
When a liquid medicine of density$\rho $is to be put in the eye, it is done with the help of a dropper. As the bulb on the top of the dropper is pressed, a drop forms at the opening of the dropper. We wish to estimate the size of the drop. We first assume that the drop formed at the opening is spherical because that requires a minimum increase in its surface energy. To determine the size, we calculate the net vertical force due to the surface tension $T$when the radius of the drop is $R$. When this force becomes smaller than the weight of the drop, the drop gets detached from the dropper. If the radius of the opening of the dropper is $r$,the vertical force due to the surface tension on the drop of the radius$R$(assuming $r < < R$) is:
A. $2\Pi rT$
B. $2\Pi RT$
C. $\dfrac{{2\Pi ({r^2})T}}{R}$
D. $\dfrac{{2\Pi ({R^2})T}}{r}$
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint:Surface tension is a property to resist an external force due to the cohesive nature of molecules. To find the surface tension on a liquid we need to know about the forces being acted on the surface of the liquid. Mercury has a strongest surface tension after water, water has highest surface tension due to hydrogen bonding in water molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
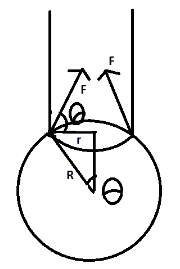
As we all can see in the above diagram firstly liquid medicine comes out of the dropper in the form of straight lines and then spreads to form a spherical drop. The upward pull is being experienced by the surface tension which we assumed to be F both sides of the lines will experience the same force as shown. Here $R$ is the radius of the drop and r is the base of the triangle which is making $\theta $ with the center. Now we all know tension is being observed on a surface, hence
From $\Delta ABC$
$sin\theta = \dfrac{r}{R}$
We wrote the above equation from the basic trigonometric equations where $sin\theta $ is equal to the ratio of the height $r$ to the hypotenuse $R$
From the diagram, vertical component of F be given by,
${F_V} = Fsin\theta $
$F = T\left( {2\pi r} \right)$ which is given by the tension and the circumference of the spherical drop.
${F_V} = T(2\Pi r)sin\theta $
Putting the value of $sin\theta $
${F_V} = T(2\Pi r)\dfrac{r}{R}$
Hence,
$\therefore{F_V} = 2\Pi T\dfrac{{{r^2}}}{R}$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Surface tension mainly depends on the force of attraction between particles inside liquid and atoms in the gas. Surface tension is inversely proportional to the temperature and is less dependent on the surface area as given in the question sphere has the least surface area. As pressure is inversely proportional to the area hence surface tension decreases with increase of area.
Complete step by step answer:

As we all can see in the above diagram firstly liquid medicine comes out of the dropper in the form of straight lines and then spreads to form a spherical drop. The upward pull is being experienced by the surface tension which we assumed to be F both sides of the lines will experience the same force as shown. Here $R$ is the radius of the drop and r is the base of the triangle which is making $\theta $ with the center. Now we all know tension is being observed on a surface, hence
From $\Delta ABC$
$sin\theta = \dfrac{r}{R}$
We wrote the above equation from the basic trigonometric equations where $sin\theta $ is equal to the ratio of the height $r$ to the hypotenuse $R$
From the diagram, vertical component of F be given by,
${F_V} = Fsin\theta $
$F = T\left( {2\pi r} \right)$ which is given by the tension and the circumference of the spherical drop.
${F_V} = T(2\Pi r)sin\theta $
Putting the value of $sin\theta $
${F_V} = T(2\Pi r)\dfrac{r}{R}$
Hence,
$\therefore{F_V} = 2\Pi T\dfrac{{{r^2}}}{R}$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Surface tension mainly depends on the force of attraction between particles inside liquid and atoms in the gas. Surface tension is inversely proportional to the temperature and is less dependent on the surface area as given in the question sphere has the least surface area. As pressure is inversely proportional to the area hence surface tension decreases with increase of area.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




