
A liquid will not wet the surface of a solid if its angle of contact is
A. Zero
B. Less than ${90^ \circ }$
C. More than ${90^ \circ }$
D. ${90^ \circ }$
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Relate the angel of contact with the wettability of the surface by using the concept of cohesive and adhesive forces. Also the wettability of the surface not only depends on contact angle, it also depends on molecular forces.
Complete step-by-step answer:
At the interface of a liquid and a solid, the angle between the surface of the liquid and the outline of the contact surface is defined as angle of contact (θ). This angle of contact (θ) is used for checking the wettability of solid surfaces.
This angel of contact and the wettability of the solid surface is also depend on two type forces which are:
1. Cohesive Force: the intermolecular attractive force between the same types of molecules are known as cohesive force.
2. Adhesive Force: the intramolecular attractive force between the different-different types of molecules is called an adhesive force.
Now, at the contact surface between liquid and solid these attractive forces are responsible for wetting.
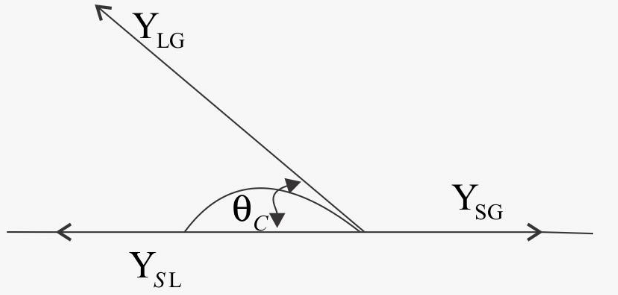
Here, many conditions for forces and angle of contact:
When, 0≤ angle of contact ≤ ${90^ \circ }$ adhesive force> cohesive force ……… (i)
And when angle of contact >${90^ \circ }$ cohesive force > adhesive force ……… (ii)
So, from equation (ii) the intermolecular attractive force (cohesive force) is larger than adhesive force hence there will be no holding force acting between the molecules of liquid and solid surface. Hence there will be no wetting in case of obtuse angle.
$\therefore $Option (C) is correct.
Note: This angle of contact completely depends on the properties of a particular liquid and contacting surface. Also it depends on the surface tension of the liquid. Surface tension is the property by which the force exerted by the intermolecular forces by unit length.
Complete step-by-step answer:
At the interface of a liquid and a solid, the angle between the surface of the liquid and the outline of the contact surface is defined as angle of contact (θ). This angle of contact (θ) is used for checking the wettability of solid surfaces.
This angel of contact and the wettability of the solid surface is also depend on two type forces which are:
1. Cohesive Force: the intermolecular attractive force between the same types of molecules are known as cohesive force.
2. Adhesive Force: the intramolecular attractive force between the different-different types of molecules is called an adhesive force.
Now, at the contact surface between liquid and solid these attractive forces are responsible for wetting.

Here, many conditions for forces and angle of contact:
When, 0≤ angle of contact ≤ ${90^ \circ }$ adhesive force> cohesive force ……… (i)
And when angle of contact >${90^ \circ }$ cohesive force > adhesive force ……… (ii)
So, from equation (ii) the intermolecular attractive force (cohesive force) is larger than adhesive force hence there will be no holding force acting between the molecules of liquid and solid surface. Hence there will be no wetting in case of obtuse angle.
$\therefore $Option (C) is correct.
Note: This angle of contact completely depends on the properties of a particular liquid and contacting surface. Also it depends on the surface tension of the liquid. Surface tension is the property by which the force exerted by the intermolecular forces by unit length.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




