
A liquid is allowed into a tube of truncated cone shape. Identify the correct statement from the following.
A. The speed is high at the wider end and low at the narrow end
B. The speed is low at the wider and high at the narrow end
C. The speed is same at both ends in a streamline flow
D. The liquid flows with uniform velocity in the tube.
Answer
602.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem mathematically, we will use the principle of conservation of mass. We will calculate the mass that enters the tube and the mass that leaves it in infinitesimal time dt.
Formula used: $$A_1v_1=A_2v_2$$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let the velocity at the wider end be $v_1$ and the velocity at the narrow end be $v_2$. Also let the area of the cross section at the wider end be $A_1$ and that at the narrower end be $A_2$.
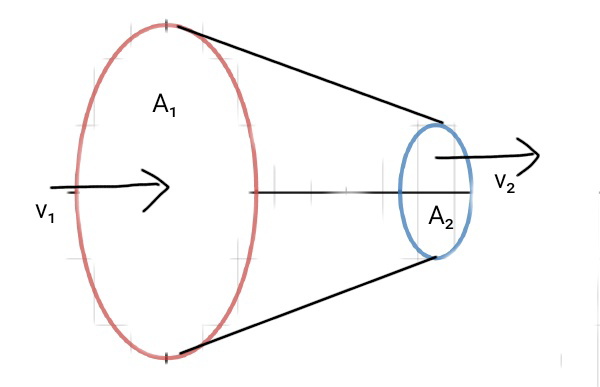
Through the wider end, liquid that enters in time dt travels distance $v_1.dt$ . Hence, the volume of this liquid in this end is $A_1.v_1.dt$ . Now, if $\rho$ be the density of the liquid, the mass that enters in time dt is $\rho A_1.v_1.dt$ .
Similarly, the mass that exits in time dt through the narrow end is $\rho A_2.v_2.dt$ .
From conservation of mass, these two masses must be equal.
$$\rho A_1.v_1.dt=\rho A_2.v_2.dt \\ \dfrac{v_1}{v_2}=\dfrac{A_2}{A_1}<1 $$
So, $v_1$ is less than $v_2$.
Hence option B is the correct answer.
Additional information:
The term "fluid" refers to both the liquid and the gas. The liquids are incompressible but gases are compressible. But the law of conservation of mass is obeyed by both.
Note: This formula can only be used when the liquid has uniform density. It means $\rho$ has to be constant. If the density is said to be changed in the question, then the formula would look like,
$$\rho _1 A_1.v_1=\rho _2A_2.v_2$$
This is the general formula.
Formula used: $$A_1v_1=A_2v_2$$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let the velocity at the wider end be $v_1$ and the velocity at the narrow end be $v_2$. Also let the area of the cross section at the wider end be $A_1$ and that at the narrower end be $A_2$.

Through the wider end, liquid that enters in time dt travels distance $v_1.dt$ . Hence, the volume of this liquid in this end is $A_1.v_1.dt$ . Now, if $\rho$ be the density of the liquid, the mass that enters in time dt is $\rho A_1.v_1.dt$ .
Similarly, the mass that exits in time dt through the narrow end is $\rho A_2.v_2.dt$ .
From conservation of mass, these two masses must be equal.
$$\rho A_1.v_1.dt=\rho A_2.v_2.dt \\ \dfrac{v_1}{v_2}=\dfrac{A_2}{A_1}<1 $$
So, $v_1$ is less than $v_2$.
Hence option B is the correct answer.
Additional information:
The term "fluid" refers to both the liquid and the gas. The liquids are incompressible but gases are compressible. But the law of conservation of mass is obeyed by both.
Note: This formula can only be used when the liquid has uniform density. It means $\rho$ has to be constant. If the density is said to be changed in the question, then the formula would look like,
$$\rho _1 A_1.v_1=\rho _2A_2.v_2$$
This is the general formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




