
A list of species having the formula $X{Z_4}$is given below.
$Xe{F_4}$, $S{F_4}$, $Si{F_4}$, $BF_4^ - $, $BrF_4^ - $, ${[Cu{(N{H_3})_4}]^{2 + }}$, ${[FeC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$, ${[CoC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$ and ${[PtC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$
Defining shape on the basis of location of X and Z atoms, the total number of species having a square planar shape is :
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The species that involves use of s, p and d orbitals form square planar structure. In molecules with four ligands, basically two types of geometries are possible. The molecules that have hybridisation $s{p^3}$ will have tetrahedral structure while those with $ds{p^2}$ will have square planar arrangement. So, by finding the hybridisation also, one can know about the shape of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
A square planar complex is the one that has four bond pairs to which ligands are attached forming the shape of a square. To see the shape, we have to draw their structures based on the number of lone pairs and the ligands attached to them.
So, the first molecule is$Xe{F_4}$. The Xe belongs to the 18th group and is a noble gas. It has the structure as-
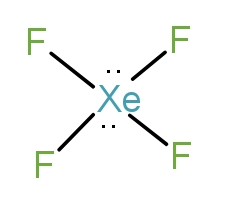
Thus, it has two lone pairs and four bond pairs. The hybridisation is $s{p^3}{d^2}$. Thus, it is a square planar complex.
The second molecule is $S{F_4}$. The Sulphur has six valence electrons and it forms the structure as-
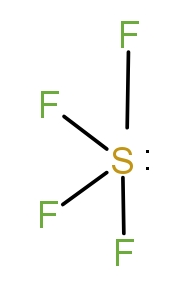
Thus, it has see saw shape. So, this is not the correct answer.
The third molecule given is $Si{F_4}$. The silicon has four valence electrons which are used up in bonding. It has structure as-

Silicon belongs to the carbon family. So, it forms a tetrahedral structure like the carbon. Hence, it is not the correct option.
The fourth molecule given is $BF_4^ - $. The boron tetrafluoride will form the structure as-

It has a tetrahedral structure with four bond pairs and no lone pair. This is not the correct answer.
The fifth molecule is $BrF_4^ - $. This molecule forms four bonds with F atoms and there are two lone pairs present. The structure is as-
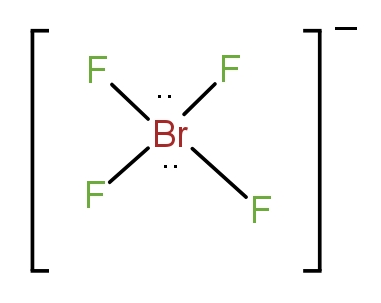
It has a square planar arrangement of atoms. Thus, it is the correct answer.
The sixth molecule given is ${[Cu{(N{H_3})_4}]^{2 + }}$. Here, the Cu is in +2 oxidation state. It will have nine electrons in 3d. The ammonia here excites one electron from 3d to 4p and forms four bonds with Cu. It will have hybridisation $ds{p^2}$. The structure of complex is square planar which is as-
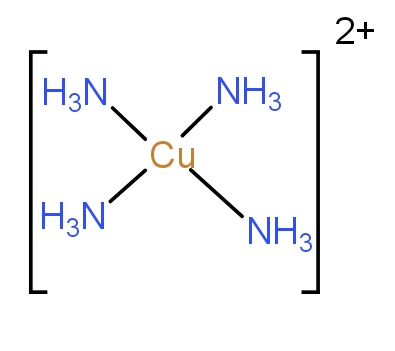
Thus, it is also the correct answer.
The seventh molecule is ${[FeC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$. The Cl is a weak field ligand. There will be no pairing of orbitals. As a result, Fe will form an outer orbital complex. Thus, it will have tetrahedral geometry. The structure can be seen as-

The eighth molecule is ${[CoC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$. The Cl is a weak field ligand. There will be no pairing of orbitals. As a result, Co will form an outer orbital complex. Thus, it will have tetrahedral geometry. The structure can be seen as-
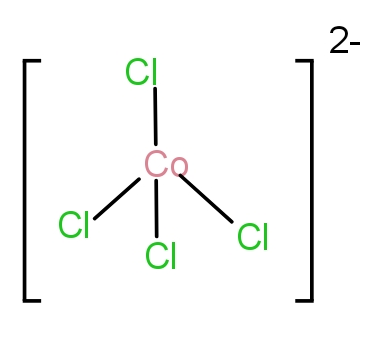
The ninth and the last molecule is ${[PtC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$. This forms square planar complex as-

So, the total number of molecules with square planar arrangement are 4.
Note: It must be noted that first we said that Cl is a weak field ligand and thus it will not do pairing up. But with Pt it has formed a square planar complex only. This is because Pt belongs to 4d. There is no concept of weak field and strong field in case of 4d and 5d. The Cl will behave as a strong field only and thus will form a square planar complex with Pt.
Complete step by step answer:
A square planar complex is the one that has four bond pairs to which ligands are attached forming the shape of a square. To see the shape, we have to draw their structures based on the number of lone pairs and the ligands attached to them.
So, the first molecule is$Xe{F_4}$. The Xe belongs to the 18th group and is a noble gas. It has the structure as-

Thus, it has two lone pairs and four bond pairs. The hybridisation is $s{p^3}{d^2}$. Thus, it is a square planar complex.
The second molecule is $S{F_4}$. The Sulphur has six valence electrons and it forms the structure as-

Thus, it has see saw shape. So, this is not the correct answer.
The third molecule given is $Si{F_4}$. The silicon has four valence electrons which are used up in bonding. It has structure as-

Silicon belongs to the carbon family. So, it forms a tetrahedral structure like the carbon. Hence, it is not the correct option.
The fourth molecule given is $BF_4^ - $. The boron tetrafluoride will form the structure as-

It has a tetrahedral structure with four bond pairs and no lone pair. This is not the correct answer.
The fifth molecule is $BrF_4^ - $. This molecule forms four bonds with F atoms and there are two lone pairs present. The structure is as-

It has a square planar arrangement of atoms. Thus, it is the correct answer.
The sixth molecule given is ${[Cu{(N{H_3})_4}]^{2 + }}$. Here, the Cu is in +2 oxidation state. It will have nine electrons in 3d. The ammonia here excites one electron from 3d to 4p and forms four bonds with Cu. It will have hybridisation $ds{p^2}$. The structure of complex is square planar which is as-

Thus, it is also the correct answer.
The seventh molecule is ${[FeC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$. The Cl is a weak field ligand. There will be no pairing of orbitals. As a result, Fe will form an outer orbital complex. Thus, it will have tetrahedral geometry. The structure can be seen as-

The eighth molecule is ${[CoC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$. The Cl is a weak field ligand. There will be no pairing of orbitals. As a result, Co will form an outer orbital complex. Thus, it will have tetrahedral geometry. The structure can be seen as-

The ninth and the last molecule is ${[PtC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$. This forms square planar complex as-

So, the total number of molecules with square planar arrangement are 4.
Note: It must be noted that first we said that Cl is a weak field ligand and thus it will not do pairing up. But with Pt it has formed a square planar complex only. This is because Pt belongs to 4d. There is no concept of weak field and strong field in case of 4d and 5d. The Cl will behave as a strong field only and thus will form a square planar complex with Pt.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




