
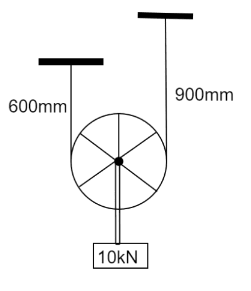
A load of $ 10kN $ is supported from a pulley which in turn is supported by a rope of sectional area, $ {10^3}m{m^2} $ and modulus of elasticity $ {10^3}Nm{m^{ - 2}} $ , as shown in Fig. 5.18. Neglecting the friction at the pulley, then downward deflection of the load is
(A) $ 3.75 $
(B) $ 4.25 $
(C) $ 2.75 $
(D) $ 4.00 $

Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: We can see in the given figure a single rope is attached on the two ends and there is downward force of $ 10kN $ . So tension will act upwards to balance the rope. And because of this tension there will be some extension in the given rope. Use the equation of equilibrium to find that extension.
Complete answer:
We have been given load $ F = 10kN $
Area of cross section $ A = {10^3}m{m^2} $
Modulus of elasticity $ y = {10^3}Nm{m^{ - 2}} $
Length of the rope $ {l_1} = 600mm $ and $ {l_2} = 900mm $
Using equation of equilibrium we will get,
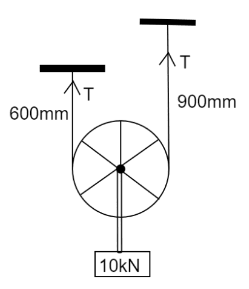
When a rope is holding the weight of an object at rest, the tension of the rope is equal to the weight of the object. On both the wire upward tension $ T $ is applied which will balance the downward force by mass of $ 10kN $
Therefore, $ 2T - 10 = 0 $
$ \Rightarrow T = 5kN = 5 \times {10^3}N $
Now total extension is equal to the extension in the left part of the wire and the extension in the right part of the wire.
$ Extension = \Delta {l_1} + \Delta {l_2} $
$ \Rightarrow Extension = \dfrac{{T{l_1}}}{{Ay}} + \dfrac{{T{l_2}}}{{Ay}} $
$ \Rightarrow Extension = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^3}}}{{{{10}^3} \times {{10}^3}}}(600 + 900) $
$ \Rightarrow Extension = 7.5mm $
This is the total extension in the wire so it will distribute equally in both the parts of the single wire
Therefore, $ \dfrac{{7.5}}{2}mm $
$ \Rightarrow 3.75mm $
Hence, option A) $ 3.75mm $ is the correct option.
Note:
We can also solve this problem by using the relation between stress, tension and area.
Longitudinal stress on the rope is given by
$ stress(\sigma ) = \dfrac{{tension(T)}}{{area(A)}} $
$ \sigma = 5\dfrac{N}{{m{m^2}}} $
Now using the relation between extension in the rope, stress, modulus of elasticity $ (y) $ and length of rope.
$ extension = \dfrac{{stress}}{y} \times l $
$ extension = \dfrac{{7.5}}{2} = 3.75mm $ .
Complete answer:
We have been given load $ F = 10kN $
Area of cross section $ A = {10^3}m{m^2} $
Modulus of elasticity $ y = {10^3}Nm{m^{ - 2}} $
Length of the rope $ {l_1} = 600mm $ and $ {l_2} = 900mm $
Using equation of equilibrium we will get,

When a rope is holding the weight of an object at rest, the tension of the rope is equal to the weight of the object. On both the wire upward tension $ T $ is applied which will balance the downward force by mass of $ 10kN $
Therefore, $ 2T - 10 = 0 $
$ \Rightarrow T = 5kN = 5 \times {10^3}N $
Now total extension is equal to the extension in the left part of the wire and the extension in the right part of the wire.
$ Extension = \Delta {l_1} + \Delta {l_2} $
$ \Rightarrow Extension = \dfrac{{T{l_1}}}{{Ay}} + \dfrac{{T{l_2}}}{{Ay}} $
$ \Rightarrow Extension = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^3}}}{{{{10}^3} \times {{10}^3}}}(600 + 900) $
$ \Rightarrow Extension = 7.5mm $
This is the total extension in the wire so it will distribute equally in both the parts of the single wire
Therefore, $ \dfrac{{7.5}}{2}mm $
$ \Rightarrow 3.75mm $
Hence, option A) $ 3.75mm $ is the correct option.
Note:
We can also solve this problem by using the relation between stress, tension and area.
Longitudinal stress on the rope is given by
$ stress(\sigma ) = \dfrac{{tension(T)}}{{area(A)}} $
$ \sigma = 5\dfrac{N}{{m{m^2}}} $
Now using the relation between extension in the rope, stress, modulus of elasticity $ (y) $ and length of rope.
$ extension = \dfrac{{stress}}{y} \times l $
$ extension = \dfrac{{7.5}}{2} = 3.75mm $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




