
A man crosses the river, perpendicular to river flow in time \[{\text{t}}\] seconds and travels an equal distance down the stream in \[{\text{T}}\] seconds. The ratio of man’s speed in still water to the speed of river water will be:
A. \[\dfrac{{{{\text{t}}^2} - {{\text{T}}^2}}}{{{{\text{t}}^2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{T}}^2}}}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{{{\text{T}}^2} - {{\text{t}}^2}}}{{{{\text{T}}^2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{t}}^2}}}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{{{\text{t}}^2} + {{\text{T}}^2}}}{{{{\text{t}}^2} - {{\text{T}}^2}}}\]
D. \[\dfrac{{{{\text{T}}^2} + {{\text{t}}^2}}}{{{{\text{T}}^2} - {{\text{t}}^2}}}\]
Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: In this question, the man crosses the river perpendicular to the river flow, so assuming the velocity of man as \[{{\text{v}}_m}\] and velocity of the river as \[{{\text{v}}_{_w}}\] , using vectors we can find out the resultant velocity which is perpendicular to the river flow. Now the speed of the man downstream will be \[{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}\]. As they cover the same distance on taking the ratio, express speed as \[\dfrac{{dis\tan ce}}{{time}}\] and solve to get a relation of the speed of the ratio in time.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given,
The man crosses the river, with resultant velocity perpendicular to the flow of the river in \[{\text{t}}\] seconds.
Let the speed of river be \[{{\text{v}}_{_w}}\]
Let the velocity of man in still river be \[{{\text{v}}_m}\]
Let the resultant velocity be \[{\text{V}}\]
Let’s draw the vector diagram
Since resultant velocity is perpendicular to the river flow velocity of man must be in the opposite direction
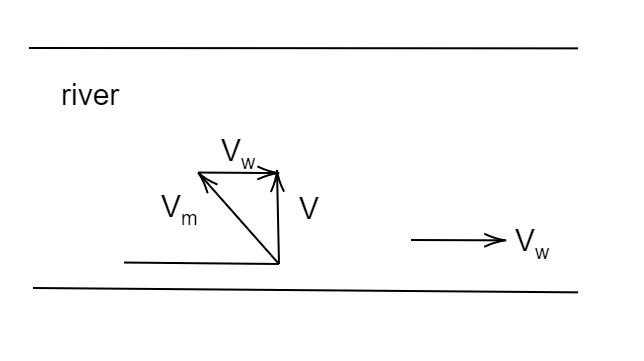
Thus, from this, we can say,
The Resultant velocity of the man or velocity of man with respect to ground, \[{\text{V = }}\sqrt {{{\text{v}}_m}^2 - } {{\text{v}}_{_w}}^2\]
Now suppose the man covers a distance \[{\text{d}}\] in time \[{\text{t}}\]
\[{\text{V = }}\sqrt {{{\text{v}}_m}^2 - } {{\text{v}}_{_w}}^2 = \dfrac{d}{t}\]
Now the man travels an equal distance downstream in time \[{\text{T}}\] second
Let the velocity of the man downstream be \[{\text{u}}\]
\[{\text{u = }}{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}\]
Since now the man travels \[{\text{d}}\] distance in \[{\text{T}}\] seconds
\[{\text{u = }}{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}} = \dfrac{d}{T}\]
We need to find the ratio of man’s speed in still water to the speed of river water
Divide resultant velocity of man in river water and velocity of man downstream
\[\dfrac{{\text{V}}}{u} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\text{v}}_m}^2 - } {{\text{v}}_{_w}}^2}}{{{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{d}{t}}}{{\dfrac{d}{T}}}\]
On simplifying,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\text{v}}_m}^2 - } {{\text{v}}_{_w}}^2}}{{{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}}} = \dfrac{T}{t}\]
Cross multiplying both the sides we get,
\[ \Rightarrow t\sqrt {{{\text{v}}_m}^2 - } {{\text{v}}_{_w}}^2 = T\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}} \right)\]
Squaring both the sides we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {t^2}\left( {{\text{v}}_m^2 - {\text{v}}_w^2} \right) = {T^2}{\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}} \right)^2}\]
Using the formula \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\] we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {t^2}\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} - {{\text{v}}_w}} \right)\left( {{{\text{v}}_m}{\text{ + }}{{\text{v}}_w}} \right) = {T^2}{\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {t^2}\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} - {{\text{v}}_w}} \right) = {T^2}\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}} \right)\]
On rearranging we get,
\[\dfrac{{\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}} \right)}}{{\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} - {{\text{v}}_w}} \right)}} = \dfrac{{{t^2}}}{{{T^2}}}\]
On taking Componendo-Dividendo on both sides we get,
\[\dfrac{{{{\text{v}}_m}}}{{{{\text{v}}_w}}} = \dfrac{{{{\text{t}}^2} + {{\text{T}}^2}}}{{{{\text{t}}^2} - {{\text{T}}^2}}}\]
Thus, ratio of speed of man in still water and speed of river is \[\dfrac{{{{\text{v}}_m}}}{{{{\text{v}}_w}}} = \dfrac{{{{\text{t}}^2} + {{\text{T}}^2}}}{{{{\text{t}}^2} - {{\text{T}}^2}}}\]
The correct option is option C.
Note: If the body is flowing in the opposite direction to the stream, it is called upstream. In this case, the net speed of the boat is called the upstream speed and if the body is flowing along the direction of the stream, it is called downstream. In this case, the net speed of the boat is called downstream speed.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given,
The man crosses the river, with resultant velocity perpendicular to the flow of the river in \[{\text{t}}\] seconds.
Let the speed of river be \[{{\text{v}}_{_w}}\]
Let the velocity of man in still river be \[{{\text{v}}_m}\]
Let the resultant velocity be \[{\text{V}}\]
Let’s draw the vector diagram
Since resultant velocity is perpendicular to the river flow velocity of man must be in the opposite direction

Thus, from this, we can say,
The Resultant velocity of the man or velocity of man with respect to ground, \[{\text{V = }}\sqrt {{{\text{v}}_m}^2 - } {{\text{v}}_{_w}}^2\]
Now suppose the man covers a distance \[{\text{d}}\] in time \[{\text{t}}\]
\[{\text{V = }}\sqrt {{{\text{v}}_m}^2 - } {{\text{v}}_{_w}}^2 = \dfrac{d}{t}\]
Now the man travels an equal distance downstream in time \[{\text{T}}\] second
Let the velocity of the man downstream be \[{\text{u}}\]
\[{\text{u = }}{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}\]
Since now the man travels \[{\text{d}}\] distance in \[{\text{T}}\] seconds
\[{\text{u = }}{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}} = \dfrac{d}{T}\]
We need to find the ratio of man’s speed in still water to the speed of river water
Divide resultant velocity of man in river water and velocity of man downstream
\[\dfrac{{\text{V}}}{u} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\text{v}}_m}^2 - } {{\text{v}}_{_w}}^2}}{{{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{d}{t}}}{{\dfrac{d}{T}}}\]
On simplifying,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\text{v}}_m}^2 - } {{\text{v}}_{_w}}^2}}{{{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}}} = \dfrac{T}{t}\]
Cross multiplying both the sides we get,
\[ \Rightarrow t\sqrt {{{\text{v}}_m}^2 - } {{\text{v}}_{_w}}^2 = T\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}} \right)\]
Squaring both the sides we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {t^2}\left( {{\text{v}}_m^2 - {\text{v}}_w^2} \right) = {T^2}{\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}} \right)^2}\]
Using the formula \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\] we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {t^2}\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} - {{\text{v}}_w}} \right)\left( {{{\text{v}}_m}{\text{ + }}{{\text{v}}_w}} \right) = {T^2}{\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {t^2}\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} - {{\text{v}}_w}} \right) = {T^2}\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}} \right)\]
On rearranging we get,
\[\dfrac{{\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} + {{\text{v}}_{_w}}} \right)}}{{\left( {{{\text{v}}_m} - {{\text{v}}_w}} \right)}} = \dfrac{{{t^2}}}{{{T^2}}}\]
On taking Componendo-Dividendo on both sides we get,
\[\dfrac{{{{\text{v}}_m}}}{{{{\text{v}}_w}}} = \dfrac{{{{\text{t}}^2} + {{\text{T}}^2}}}{{{{\text{t}}^2} - {{\text{T}}^2}}}\]
Thus, ratio of speed of man in still water and speed of river is \[\dfrac{{{{\text{v}}_m}}}{{{{\text{v}}_w}}} = \dfrac{{{{\text{t}}^2} + {{\text{T}}^2}}}{{{{\text{t}}^2} - {{\text{T}}^2}}}\]
The correct option is option C.
Note: If the body is flowing in the opposite direction to the stream, it is called upstream. In this case, the net speed of the boat is called the upstream speed and if the body is flowing along the direction of the stream, it is called downstream. In this case, the net speed of the boat is called downstream speed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




