
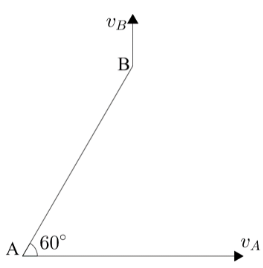
A link $\;AB$ is moving in a vertical plane. At a certain instant when the link is inclined $60^{\circ}$ to the horizontal, the point $A$ is moving horizontally at $3ms^{-1}$ , while $B$ is moving in the vertical direction. What is the velocity of $B$ ?
A. $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}m{{s}^{-1}}$
B. $2\sqrt{3}m{{s}^{-1}}$
C. $\sqrt{3}m{{s}^{-1}}$
D. $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}m{{s}^{-1}}$

Answer
515.7k+ views
Hint: Here, we are given the velocities of both the ends of the link. We know that the link is rigid, and hence the length of the link will be fixed. Thus the resultant velocity of both the components along the link will be the same. Hence, from the given velocity, we can find the velocity along the link and from that, we can find the velocity of the required component.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we are given a rigid link, whose length remains constant. The link is moving at $60^ \circ$ with the horizontal, with both the ends having velocity of different magnitude and directions. Here, we are given the velocity of the point $A$ as $v_A=3ms^{-1}$.
Now, this is the velocity of the point itself. We can find the velocity of the point along the link $\;AB$ by considering the component of the velocity in the direction of the link as shown in figure.
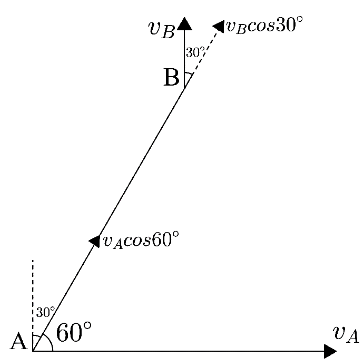
Hence, the velocity of the point $A$ along the link as shown in the figure is given as
$v'={{v}_{A}}\cos 60{}^\circ $
Substituting the values,
$\therefore v'=\dfrac{3}{2}m{{s}^{-1}}$…… $(1)$
Now, as the link is rigid, the velocity of the point $B$ along the link $\;AB$ will be equal to the velocity of the point $A$ along the link.
From the above figure, the velocity of point $B$ along the link is given as
$v'={{v}_{B}}\cos 30{}^\circ $…… $(2)$
Equating both the equations,
$\therefore \dfrac{3}{2}={{v}_{B}}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\therefore {{v}_{B}}=\sqrt{3}m{{s}^{-1}}$
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: We can also solve the given question, by assuming links for the given velocities. We know that the velocity is always perpendicular to the link. Hence, we can draw the links for the given velocities, we can draw the links as shown below,
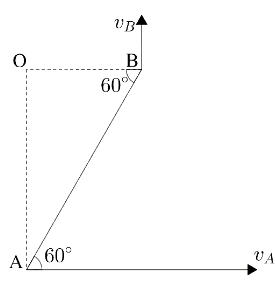
From the figure, we can find the ratio of the links $\cot 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{OB}{OA}$ . Now, we know that $\dfrac{OB}{OA}=\dfrac{{{v}_{B}}}{{{v}_{A}}}$
Hence, we can get the formula as ${{v}_{B}}=\cot 60{}^\circ \times {{v}_{A}}$
$\therefore {{v}_{B}}=\sqrt{3}m{{s}^{-1}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we are given a rigid link, whose length remains constant. The link is moving at $60^ \circ$ with the horizontal, with both the ends having velocity of different magnitude and directions. Here, we are given the velocity of the point $A$ as $v_A=3ms^{-1}$.
Now, this is the velocity of the point itself. We can find the velocity of the point along the link $\;AB$ by considering the component of the velocity in the direction of the link as shown in figure.

Hence, the velocity of the point $A$ along the link as shown in the figure is given as
$v'={{v}_{A}}\cos 60{}^\circ $
Substituting the values,
$\therefore v'=\dfrac{3}{2}m{{s}^{-1}}$…… $(1)$
Now, as the link is rigid, the velocity of the point $B$ along the link $\;AB$ will be equal to the velocity of the point $A$ along the link.
From the above figure, the velocity of point $B$ along the link is given as
$v'={{v}_{B}}\cos 30{}^\circ $…… $(2)$
Equating both the equations,
$\therefore \dfrac{3}{2}={{v}_{B}}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\therefore {{v}_{B}}=\sqrt{3}m{{s}^{-1}}$
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: We can also solve the given question, by assuming links for the given velocities. We know that the velocity is always perpendicular to the link. Hence, we can draw the links for the given velocities, we can draw the links as shown below,

From the figure, we can find the ratio of the links $\cot 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{OB}{OA}$ . Now, we know that $\dfrac{OB}{OA}=\dfrac{{{v}_{B}}}{{{v}_{A}}}$
Hence, we can get the formula as ${{v}_{B}}=\cot 60{}^\circ \times {{v}_{A}}$
$\therefore {{v}_{B}}=\sqrt{3}m{{s}^{-1}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




