
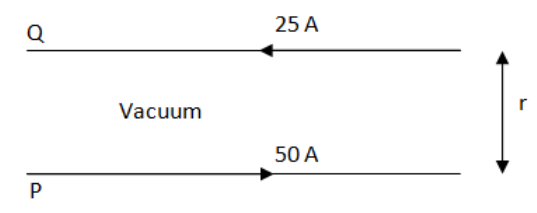
A long horizontal wire P carries a current of 50 A. It is rigidly fixed. Another wire Q is placed directly above and parallel to P, as shown in Figure. The weight per unit length of the wire Q is $0.025N{m^{ - 1}}$ and it carries a current of 25 A. Find the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest.

Answer
617.1k+ views
Hint- In order to solve this question we will use the basic concept that the wire Q to be in equilibrium, F=mg where F, is the repel force acting on the wire Q due to P and mg is the weight of wire Q.
Formula used- \[{\text{weight}} = m\left( {{\text{mass per unit length}}} \right) \times l\left( {{\text{length}}} \right),F = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}l}}{{2\pi r}}\].
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let the length of the given wire Q is 1 m
$ \Rightarrow l = 1m$
So the weight of wire Q
$
\Rightarrow {\text{weight}} = m\left( {{\text{mass per unit length}}} \right) \times l\left( {{\text{length}}} \right) \\
= 0.025N{m^{ - 1}} \times 1m \\
= 0.025N.........(1) \\
$
Since the current in both the wires is flowing in opposite directions, so both wires will repel each other.
Force acting on the wire Q due to P,
$F = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}l}}{{2\pi r}}$
Substitute the value of both the current and length of wire, we get
\[
\because F = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}l}}{{2\pi r}} \\
\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{4\pi \times {{10}^{ - 7}} \times 50 \times 25 \times 1}}{{2\pi \times r}} \\
\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{25 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}{r}N.............(2) \\
\]
For the wire Q to be in equilibrium,
$F = mg$
Let us compare both the force as given in the problem to find the value of r
So equating equation (1) and equation (2) we get:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{25 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}{r}N = 0.025N$
Let us solve the equation to find the value of r
$
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{{25 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}{{0.025}} \\
\Rightarrow r = 0.01m \\
\Rightarrow r = 1cm \\
$
Hence, the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest is 1cm.
Note- $\dfrac{F}{l}$ is the force per unit length between two parallel currents \[{I_1}\] and \[{I_2}\] separated by a distance r. The force is desirable if the currents are in the same direction and if they are in opposite directions they are repulsive. During electric arcs and plasmas, this force is responsible for the pinch effect. Volume is the measure of the volume of matter that comprises it, while Weight is the measure of the force of gravity on an object.
Formula used- \[{\text{weight}} = m\left( {{\text{mass per unit length}}} \right) \times l\left( {{\text{length}}} \right),F = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}l}}{{2\pi r}}\].
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let the length of the given wire Q is 1 m
$ \Rightarrow l = 1m$
So the weight of wire Q
$
\Rightarrow {\text{weight}} = m\left( {{\text{mass per unit length}}} \right) \times l\left( {{\text{length}}} \right) \\
= 0.025N{m^{ - 1}} \times 1m \\
= 0.025N.........(1) \\
$
Since the current in both the wires is flowing in opposite directions, so both wires will repel each other.
Force acting on the wire Q due to P,
$F = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}l}}{{2\pi r}}$
Substitute the value of both the current and length of wire, we get
\[
\because F = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}l}}{{2\pi r}} \\
\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{4\pi \times {{10}^{ - 7}} \times 50 \times 25 \times 1}}{{2\pi \times r}} \\
\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{25 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}{r}N.............(2) \\
\]
For the wire Q to be in equilibrium,
$F = mg$
Let us compare both the force as given in the problem to find the value of r
So equating equation (1) and equation (2) we get:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{25 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}{r}N = 0.025N$
Let us solve the equation to find the value of r
$
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{{25 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}{{0.025}} \\
\Rightarrow r = 0.01m \\
\Rightarrow r = 1cm \\
$
Hence, the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest is 1cm.
Note- $\dfrac{F}{l}$ is the force per unit length between two parallel currents \[{I_1}\] and \[{I_2}\] separated by a distance r. The force is desirable if the currents are in the same direction and if they are in opposite directions they are repulsive. During electric arcs and plasmas, this force is responsible for the pinch effect. Volume is the measure of the volume of matter that comprises it, while Weight is the measure of the force of gravity on an object.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




