
A man 2 metres high walks at a uniform speed of 5km/hr away from a lamp post 6 metres high. Find the rate at which the length of his shadow increases.
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Assume that the angle made by the BE with AE be $ \theta $ . Use the fact that in a right-angled triangle the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side is the tangent of the angle. Hence prove that $ CE=CD\cot \theta $ . Use the fact that the triangle ABE and DCE are similar and hence prove that $ \dfrac{AB}{DC}=\dfrac{AE}{CE} $ and hence find the length AC. Differentiate with respect to t and hence find the value of $ \dfrac{d\theta }{dt} $ . Differentiate the expression of CE to and substitute the value of $ \dfrac{d\theta }{dt} $ and hence find the speed of the shadow.
Complete step-by-step answer:
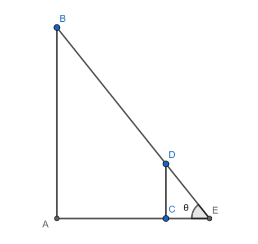
Given: A lamppost AB of height 6 metres and a man DC of height 2 metres is moving away from the post with speed of 5 metres per second.
To determine: The speed of the head of the shadow E.
Let $ \angle DEC=\theta $
In triangle EDC, we have DC is the side opposite to E and CE is the side adjacent to E.
Hence, we have
$ \tan \theta =\dfrac{DC}{CE} $
Multiplying both sides by CE and dividing both sides by $ \tan \theta $ , we get
$ CE=DC\cot \theta $
Differentiating with respect to t(time), we get
$ \dfrac{d\left( CE \right)}{dt}=-DC{{\csc }^{2}}\theta \dfrac{d\theta }{dt}\text{ }\left( i \right) $
Similarly in triangle ABE, we have
$ AE=AB\cot \theta $
Also, we have triangle ABE and DCE are similar (Since AB||DC).
Hence, we have
$ \dfrac{AB}{DC}=\dfrac{AE}{CE} $ (Ratios of corresponding sides of two similar triangles is same)
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{6}{2}=\dfrac{AE}{CE} \\
& \Rightarrow AE=3CE \\
\end{align} $
Hence, we have
$ AC=2CE=4\cot \theta $
Hence, we have
$ \dfrac{d\left( AC \right)}{dt}=-4{{\csc }^{2}}\theta \dfrac{d\theta }{dt} $
Since the person moves with velocity of $ 5m{{s}^{-1}} $ , we have
$ \dfrac{d\left( AC \right)}{dt}=5 $
Hence, we have
$ {{\csc }^{2}}\theta \dfrac{d\theta }{dt}=\dfrac{-5}{4} $
Substituting in equation (i), we get
$ \dfrac{d\left( CE \right)}{dt}=-2\left( \dfrac{-5}{4} \right)=\dfrac{5}{2}m{{s}^{-1}} $
Hence the speed of the shadow is $ \dfrac{5}{2}m{{s}^{-1}} $ .
Note: Instead of trigonometry, we can also use simple geometry to solve the question.
We have
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{AE}=\dfrac{DC}{CE} \\
& \Rightarrow AE=\dfrac{6CE}{2}=3CE \\
\end{align} $
Hence, we have
$ AC=2CE $
Differentiating both sides with respect to t, we get
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{d\left( AC \right)}{dt}=2\times \dfrac{d\left( CE \right)}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{d\left( CE \right)}{dt}=\dfrac{5}{2} \\
\end{align} $
Which is the same as obtained above.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Given: A lamppost AB of height 6 metres and a man DC of height 2 metres is moving away from the post with speed of 5 metres per second.
To determine: The speed of the head of the shadow E.
Let $ \angle DEC=\theta $
In triangle EDC, we have DC is the side opposite to E and CE is the side adjacent to E.
Hence, we have
$ \tan \theta =\dfrac{DC}{CE} $
Multiplying both sides by CE and dividing both sides by $ \tan \theta $ , we get
$ CE=DC\cot \theta $
Differentiating with respect to t(time), we get
$ \dfrac{d\left( CE \right)}{dt}=-DC{{\csc }^{2}}\theta \dfrac{d\theta }{dt}\text{ }\left( i \right) $
Similarly in triangle ABE, we have
$ AE=AB\cot \theta $
Also, we have triangle ABE and DCE are similar (Since AB||DC).
Hence, we have
$ \dfrac{AB}{DC}=\dfrac{AE}{CE} $ (Ratios of corresponding sides of two similar triangles is same)
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{6}{2}=\dfrac{AE}{CE} \\
& \Rightarrow AE=3CE \\
\end{align} $
Hence, we have
$ AC=2CE=4\cot \theta $
Hence, we have
$ \dfrac{d\left( AC \right)}{dt}=-4{{\csc }^{2}}\theta \dfrac{d\theta }{dt} $
Since the person moves with velocity of $ 5m{{s}^{-1}} $ , we have
$ \dfrac{d\left( AC \right)}{dt}=5 $
Hence, we have
$ {{\csc }^{2}}\theta \dfrac{d\theta }{dt}=\dfrac{-5}{4} $
Substituting in equation (i), we get
$ \dfrac{d\left( CE \right)}{dt}=-2\left( \dfrac{-5}{4} \right)=\dfrac{5}{2}m{{s}^{-1}} $
Hence the speed of the shadow is $ \dfrac{5}{2}m{{s}^{-1}} $ .
Note: Instead of trigonometry, we can also use simple geometry to solve the question.
We have
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{AE}=\dfrac{DC}{CE} \\
& \Rightarrow AE=\dfrac{6CE}{2}=3CE \\
\end{align} $
Hence, we have
$ AC=2CE $
Differentiating both sides with respect to t, we get
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{d\left( AC \right)}{dt}=2\times \dfrac{d\left( CE \right)}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{d\left( CE \right)}{dt}=\dfrac{5}{2} \\
\end{align} $
Which is the same as obtained above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




