
A man of mass m climbs on a rope of length L suspended below a balloon of mass H. The balloon is stationary with respect to ground. If the man begins to climb up the rope at a speed ${v_{rel}}$ $($relative to rope$)$. In what direction and with what speed $($relative to ground$)$ will the balloon move ?
(A) downwards, $\dfrac{{m{v_{rel}}}}{{m + H}}$
(B) upwards, $\dfrac{{m{v_{rel}}}}{{m + H}}$
(C) downwards, $\dfrac{{m{v_{rel}}}}{M}$
(D) downwards, $\dfrac{{(m + m){v_{rel}}}}{M}$
Answer
576k+ views
Hint:In order to solve above problem, first we have to remember the concept of relative motion.Now using conservation of momentum we can calculate the relative speed of the balloon with respect to ground.
Complete step by step solution:
Here given that velocity of man with respect to rope is ${v_{rel}}$.
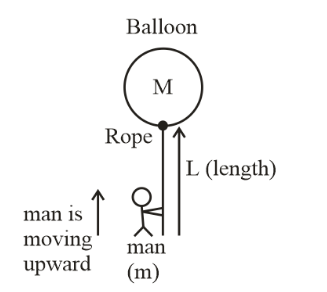
Let velocity of man respect to ground, velocity of balloon respect to ground and velocity of man respect to balloon is ${v_{MG}}$, ${v_{BG}}$ and ${v_{MB}}$ respectively.
According to diagram we can write
${v_{MB}} = {v_{MG}} - {v_{BG}}$
So, ${v_{MG}} = {v_{MG}} + {v_{BG}}$ …..(1)
Now, on applying conservation of momentum
$m{v_{MG}} + m{v_{BG}} = 0$
Given that
$m = $ mass of man
$M = $ mass of balloon
From equation 1
$m({v_{MB}} + {v_{BG}}) + m{v_{BG}} = 0$
$\Rightarrow m{v_{MB}} + {v_{BG}}(m + M) = 0$
$\Rightarrow m{v_{MB}} = - (m + H){v_{BG}}$
$\Rightarrow{v_{BG}} = \dfrac{{ - m}}{{(m + M)}}{v_{MB}}$
Given that ${v_{MB}} = {v_{rel}}$
$\therefore {v_{BG}} = \dfrac{{ - m}}{{(m + M)}}{v_{rel}}$
Here negative sign represents the direction balloon i.e., downwards respect to ground.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note:Many time students may get confused with the concept of relative motion and frame of reference. Always remember that time does not depend on the frame of ref. and relative motion with the help of relative motion numerical can be solved easier.
Complete step by step solution:
Here given that velocity of man with respect to rope is ${v_{rel}}$.

Let velocity of man respect to ground, velocity of balloon respect to ground and velocity of man respect to balloon is ${v_{MG}}$, ${v_{BG}}$ and ${v_{MB}}$ respectively.
According to diagram we can write
${v_{MB}} = {v_{MG}} - {v_{BG}}$
So, ${v_{MG}} = {v_{MG}} + {v_{BG}}$ …..(1)
Now, on applying conservation of momentum
$m{v_{MG}} + m{v_{BG}} = 0$
Given that
$m = $ mass of man
$M = $ mass of balloon
From equation 1
$m({v_{MB}} + {v_{BG}}) + m{v_{BG}} = 0$
$\Rightarrow m{v_{MB}} + {v_{BG}}(m + M) = 0$
$\Rightarrow m{v_{MB}} = - (m + H){v_{BG}}$
$\Rightarrow{v_{BG}} = \dfrac{{ - m}}{{(m + M)}}{v_{MB}}$
Given that ${v_{MB}} = {v_{rel}}$
$\therefore {v_{BG}} = \dfrac{{ - m}}{{(m + M)}}{v_{rel}}$
Here negative sign represents the direction balloon i.e., downwards respect to ground.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note:Many time students may get confused with the concept of relative motion and frame of reference. Always remember that time does not depend on the frame of ref. and relative motion with the help of relative motion numerical can be solved easier.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




