
A man on the top of an observation tower finds an object at an angle of depression $30^\circ $. After the object was moved 30 metres in a straight line towards the tower, he finds the angle of depression to be $45^\circ $. The distance of the object now from the foot of the tower in metres is
(A) $15\sqrt 3 $
(B) $15\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)$
(C) $15\left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)$
(D) $15\left( {2 + \sqrt 3 } \right)$
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint:
In this question we will use trigonometric ratios. Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics which deals with the measurement of sides and angles of a triangle and the problems based on them. Trigonometry helps us to find angles and distances, and is used a lot in science, engineering, and many more.
There are many trigonometry formulas and trigonometric identities, which are used to solve complex equations in geometry.
The ratios of sides of a right-angled triangle with respect to any of its acute angles are known as the trigonometric ratios of that particular angle. They are defined by parameters namely hypotenuse, base and perpendicular.
In ∆ABC
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{Perpendicular}}{{Base}}$
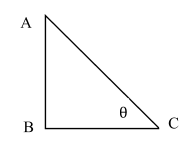
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}$
And the value of \[\tan 30^\circ \] is $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ and \[\tan 45^\circ \] is 1.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the given problem we make a diagram.
Angle of depression is the angle formed by the line sight with the horizontal, when the point viewed is below the horizontal level.
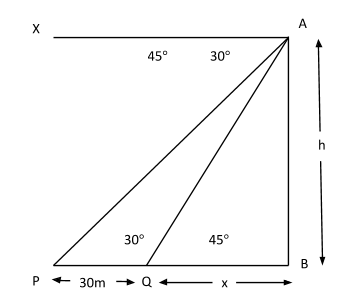
Initially the object is at position P and then after a 30m move reached at Q.
Let the height of tower AB = h
And required distance = x
In ∆APB,
$\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{AB}}{{PB}}{\text{ }}\left[ {\tan \theta = \dfrac{{Perpendicular}}{{Base}}} \right]$
$
\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{h}{{x + 30}} \\
h = \dfrac{{x + 30}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \ldots \left( 1 \right) \\
$
In ∆AQB,
$
\tan 45^\circ = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BQ}} \\
1 = \dfrac{h}{x} \\
x = h{\text{ }}\left[ {{\text{using equation }}\left( 1 \right)} \right] \\
x = \dfrac{{x + 30}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\sqrt 3 x - x = 30 \\
x = \left( {\dfrac{{30}}{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}} \right) \\
$
$
x = \dfrac{{\left( {30} \right)\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{{\left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{\text{ }}\left[ {{\text{Rationalizing}}} \right] \\
x = \dfrac{{30\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{{\left( {3 - 1} \right)}} \\
x = 15\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right) \\
$
Therefore, the distance of the object from the foot of the tower is $15\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)m$
∴Option (B) is correct.
Note:
Some of the basic applications of trigonometry are
1. Measuring the heights of towers or buildings.
2. Determining the distance of the shore from the sea.
3. Finding the distance between two bodies.
4. Determining the power output of solar cell panels at different inclinations.
In this question we will use trigonometric ratios. Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics which deals with the measurement of sides and angles of a triangle and the problems based on them. Trigonometry helps us to find angles and distances, and is used a lot in science, engineering, and many more.
There are many trigonometry formulas and trigonometric identities, which are used to solve complex equations in geometry.
The ratios of sides of a right-angled triangle with respect to any of its acute angles are known as the trigonometric ratios of that particular angle. They are defined by parameters namely hypotenuse, base and perpendicular.
In ∆ABC
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{Perpendicular}}{{Base}}$

$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}$
And the value of \[\tan 30^\circ \] is $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ and \[\tan 45^\circ \] is 1.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the given problem we make a diagram.
Angle of depression is the angle formed by the line sight with the horizontal, when the point viewed is below the horizontal level.

Initially the object is at position P and then after a 30m move reached at Q.
Let the height of tower AB = h
And required distance = x
In ∆APB,
$\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{AB}}{{PB}}{\text{ }}\left[ {\tan \theta = \dfrac{{Perpendicular}}{{Base}}} \right]$
$
\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{h}{{x + 30}} \\
h = \dfrac{{x + 30}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \ldots \left( 1 \right) \\
$
In ∆AQB,
$
\tan 45^\circ = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BQ}} \\
1 = \dfrac{h}{x} \\
x = h{\text{ }}\left[ {{\text{using equation }}\left( 1 \right)} \right] \\
x = \dfrac{{x + 30}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\sqrt 3 x - x = 30 \\
x = \left( {\dfrac{{30}}{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}} \right) \\
$
$
x = \dfrac{{\left( {30} \right)\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{{\left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{\text{ }}\left[ {{\text{Rationalizing}}} \right] \\
x = \dfrac{{30\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{{\left( {3 - 1} \right)}} \\
x = 15\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right) \\
$
Therefore, the distance of the object from the foot of the tower is $15\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)m$
∴Option (B) is correct.
Note:
Some of the basic applications of trigonometry are
1. Measuring the heights of towers or buildings.
2. Determining the distance of the shore from the sea.
3. Finding the distance between two bodies.
4. Determining the power output of solar cell panels at different inclinations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?




