
A machine pulls a 40kg trunk 2m up a \[{{40}^{0}}\] ramp at constant velocity, with the machine's force on the trunk directed parallel to the ramp. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the trunk and the ramp is 0.40. What are (a) the work done on the trunk by the machine's force and (b) the increase in thermal energy of the trunk and the ramp?
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: We can find the work done by machine on the trunk by just equating the components of different forces acting on the trunk. Also, the thermal energy is nothing but the frictional force component acting along the direction of motion of the trunk.
Complete answer:
We are given a mechanical setup in which a machine pulls a trunk of 40kg mass along an inclined ramp at a constant velocity ‘v’. The figure below gives the idea on the mechanism of the pulling employed. We have to resolve the different components of the forces involved as shown in the figure.
Here, we are to consider the forces only along the direction of force ’F’ applied by the machine.
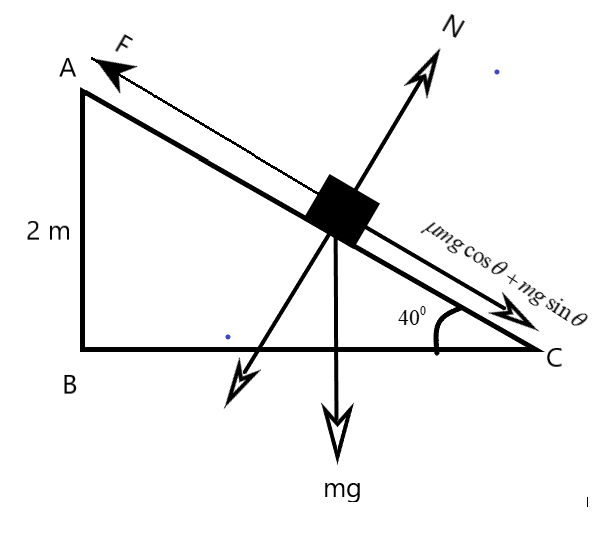
We can understand from the figure that the machine's force has two other opponents – the components of frictional force and the normal reaction. We can equate them as
\[F-\mu mg\cos \theta -mg\sin \theta =ma\]
But, we know that the mass moves with a constant velocity, that removes the acceleration from the above equation –
\[F=\mu mg\cos \theta +mg\sin \theta \]
We can find the work done by the machine using the formula –
\[W=F.S\]
But for the machine and the trunk, the angle between them is 0. Therefore, we can find the work done as –
\[\begin{align}
& W=(\mu mg\cos \theta +mg\sin \theta )S \\
& \text{but,} \\
& \text{S}=2m, \\
& \mu =0.40 \\
& m=40kg \\
& g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}} \\
& \Rightarrow W=(0.40\times 40\times 9.8\times \cos {{40}^{0}}+40\times 9.8\times \sin {{40}^{0}})2 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }W=744J \\
\end{align}\]
Now we can find the thermal energy of the machine and the trunk as –
\[\begin{align}
& {{W}_{thermal}}=(\mu mg\cos \theta )S \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{W}_{thermal}}=0.40\times 40\times 9.8\times \cos {{40}^{0}}\times 2 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{W}_{thermal}}=240J \\
\end{align}\]
We have the solution for both the questions as –
(a) 744J
(b) 240J
Note:
The solving of mechanical problems involves resolving the different components of force in the correct method. Any misinterpretation of data can end in erroneous solutions which can in no way be practical. The frictional forces and the normal reaction are present everywhere.
Complete answer:
We are given a mechanical setup in which a machine pulls a trunk of 40kg mass along an inclined ramp at a constant velocity ‘v’. The figure below gives the idea on the mechanism of the pulling employed. We have to resolve the different components of the forces involved as shown in the figure.
Here, we are to consider the forces only along the direction of force ’F’ applied by the machine.

We can understand from the figure that the machine's force has two other opponents – the components of frictional force and the normal reaction. We can equate them as
\[F-\mu mg\cos \theta -mg\sin \theta =ma\]
But, we know that the mass moves with a constant velocity, that removes the acceleration from the above equation –
\[F=\mu mg\cos \theta +mg\sin \theta \]
We can find the work done by the machine using the formula –
\[W=F.S\]
But for the machine and the trunk, the angle between them is 0. Therefore, we can find the work done as –
\[\begin{align}
& W=(\mu mg\cos \theta +mg\sin \theta )S \\
& \text{but,} \\
& \text{S}=2m, \\
& \mu =0.40 \\
& m=40kg \\
& g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}} \\
& \Rightarrow W=(0.40\times 40\times 9.8\times \cos {{40}^{0}}+40\times 9.8\times \sin {{40}^{0}})2 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }W=744J \\
\end{align}\]
Now we can find the thermal energy of the machine and the trunk as –
\[\begin{align}
& {{W}_{thermal}}=(\mu mg\cos \theta )S \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{W}_{thermal}}=0.40\times 40\times 9.8\times \cos {{40}^{0}}\times 2 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{W}_{thermal}}=240J \\
\end{align}\]
We have the solution for both the questions as –
(a) 744J
(b) 240J
Note:
The solving of mechanical problems involves resolving the different components of force in the correct method. Any misinterpretation of data can end in erroneous solutions which can in no way be practical. The frictional forces and the normal reaction are present everywhere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




