
A man is \[9\,m\] behind the door of a train when it stands moving with acceleration \[a = 2\,m/{s^2}\]. The man turns at full speed. After what time does he get into the train? What is his full speed?
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: Express the distance covered by the person in time t and also the distance covered by the person in time t. Express the velocity of the person and the train when the person reaches the door of the train. Solve these equations simultaneously to get the time t.
Formula used:
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Here, s is the distance, u is the initial velocity, t is the time and a is the acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
We assume in t second, the distance travelled by the train is x meter. But the distance travelled by the person is \[\left( {9 + x} \right)\,{\text{m}}\]. The velocity of the person is uniform.
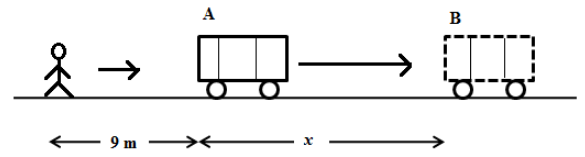
We express the distance covered by the person in t second as follows,
\[{d_1} = vt = 9 + x\] …… (1)
Here, v is the velocity of the person and t is the time.
We can express the distance travelled by the train in t second using kinematic equation as follows,
\[{d_2} = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Here, u is the initial velocity and a is the acceleration of the train.
Since the initial velocity of the train is zero, we can write the above equation as follows,
\[{d_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Substituting \[a = 2\,m/{s^2}\] and \[{d_1} = x\] in the above equation, we get,
\[x = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( 2 \right){t^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = {t^2}\] …… (2)
Using equation (2) in equation (1), we get,
\[vt = 9 + {t^2}\] …… (3)
Now, the relative velocity of the train and the person at point B is zero when the person reaches the train. Therefore, the velocity of the person should be equal to velocity of the train at point B in the above figure.
We express the velocity of the train at point B using the kinematic equation as follows,
\[{v_t} = {u_t} + at\]
Here, \[{u_t}\] is the initial velocity of the train. Since the initial velocity of the train is zero, we can write the above equation as,
\[{v_t} = at\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_t} = {v_p} = 2t\] …… (4)
Using equation (4) in equation (3), we get,
\[2{t^2} = 9 + {t^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {t^2} = 9\]
\[ \therefore t = 3\,s\]
Therefore, after 3 second, the person will get into the train.
We have discussed that the velocity of the person and velocity of the train at point B is the same. This velocity of the person is his maximum speed.
Substituting 3 s for t in equation (4), we get,
\[{v_p} = 2\left( 3 \right)\]
\[ \therefore {v_p} = 6\,m/s\]
Therefore, the full speed of the person is 6 m/s.
Note:To solve these types of questions, the kinematic equations should be on your fingertips. In equation (4), the velocity of the train \[{v_t}\] and the velocity of the person \[{v_p}\] is the same because the relative velocity between them, \[{v_p} - {v_t} = 0\]. In this question, we have assumed that the motion of the train and the person are in the same direction.
Formula used:
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Here, s is the distance, u is the initial velocity, t is the time and a is the acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
We assume in t second, the distance travelled by the train is x meter. But the distance travelled by the person is \[\left( {9 + x} \right)\,{\text{m}}\]. The velocity of the person is uniform.

We express the distance covered by the person in t second as follows,
\[{d_1} = vt = 9 + x\] …… (1)
Here, v is the velocity of the person and t is the time.
We can express the distance travelled by the train in t second using kinematic equation as follows,
\[{d_2} = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Here, u is the initial velocity and a is the acceleration of the train.
Since the initial velocity of the train is zero, we can write the above equation as follows,
\[{d_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Substituting \[a = 2\,m/{s^2}\] and \[{d_1} = x\] in the above equation, we get,
\[x = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( 2 \right){t^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = {t^2}\] …… (2)
Using equation (2) in equation (1), we get,
\[vt = 9 + {t^2}\] …… (3)
Now, the relative velocity of the train and the person at point B is zero when the person reaches the train. Therefore, the velocity of the person should be equal to velocity of the train at point B in the above figure.
We express the velocity of the train at point B using the kinematic equation as follows,
\[{v_t} = {u_t} + at\]
Here, \[{u_t}\] is the initial velocity of the train. Since the initial velocity of the train is zero, we can write the above equation as,
\[{v_t} = at\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_t} = {v_p} = 2t\] …… (4)
Using equation (4) in equation (3), we get,
\[2{t^2} = 9 + {t^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {t^2} = 9\]
\[ \therefore t = 3\,s\]
Therefore, after 3 second, the person will get into the train.
We have discussed that the velocity of the person and velocity of the train at point B is the same. This velocity of the person is his maximum speed.
Substituting 3 s for t in equation (4), we get,
\[{v_p} = 2\left( 3 \right)\]
\[ \therefore {v_p} = 6\,m/s\]
Therefore, the full speed of the person is 6 m/s.
Note:To solve these types of questions, the kinematic equations should be on your fingertips. In equation (4), the velocity of the train \[{v_t}\] and the velocity of the person \[{v_p}\] is the same because the relative velocity between them, \[{v_p} - {v_t} = 0\]. In this question, we have assumed that the motion of the train and the person are in the same direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




