
A man running at a speed of 5 kmph finds that the rain falls vertically. When he stops running, he finds that the rain is falling at an angle of ${{60}^{\circ }}$ with the horizontal. The velocity of rain with respect to the running man is:
$A.\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$ kmph
$B.\dfrac{5\sqrt{3}}{2}$ kmph
$C.\dfrac{4\sqrt{3}}{5}$ kmph
$D.5\sqrt{3}$ kmph
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: You need to draw the vector diagram and assign appropriate notations to vectors according to the question. You should note the direction of each vector. If we have the value of a vector and the angle subtended by it, then we can use trigonometric functions to find each of the remaining vectors.
Formula used:
$\tan {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{p}{b}=\dfrac{{{v}_{r}}-{{v}_{m}}}{{{v}_{m}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider the speed of the man ${{v}_{m}}=5$ kmph.
We can consider the speed of rain to be ${{v}_{r}}$.
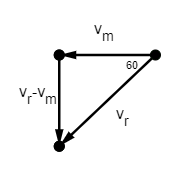
.
The horizontal vector line represents the velocity of the man. We are given that when the man is at rest, rain falls on him at an angle of ${{60}^{\circ }}$ so the vector line ${{60}^{\circ }}$ to the horizontal is the velocity of rain.
Therefore the relative velocity of the rain with respect to the man is${{v}_{r}}-{{v}_{m}}$.
$\tan {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{p}{b}=\dfrac{{{v}_{r}}-{{v}_{m}}}{{{v}_{m}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{r}}-{{v}_{m}}=\tan {{60}^{\circ }}\times {{v}_{m}}$
$\therefore {{v}_{r}}-{{v}_{m}}=5\sqrt{3}$kmph
Hence the correct option is D.
Note:
The possibility of a mistake can be by choosing option B. If the resolution of the angles is not don’t correctly then you can end up choosing the wrong option. The head and tail of the vector describes the direction of motion. Two vectors are considered to be the same only when its magnitude and direction are the same. A vector is symbolized as an alphabet with an arrow on top. Magnitude and direction are the two defining features of a vector. Vector addition and subtraction is a big helping hand in relativity.
Formula used:
$\tan {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{p}{b}=\dfrac{{{v}_{r}}-{{v}_{m}}}{{{v}_{m}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider the speed of the man ${{v}_{m}}=5$ kmph.
We can consider the speed of rain to be ${{v}_{r}}$.

.
The horizontal vector line represents the velocity of the man. We are given that when the man is at rest, rain falls on him at an angle of ${{60}^{\circ }}$ so the vector line ${{60}^{\circ }}$ to the horizontal is the velocity of rain.
Therefore the relative velocity of the rain with respect to the man is${{v}_{r}}-{{v}_{m}}$.
$\tan {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{p}{b}=\dfrac{{{v}_{r}}-{{v}_{m}}}{{{v}_{m}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{r}}-{{v}_{m}}=\tan {{60}^{\circ }}\times {{v}_{m}}$
$\therefore {{v}_{r}}-{{v}_{m}}=5\sqrt{3}$kmph
Hence the correct option is D.
Note:
The possibility of a mistake can be by choosing option B. If the resolution of the angles is not don’t correctly then you can end up choosing the wrong option. The head and tail of the vector describes the direction of motion. Two vectors are considered to be the same only when its magnitude and direction are the same. A vector is symbolized as an alphabet with an arrow on top. Magnitude and direction are the two defining features of a vector. Vector addition and subtraction is a big helping hand in relativity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




