3}}}=\sqrt{3}=\tan 60{}^\circ $
Hence, we have $\beta =60{}^\circ $
Hence our answer is verified to be correct.
Complete step-by-step solution -

Given: AB is a tree on an island in the middle of a river and B and C are points on the bank of the river directly along the foot of the tree. The angle of depression from point D to point B is $\alpha =60{}^\circ $, and to the point C is $\beta =30{}^\circ $. AD = 20m
To determine: The width of the river (BC).
We know that $DE\parallel BC$.
Hence, we have $\angle FDC=\angle DCA$ (alternate interior angles) and $\angle EDB=\angle DBA$ (alternate interior angles).
Hence, we have $\angle DBA=\alpha $ and $\angle DCA=\beta $
Now in triangle DAB, we have AD is opposite to $\angle DBA$ and AB is adjacent to $\angle DBA$.
We know that in a triangle $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite side }}{\text{Adjacent side}}$
Hence, we have $\tan \alpha =\dfrac{AD}{AB}$
Multiplying both sides by $\dfrac{AB}{\tan \alpha }$, we get
$AB=\dfrac{AD}{\tan \alpha }\text{ }\left( i \right)$
Also in triangle ADC, we have AD is the side opposite to $\angle DCA$ and AC is the side adjacent to $\angle DCA$
We know that in a triangle $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite side }}{\text{Adjacent side}}$
Hence, we have $\tan \beta =\dfrac{AD}{AC}$
Multiplying both sides by $\dfrac{AC}{\tan \beta }$, we get
$AC=\dfrac{AD}{\tan \beta }\text{ }\left( ii \right)$
Adding equation (i) and equation (ii), we get
$AC+AB=\dfrac{AD}{\tan \alpha }+\dfrac{AD}{\tan \beta }$
We know that AC+AB = BC.
Hence, we have
$BC=\dfrac{AD}{\tan \alpha }+\dfrac{AD}{\tan \beta }$
Put $AD=20,\alpha =30{}^\circ \text{ and }\beta \text{=}60{}^\circ $, we get
$BC=20\left( \dfrac{1}{\tan 30{}^\circ }+\dfrac{1}{\tan 60{}^\circ } \right)$
We know that $\tan 30{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$ and $\tan 60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3}$
Hence, we have
$BC=20\left( \sqrt{3}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right)=\dfrac{80}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{80\sqrt{3}}{3}$
Also, from equation (i), we have
$AB=20\sqrt{3}$
Hence the width of the river is $\dfrac{80\sqrt{3}}{3}m$
Note: Verification:
We have AB $=20\sqrt{3}$
Hence, we have
$\dfrac{AD}{AB}=\dfrac{20}{20\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\tan 30{}^\circ $
Hence, we have
$\alpha =30{}^\circ $
Also, we have
$AC=BC-AB=\dfrac{80}{\sqrt{3}}-\dfrac{60}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{20}{\sqrt{3}}m$
Hence, we have $\dfrac{AD}{AC}=\dfrac{20}{\dfrac{20}{\sqrt{3}}}=\sqrt{3}=\tan 60{}^\circ $
Hence, we have $\beta =60{}^\circ $
Hence our answer is verified to be correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

The highest dam in India is A Bhakra dam B Tehri dam class 10 social science CBSE

Describe the process of Unification of Italy class 10 social science CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed




