
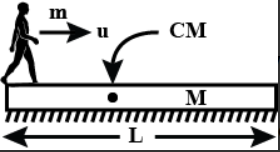
A man of mass m on a plank of mass M with a constant velocity u with respect to the plank. As shown in fig.
a) If the plank rests on a smooth horizontal surface, determine the velocity of the plank.
b) If the man travels a distance L with respect to the plank, find the distance travelled by the plank with respect to the ground.

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Here use basic law for the conservation of momentum and the velocity.Also make sure that while using basic law for conservation of momentum and velocity use the whole concept.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that –
A man of mass is $ = m$
Moves on a plank of mass is $ = M$
With a constant velocity is $ = u$
If the plank is kept on the smooth horizontal surface, find the velocity of the plank
Now, suppose the man travels on the right side of the plank, with respect to ground the absolute velocity on left side of the plank will be $ = v$
Therefore, with respect to ground the absolute speed of the man is $ = u - v$
Now, the system of the man and the plank is such a way that the plank is placed on the smooth surface. It means the man if walks by any way the momentum would remain conserved. In starting the momentum remains zero, as at initial when man was standing the speed of the man and the plank remains zero.
The momentum of the man is $ = m(u - v)$
The momentum of the plank is \[ = - Mv\] (because it velocity is in the opposite direction)
According to the law of conservation of the momentum,
$m(u - v) + ( - Mv) = 0$
Simplify the above equation –
$
mu - mv - Mv = 0 \\
mu - mv = Mv \\
$
When we move any term from the left hand side to the right hand side, the sign also changes, from positive to negative and negative to positive.
$
\Rightarrow mu = mv + Mv \\
\Rightarrow mu = v(m + M) \\
$
Make the velocity, v as the subject-
$v = \dfrac{{mu}}{{m + M}}$
Therefore, the velocity of the plank is $v = \dfrac{{mu}}{{m + M}}$
Man travels a distance L with respect to the plank
Since initially the man was stationary, Centre of mass of the man and the plank remained the same.
Therefore, the distance travelled by the plank with respect to the ground is $\dfrac{{mL}}{{m + M}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Use basic concepts of the velocity as velocity is the vector quantity the positive and negative sign with the velocity matters a lot. In starting the momentum remains zero, as at initial when man was standing the speed of the man and the plank remains zero.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that –
A man of mass is $ = m$
Moves on a plank of mass is $ = M$
With a constant velocity is $ = u$
If the plank is kept on the smooth horizontal surface, find the velocity of the plank
Now, suppose the man travels on the right side of the plank, with respect to ground the absolute velocity on left side of the plank will be $ = v$
Therefore, with respect to ground the absolute speed of the man is $ = u - v$
Now, the system of the man and the plank is such a way that the plank is placed on the smooth surface. It means the man if walks by any way the momentum would remain conserved. In starting the momentum remains zero, as at initial when man was standing the speed of the man and the plank remains zero.
The momentum of the man is $ = m(u - v)$
The momentum of the plank is \[ = - Mv\] (because it velocity is in the opposite direction)
According to the law of conservation of the momentum,
$m(u - v) + ( - Mv) = 0$
Simplify the above equation –
$
mu - mv - Mv = 0 \\
mu - mv = Mv \\
$
When we move any term from the left hand side to the right hand side, the sign also changes, from positive to negative and negative to positive.
$
\Rightarrow mu = mv + Mv \\
\Rightarrow mu = v(m + M) \\
$
Make the velocity, v as the subject-
$v = \dfrac{{mu}}{{m + M}}$
Therefore, the velocity of the plank is $v = \dfrac{{mu}}{{m + M}}$
Man travels a distance L with respect to the plank
Since initially the man was stationary, Centre of mass of the man and the plank remained the same.
Therefore, the distance travelled by the plank with respect to the ground is $\dfrac{{mL}}{{m + M}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Use basic concepts of the velocity as velocity is the vector quantity the positive and negative sign with the velocity matters a lot. In starting the momentum remains zero, as at initial when man was standing the speed of the man and the plank remains zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




