
A man donates $ 10 $ aluminium buckets to an orphanage. A bucket made of aluminium is of height $ 20 $ cm and has its upper and lowest ends of radius $ 36 $ cm and $ 21 $ cm respectively. Find the cost of preparing $ 10 $ buckets if the cost of aluminium sheet is Rs. $ 42 $ per $ 100{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}. $
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: Here, we will use total surface area for one bucket and then for ten buckets. From the area, we will find the cost of the aluminium. First we need to find the slant height from the height and radii given. Substitute values in the formula and do simplification carefully.
Complete step-by-step answer:
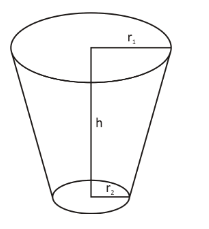
Given that the bucket has two radii, lowest and upper ends.
Therefore, let us consider that –
Upper radius of the bucket be, $ {r_1} = 36cm $
Lowest ends of radius be $ {r_2} = 21cm $
Height of the bucket, $ h = 20cm $
Now, slant height of the bucket is $ l = \sqrt {{h^2} + {{({r_1} - {r_2})}^2}} $
Place values in the above equation –
$ \therefore l = \sqrt {{{(20)}^2} + {{(36 - 21)}^2}} $
Simplify the above equation –
$ \therefore l = \sqrt {400 + {{(15)}^2}} $
Simplify –
$
\therefore l = \sqrt {400 + 225} \\
\therefore l = \sqrt {625} \;
$
Find square root on the right hand side of the equation –
$ \therefore l = \sqrt {{{(25)}^2}} $
Square and square-root cancel each other on the right hand side of the equation.
$ \Rightarrow l = 25cm $
Now, Total surface area of the bucket is $ A = \pi ({r_1} + {r_2})l + \pi {r_2}^2 $
It can be re-written as –
$ A = \pi [({r_1} + {r_2})l + {r_2}^2] $
Place values in the above equation –
$ A = \dfrac{{22}}{7}[(36 + 21) \times 25 + {(21)^2}] $
Simplify the above equation –
$
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{22}}{7}[1425 + 441] \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{22}}{7}[1866] \;
$
$ A = 5864.57\;c{m^2} $
Now area of one bucket is $ 5864.57\;c{m^2} $
Therefore area of $ 10 $ buckets is $ = 5864.57 \times 10 = 58645.7\;c{m^2} $
The cost of aluminium sheet is
$
100{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2} - 42 \\
58645.7\;c{m^2} - ? \;
$
Do cross multiplication –
Cost $ = \dfrac{{42 \times 58645.7}}{{100}} $
Simplification-
Cost $ = 24631.194{\text{ Rs}}{\text{.}} $
which approximates to 24632 Rs.
So, the correct answer is “24632 Rs”.
Note: Know the difference between the surface area of the object and the total surface area of the object. Accordingly frame the equation and substitute the values and simplify properly. Remember all the standard formulas for the solid and hollow figures.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Given that the bucket has two radii, lowest and upper ends.
Therefore, let us consider that –
Upper radius of the bucket be, $ {r_1} = 36cm $
Lowest ends of radius be $ {r_2} = 21cm $
Height of the bucket, $ h = 20cm $
Now, slant height of the bucket is $ l = \sqrt {{h^2} + {{({r_1} - {r_2})}^2}} $
Place values in the above equation –
$ \therefore l = \sqrt {{{(20)}^2} + {{(36 - 21)}^2}} $
Simplify the above equation –
$ \therefore l = \sqrt {400 + {{(15)}^2}} $
Simplify –
$
\therefore l = \sqrt {400 + 225} \\
\therefore l = \sqrt {625} \;
$
Find square root on the right hand side of the equation –
$ \therefore l = \sqrt {{{(25)}^2}} $
Square and square-root cancel each other on the right hand side of the equation.
$ \Rightarrow l = 25cm $
Now, Total surface area of the bucket is $ A = \pi ({r_1} + {r_2})l + \pi {r_2}^2 $
It can be re-written as –
$ A = \pi [({r_1} + {r_2})l + {r_2}^2] $
Place values in the above equation –
$ A = \dfrac{{22}}{7}[(36 + 21) \times 25 + {(21)^2}] $
Simplify the above equation –
$
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{22}}{7}[1425 + 441] \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{22}}{7}[1866] \;
$
$ A = 5864.57\;c{m^2} $
Now area of one bucket is $ 5864.57\;c{m^2} $
Therefore area of $ 10 $ buckets is $ = 5864.57 \times 10 = 58645.7\;c{m^2} $
The cost of aluminium sheet is
$
100{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2} - 42 \\
58645.7\;c{m^2} - ? \;
$
Do cross multiplication –
Cost $ = \dfrac{{42 \times 58645.7}}{{100}} $
Simplification-
Cost $ = 24631.194{\text{ Rs}}{\text{.}} $
which approximates to 24632 Rs.
So, the correct answer is “24632 Rs”.
Note: Know the difference between the surface area of the object and the total surface area of the object. Accordingly frame the equation and substitute the values and simplify properly. Remember all the standard formulas for the solid and hollow figures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




