
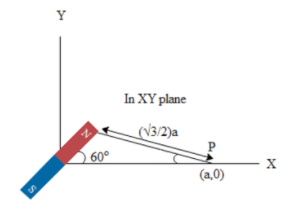
A magnet of dipole moment M is placed at origin as shown in the figure. Then select the correct alternative about the magnetic field produced by it.
$\begin{align}
& a)\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}}{8\pi }\dfrac{\sqrt{7}M}{{{a}^{3}}}\text{,at angle }\phi \text{=3}{{\text{0}}^{\circ }}withx-axis \\
& b)\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}}{8\pi }\dfrac{\sqrt{7}M}{{{a}^{3}}}\text{,at angle }\phi \text{=6}{{\text{0}}^{\circ }}withx-axis \\
& c)\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}}{8\pi }\dfrac{\sqrt{5}M}{{{a}^{3}}}\text{,at angle }\phi \text{=ta}{{\text{n}}^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)withx-axis \\
& d)\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}}{8\pi }\dfrac{\sqrt{7}M}{{{a}^{3}}}\text{,at angle }\phi \text{=ta}{{\text{n}}^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)withx-axis \\
\end{align}$

Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: In the above question we are asked to determine the magnetic field due to the above magnet with dipole moment M at the point P on the x-axis. The magnet makes an angle of 60 degrees with the x-axis. Hence we can determine the magnetic field by a magnet using the expression in which the field is given by the magnet inclined at a particular angle. The $\phi $ is half the tan of the angle made by the magnet with respect to the x-axis.
Formula used:
Let us say a magnet makes an angle $\theta $ with the x-axis placed at origin with magnetic moment M. We wish to determine the magnetic field at a distance a from the origin. Then the magnetic field at a is given by, $B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}M}{4\pi {{a}^{3}}}{{\left( 1+3Co{{s}^{2}}\theta \right)}^{1/2}}$ and $\phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta }{2} \right)$.
Complete answer:
It is given to us that the magnet makes an angle 60 degrees with the x-axis. Hence the magnetic field by the magnet with magnetic moment M at a distance a from origin is given by,
$\begin{align}
& B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}M}{4\pi {{a}^{3}}}{{\left( 1+3Co{{s}^{2}}\theta \right)}^{1/2}} \\
& B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}M}{4\pi {{a}^{3}}}{{\left( 1+3Co{{s}^{2}}60 \right)}^{1/2}}\because Cos60=\dfrac{1}{2}, \\
& \Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}M}{4\pi {{a}^{3}}}{{\left( 1+3{{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}} \right)}^{1/2}} \\
& \Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}M}{4\pi {{a}^{3}}}{{\left( \dfrac{4+3}{4} \right)}^{1/2}} \\
& \Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}\sqrt{7}M}{8\pi {{a}^{3}}} \\
\end{align}$
Now we wish to calculate $\phi $. Hence from the above definition we get the value of this angle t be,
$\begin{align}
& \phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta }{2} \right),\because \theta =60 \\
& \phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\tan 60}{2} \right)\text{, }since\tan 60=\sqrt{3}, \\
& \Rightarrow \phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note:
The magnetic moment of a magnet is defined as the pole strength times the length of the magnet. Hence greater the length of the magnet greater the intensity of the magnetic field at any given point. It is to be noted that $\phi $ is the angle formed by the resultant magnetic field at point P with respect to x-axis.
Formula used:
Let us say a magnet makes an angle $\theta $ with the x-axis placed at origin with magnetic moment M. We wish to determine the magnetic field at a distance a from the origin. Then the magnetic field at a is given by, $B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}M}{4\pi {{a}^{3}}}{{\left( 1+3Co{{s}^{2}}\theta \right)}^{1/2}}$ and $\phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta }{2} \right)$.
Complete answer:
It is given to us that the magnet makes an angle 60 degrees with the x-axis. Hence the magnetic field by the magnet with magnetic moment M at a distance a from origin is given by,
$\begin{align}
& B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}M}{4\pi {{a}^{3}}}{{\left( 1+3Co{{s}^{2}}\theta \right)}^{1/2}} \\
& B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}M}{4\pi {{a}^{3}}}{{\left( 1+3Co{{s}^{2}}60 \right)}^{1/2}}\because Cos60=\dfrac{1}{2}, \\
& \Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}M}{4\pi {{a}^{3}}}{{\left( 1+3{{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}} \right)}^{1/2}} \\
& \Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}M}{4\pi {{a}^{3}}}{{\left( \dfrac{4+3}{4} \right)}^{1/2}} \\
& \Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{\circ }}\sqrt{7}M}{8\pi {{a}^{3}}} \\
\end{align}$
Now we wish to calculate $\phi $. Hence from the above definition we get the value of this angle t be,
$\begin{align}
& \phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta }{2} \right),\because \theta =60 \\
& \phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\tan 60}{2} \right)\text{, }since\tan 60=\sqrt{3}, \\
& \Rightarrow \phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note:
The magnetic moment of a magnet is defined as the pole strength times the length of the magnet. Hence greater the length of the magnet greater the intensity of the magnetic field at any given point. It is to be noted that $\phi $ is the angle formed by the resultant magnetic field at point P with respect to x-axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




