
What is a major consequence of the partial double bond character?
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint :A pi bond can interact between two adjacent p-orbital due to resonance, they tend to have bond length in between that of a single bond and a double bond. This has major consequences on the stereochemistry of the molecule and also on the different properties of the molecule like reactivity.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Partial double bonds are a consequence of resonance in an organic molecule. The transfer of pi electrons from one p-orbital to another causes the partial double bond character. A very important example of this phenomenon is the peptide bonds that are present between the amino acids in proteins. The stability of the peptide bond is due to the resonance of amides. Due to resonance, the nitrogen is able to donate its lone pair of electrons to the carbonyl carbon and push electrons from the carbonyl double bond towards the oxygen, forming the oxygen anion. This gives a partial double bond character to the \[CO\] and \[CN\] bonds.
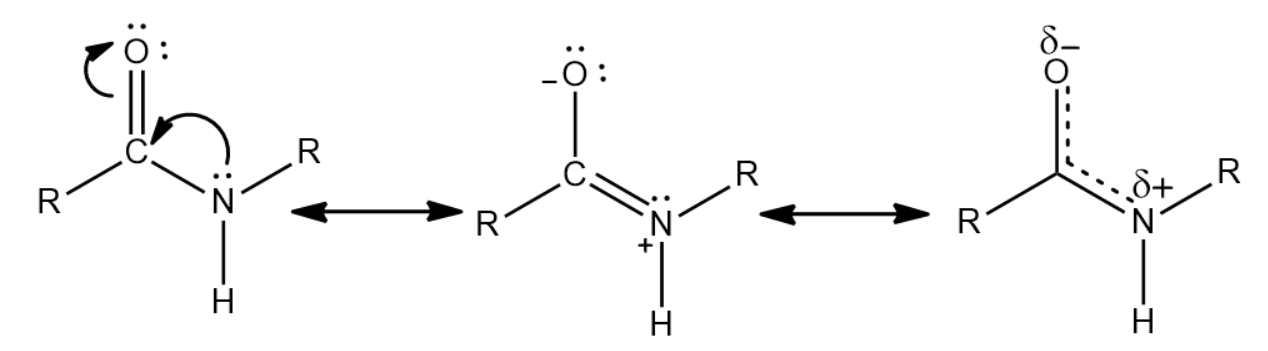
Some of the consequences of partial double bond is:
The partial double bond is responsible for the amide group being planar in the peptide link, thereby causing them to be either in a cis or a trans conformation.
Due to the presence of the partial double bond there is a restriction in the rotation in the molecule. This causes the rate of interconversion of conformers to be very slow. The barrier to rotate the amide is in the range of \[15 - 20{\text{ }}kcal/mol\] .
Note :
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions because there is a partial double bond character for the \[X - Cl\] bond and therefore makes bond cleavage difficult.
Partial double bonds make it difficult to break the bonds which appear as single bonds. Also the bond length of the single bond increases when it acquires a partial double bond character.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Partial double bonds are a consequence of resonance in an organic molecule. The transfer of pi electrons from one p-orbital to another causes the partial double bond character. A very important example of this phenomenon is the peptide bonds that are present between the amino acids in proteins. The stability of the peptide bond is due to the resonance of amides. Due to resonance, the nitrogen is able to donate its lone pair of electrons to the carbonyl carbon and push electrons from the carbonyl double bond towards the oxygen, forming the oxygen anion. This gives a partial double bond character to the \[CO\] and \[CN\] bonds.

Some of the consequences of partial double bond is:
The partial double bond is responsible for the amide group being planar in the peptide link, thereby causing them to be either in a cis or a trans conformation.
Due to the presence of the partial double bond there is a restriction in the rotation in the molecule. This causes the rate of interconversion of conformers to be very slow. The barrier to rotate the amide is in the range of \[15 - 20{\text{ }}kcal/mol\] .
Note :
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions because there is a partial double bond character for the \[X - Cl\] bond and therefore makes bond cleavage difficult.
Partial double bonds make it difficult to break the bonds which appear as single bonds. Also the bond length of the single bond increases when it acquires a partial double bond character.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




