
When a load of$10\,kg$ is suspended on a metallic wire, its length increases by $2\,mm.$The force constant of the wire is
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Load is given which is $10\,kg$and when it is applied the length increases by$2\,mm.$So, here the concept of Hooke’s Law applies $(F = - Kx)$ .
Complete step by step answer:
According to question, here are two forces apply on wire which holds the wire equilibrium; the forces are:
(i) Restoring force$(F = - Kx)$
(ii) Weight$(mg)$
$m$ is the mass of load$ = 10\,kg$
$K$ is force constant of wire
$x$ is expansion on wire
$g$ is gravity acceleration
Now according to Hooke's law, Restoring force is proportional to the extension in wire
So, $F = Kx$
Also the force applied that causes extension is the weight
So,
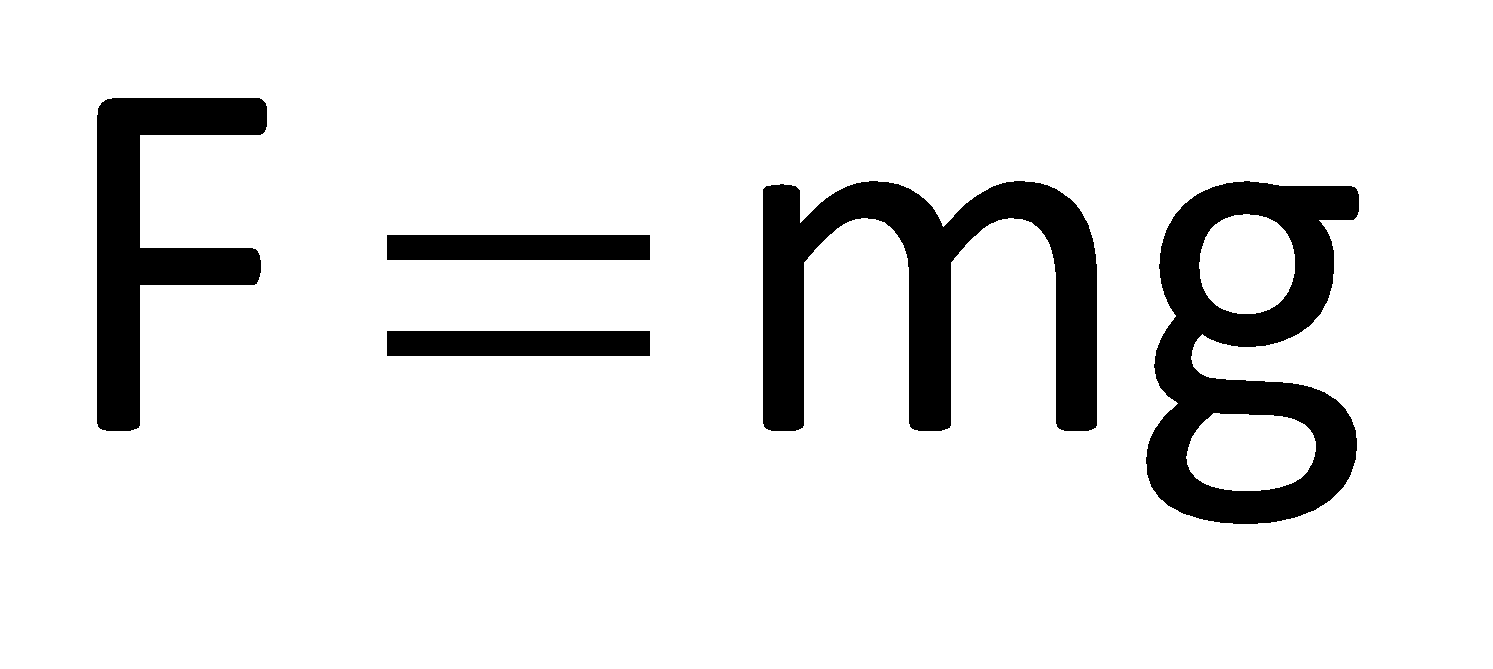 (weight of load)
(weight of load)
Here, wire is in equilibrium that means both the forces will be equal that is:
$Kx = mg$
$K = \dfrac{{mg}}{x} \\$
$ K = \dfrac{{10 \times 10}}{{2 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}} \\$
$ \left[ {K = 5 \times {{10}^4}\,N/m} \right] \\ $
So, the force constant of wire $5 \times {10^4}\,N/m$
Additional Information:
To solve the question we should remember that:
(i) If increase or decrease of wire is given and we have to calculate force constant then use Hooker’s Law.
(ii) Wire is in equilibrium, so net force$ = 0$.
Note:
All the quantities need to be in the same units. As the value of x is in mm while all others are in SI units so in order to get the correct answer x need to be converted into meters.Also remember there are two forces in the given diagram.
Complete step by step answer:
According to question, here are two forces apply on wire which holds the wire equilibrium; the forces are:
(i) Restoring force$(F = - Kx)$
(ii) Weight$(mg)$
$m$ is the mass of load$ = 10\,kg$
$K$ is force constant of wire
$x$ is expansion on wire
$g$ is gravity acceleration
Now according to Hooke's law, Restoring force is proportional to the extension in wire
So, $F = Kx$
Also the force applied that causes extension is the weight
So,
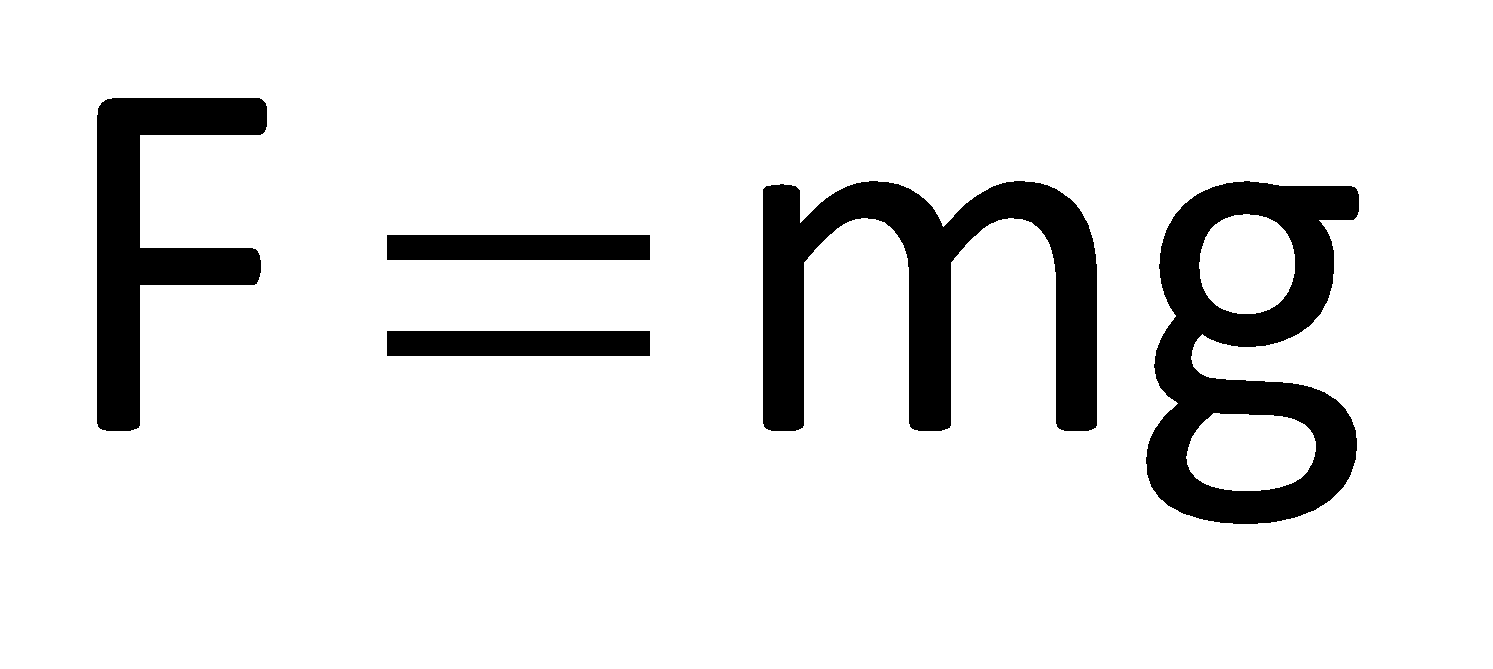
Here, wire is in equilibrium that means both the forces will be equal that is:
$Kx = mg$
$K = \dfrac{{mg}}{x} \\$
$ K = \dfrac{{10 \times 10}}{{2 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}} \\$
$ \left[ {K = 5 \times {{10}^4}\,N/m} \right] \\ $
So, the force constant of wire $5 \times {10^4}\,N/m$
Additional Information:
To solve the question we should remember that:
(i) If increase or decrease of wire is given and we have to calculate force constant then use Hooker’s Law.
(ii) Wire is in equilibrium, so net force$ = 0$.
Note:
All the quantities need to be in the same units. As the value of x is in mm while all others are in SI units so in order to get the correct answer x need to be converted into meters.Also remember there are two forces in the given diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




